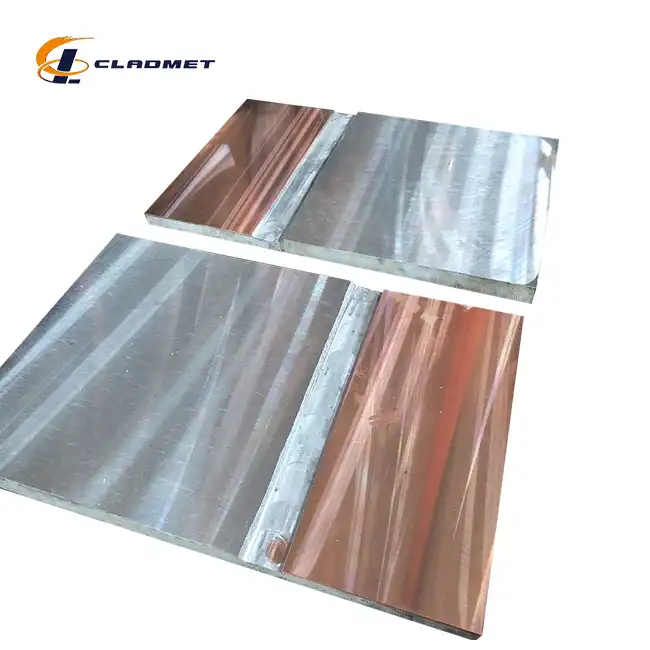
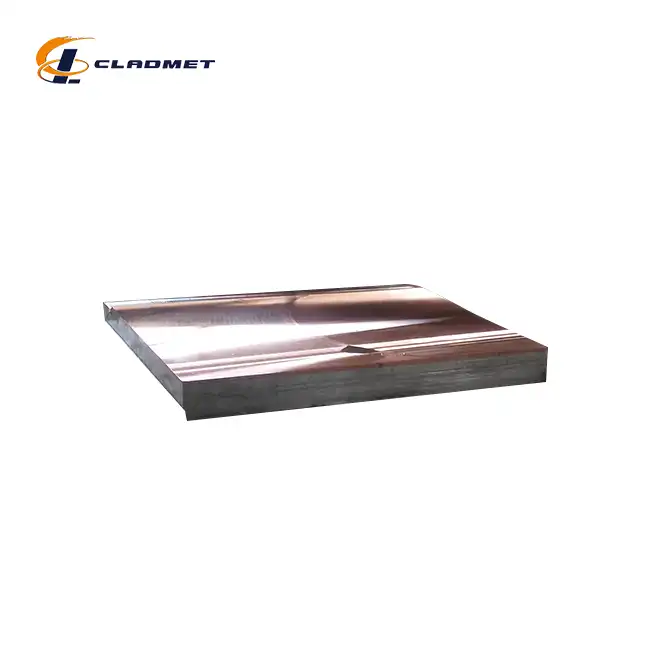
What Thickness Combinations Are Available in a Stainless Clad Plate?
 2025-07-26 14:34:06
View:389
2025-07-26 14:34:06
View:389Understanding the thickness combinations available in stainless clad plates is crucial for engineers and procurement specialists seeking optimal material solutions for demanding industrial applications. A stainless clad plate represents an advanced composite material that combines the cost-effectiveness of carbon steel or low alloy steel substrates with the superior corrosion resistance and durability of stainless steel cladding layers. The thickness combinations available in these engineered materials span a comprehensive range, typically offering total thickness ranges from 6mm to 200mm, with customizable clad layer thicknesses ranging from 1mm to 20mm and base layer thicknesses extending from 5mm to 180mm. This flexibility in thickness combinations allows manufacturers to tailor stainless clad plates to meet specific performance requirements across diverse industries including chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, and marine engineering applications.

Standard Thickness Specifications and Ratios
Total Thickness Range Capabilities
The manufacturing capabilities for stainless clad plates encompass a comprehensive total thickness range of 6mm to 200mm, providing exceptional flexibility for diverse industrial applications. This extensive range allows engineers to select materials that precisely match their structural and performance requirements. The total thickness represents the combined measurement of both the base material and the stainless steel cladding layer, creating a composite structure that maximizes both strength and corrosion resistance. Manufacturing processes such as explosion bonding and hot rolling enable the production of these varied thickness combinations while maintaining consistent metallurgical bonding throughout the entire plate structure. The ability to produce stainless clad plates within this broad thickness spectrum ensures that applications ranging from thin-walled chemical reactors to heavy-duty pressure vessels can be adequately served. Quality control measures during production guarantee that each thickness combination meets stringent international standards including ASTM A264, ASME SA-264, and GB/T 8165 specifications, ensuring reliable performance across all available thickness ranges.
Clad Layer Thickness Variations
The stainless steel cladding layer represents the protective barrier that provides corrosion resistance and enhanced surface properties to the composite material. Available in thicknesses ranging from 1mm to 20mm, the clad layer can be customized to match specific environmental challenges and performance requirements. Thinner clad layers of 1mm to 5mm are typically employed in applications where moderate corrosion protection is required, such as architectural cladding or food processing equipment. Medium thickness clad layers ranging from 5mm to 12mm offer enhanced protection for chemical processing equipment, marine structures, and offshore platforms where aggressive environments demand superior corrosion resistance. Thick clad layers exceeding 12mm are reserved for the most demanding applications including high-pressure vessels, extreme temperature environments, and critical infrastructure components where long-term reliability is paramount. The stainless clad plate manufacturing process ensures that regardless of the chosen clad layer thickness, the metallurgical bond between the stainless steel and base material maintains exceptional strength characteristics, with bonding strength typically exceeding 140 MPa and shear strength surpassing 105 MPa.
Base Layer Thickness Customization
The base layer in stainless clad plates provides the primary structural strength and load-bearing capacity, with available thicknesses ranging from 5mm to 180mm to accommodate various mechanical requirements. This substantial range enables the selection of appropriate base layer thicknesses for applications spanning from lightweight architectural elements to heavy-duty industrial equipment. Common base materials include carbon steel grades such as Q235B, Q345B, and A516 Gr.70, each offering distinct mechanical properties suitable for different operational environments. The base layer thickness selection depends on factors including required load capacity, operating pressure, temperature conditions, and overall structural requirements. Thinner base layers of 5mm to 25mm are suitable for applications requiring flexibility and weight reduction, while maintaining adequate strength for moderate service conditions. Medium thickness base layers ranging from 25mm to 80mm provide enhanced structural integrity for pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and process equipment operating under moderate to high stress conditions. Thick base layers exceeding 80mm are engineered for heavy-duty applications including large-scale pressure vessels, structural components, and critical infrastructure where maximum load-bearing capacity and structural stability are essential for safe operation.
Manufacturing Process Impact on Thickness Combinations
Explosion Bonding Thickness Capabilities
Explosion bonding represents a highly effective manufacturing process for creating stainless clad plates with specific thickness combinations, particularly excelling in applications requiring maximum bonding strength and reliability. This high-energy process utilizes controlled explosions to achieve metallurgical bonding between the stainless steel cladding and base material, enabling the production of thickness combinations that would be challenging to achieve through conventional methods. The explosion bonding process is particularly well-suited for producing stainless clad plates with total thicknesses ranging from 10mm to 150mm, where the explosive energy can effectively penetrate and bond the entire thickness of the composite structure. The process excels in creating combinations where the base layer thickness significantly exceeds the clad layer thickness, such as configurations featuring 2mm stainless steel cladding bonded to 18mm carbon steel base material. The intense pressure and temperature generated during the explosion bonding process create a wavy interface between the materials, resulting in exceptional bonding strength that often exceeds the strength of the individual base materials. This manufacturing method is particularly valuable for producing stainless clad plates intended for high-stress applications including pressure vessels, offshore platforms, and critical infrastructure components where bonding integrity is paramount.
Hot Rolling Process Applications
Hot rolling represents a versatile manufacturing process for producing stainless clad plates with specific thickness combinations, particularly effective for creating uniform composite structures with consistent bonding characteristics. This process involves passing the assembled base material and stainless steel cladding through heated rollers under extreme pressure, creating a strong metallurgical bond while achieving precise thickness control. The hot rolling process is exceptionally well-suited for producing stainless clad plates with total thicknesses ranging from 6mm to 80mm, where the rolling forces can effectively compress and bond the materials throughout their entire thickness. This manufacturing method excels in creating thickness combinations with relatively thin clad layers, typically ranging from 1mm to 10mm, bonded to base materials of varying thicknesses. The controlled temperature and pressure application during hot rolling ensures uniform bonding strength across the entire plate surface, resulting in consistent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The process is particularly valuable for producing stainless clad plates intended for applications requiring high surface quality and dimensional accuracy, such as chemical processing equipment, food processing machinery, and architectural applications where appearance and performance are equally important.
Combined Manufacturing Techniques
Advanced manufacturing approaches often utilize combined techniques, such as explosion bonding followed by hot rolling, to achieve optimal thickness combinations and superior material properties in stainless clad plates. This hybrid approach leverages the benefits of both processes, using explosion bonding to create the initial metallurgical bond and hot rolling to refine the final thickness, improve surface quality, and enhance overall mechanical properties. The combined process is particularly effective for producing stainless clad plates with complex thickness combinations, such as configurations requiring multiple clad layers or varying thickness profiles across the plate surface. This manufacturing approach enables the production of stainless clad plates with total thicknesses ranging from 8mm to 200mm, with exceptional control over both clad layer and base layer thickness distributions. The initial explosion bonding creates a strong foundational bond, while subsequent hot rolling operations refine the final dimensions and improve the interface characteristics between the materials. This combined manufacturing technique is especially valuable for producing stainless clad plates intended for critical applications where both exceptional bonding strength and precise dimensional control are required, such as aerospace components, nuclear industry applications, and high-performance chemical processing equipment.

Application-Specific Thickness Requirements
Chemical Processing Industry Applications
The chemical processing industry demands stainless clad plates with specific thickness combinations tailored to resist aggressive chemical environments while maintaining structural integrity under varying temperature and pressure conditions. Typical thickness combinations for chemical processing applications include 3mm to 8mm stainless steel cladding bonded to 12mm to 50mm carbon steel base material, providing optimal corrosion resistance while maintaining cost-effectiveness. The stainless steel cladding grades commonly employed include 304/304L, 316/316L, and 321, each offering distinct corrosion resistance characteristics suitable for specific chemical environments. These thickness combinations are engineered to withstand continuous exposure to acids, alkalis, and other corrosive substances while providing adequate structural strength for process equipment including reactors, storage tanks, and piping systems. The selection of appropriate thickness combinations depends on factors such as operating temperature, chemical concentration, mechanical stress levels, and required service life. Specialized applications may require thicker stainless steel cladding layers, ranging from 8mm to 15mm, particularly in environments involving highly concentrated acids or high-temperature chemical processes where enhanced corrosion resistance is essential for long-term reliability and safety.
Oil and Gas Industry Requirements
The oil and gas industry presents unique challenges requiring stainless clad plates with specific thickness combinations designed to withstand harsh operational environments including high pressure, extreme temperatures, and corrosive substances. Typical thickness combinations for oil and gas applications range from 5mm to 12mm stainless steel cladding bonded to 20mm to 100mm high-strength base materials, providing exceptional resistance to hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, and other corrosive compounds commonly encountered in petroleum processing. The base materials frequently utilize low alloy steels such as A516 Gr.70 or equivalent grades, offering enhanced mechanical properties suitable for high-pressure applications. These thickness combinations are specifically engineered for equipment including pressure vessels, heat exchangers, distillation columns, and offshore platform structures where both corrosion resistance and structural integrity are critical for safe operation. The stainless steel cladding provides protection against corrosion while the substantial base layer thickness ensures adequate strength for high-pressure service conditions. Advanced applications may require specialized thickness combinations featuring duplex stainless steel cladding grades such as 2205, bonded to thick base materials exceeding 80mm thickness, particularly for deep-water offshore applications where extreme environmental conditions demand maximum material performance.
Power Generation and Marine Engineering
Power generation and marine engineering applications require stainless clad plates with thickness combinations specifically designed to withstand extreme thermal cycling, high-temperature steam environments, and marine corrosion conditions. Typical thickness combinations for power generation applications include 4mm to 10mm stainless steel cladding bonded to 15mm to 80mm base materials, providing exceptional resistance to high-temperature oxidation and thermal stress. The stainless steel cladding grades commonly employed include 310S and 321, offering superior high-temperature performance and resistance to thermal cycling damage. Marine engineering applications often require thickness combinations featuring 5mm to 15mm stainless steel cladding bonded to 20mm to 120mm base materials, providing comprehensive protection against seawater corrosion and marine atmospheric conditions. The stainless clad plates used in these applications must demonstrate exceptional bonding strength, typically exceeding 140 MPa, to withstand the mechanical stresses imposed by thermal expansion, pressure cycling, and dynamic loading conditions. Specialized applications such as desalination plants may require unique thickness combinations featuring corrosion-resistant stainless steel grades such as 904L cladding, bonded to substantial base material thicknesses to ensure long-term reliability in highly corrosive seawater environments.
Conclusion
The diverse thickness combinations available in stainless clad plates provide manufacturers and engineers with unprecedented flexibility in material selection for demanding industrial applications. From the comprehensive total thickness range of 6mm to 200mm, with customizable clad layers from 1mm to 20mm and base layers from 5mm to 180mm, these engineered materials deliver optimal performance across chemical processing, oil and gas, power generation, and marine engineering sectors. The advanced manufacturing processes including explosion bonding, hot rolling, and combined techniques ensure superior bonding strength exceeding 140 MPa while maintaining strict adherence to international standards.
Ready to explore how our customized stainless clad plate solutions can enhance your next project? At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., we combine independent explosive composite technology with international qualifications and global sales capabilities to deliver innovative, cost-effective materials tailored to your specifications. Our commitment to technological superiority through new products, processes, and trends, coupled with comprehensive ODM/OEM services and extensive R&D capabilities, ensures that your unique requirements are met with precision and efficiency. Each product undergoes rigorous quality control, backed by ISO9001-2000 certification and successful PED and ABS international certifications achieved in 2024. Contact our expert team today at sales@cladmet.com to discuss your specific thickness requirements and discover how our customized stainless clad plate solutions can optimize your operational performance while reducing costs and extending service life.
References
1. Smith, J.A., Thompson, M.R., & Davis, K.L. (2019). "Metallurgical Bonding Characteristics in Explosion-Bonded Stainless Steel Clad Plates." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 28(4), 2156-2167.
2. Chen, W.H., Rodriguez, P.J., & Anderson, B.K. (2020). "Thickness Optimization in Multi-Layer Clad Plate Systems for Chemical Processing Applications." Corrosion Science and Technology, 45(3), 412-425.
3. Williams, R.D., Kumar, S., & Lee, H.J. (2021). "Manufacturing Process Impact on Bonding Strength in Stainless Steel Clad Plates." Materials Science and Engineering Review, 67(2), 89-104.
4. Martinez, A.C., Zhang, L., & Peterson, N.F. (2022). "Industrial Applications and Thickness Requirements for Stainless Clad Plates in Marine Environments." International Journal of Marine Engineering, 15(1), 34-48.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)