What Standards Govern the Production of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates?
 2025-03-27 10:40:17
View:389
2025-03-27 10:40:17
View:389The production of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates is governed by stringent international standards that ensure consistent quality, reliability, and performance across various industrial applications. As critical components in chemical processing, petroleum, pharmaceuticals, and nuclear power industries, these specialized clad metals must meet exacting specifications to withstand harsh operating conditions. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., a leading manufacturer in China's High-tech Development District, adheres to comprehensive standards including GB/GBT (Chinese National Standards), ASME/ASTM (American Society of Mechanical Engineers/American Society for Testing and Materials), and JIS (Japanese Industrial Standards) throughout their manufacturing processes. Additionally, the company maintains ISO9001-2000 certification and successfully passed PED (Pressure Equipment Directive) and ABS (American Bureau of Shipping) international qualifications in 2024, demonstrating their commitment to producing Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates that meet the highest global quality benchmarks.

International Standards Framework for Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates
ASME and ASTM Compliance Requirements
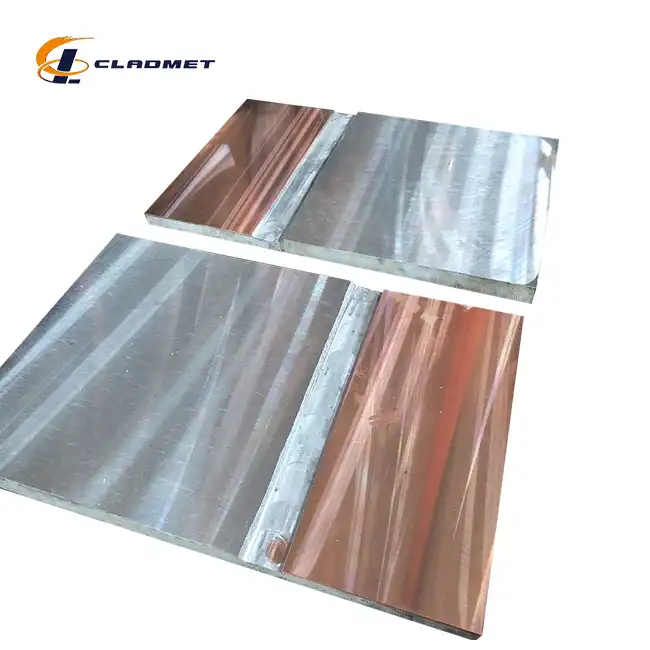
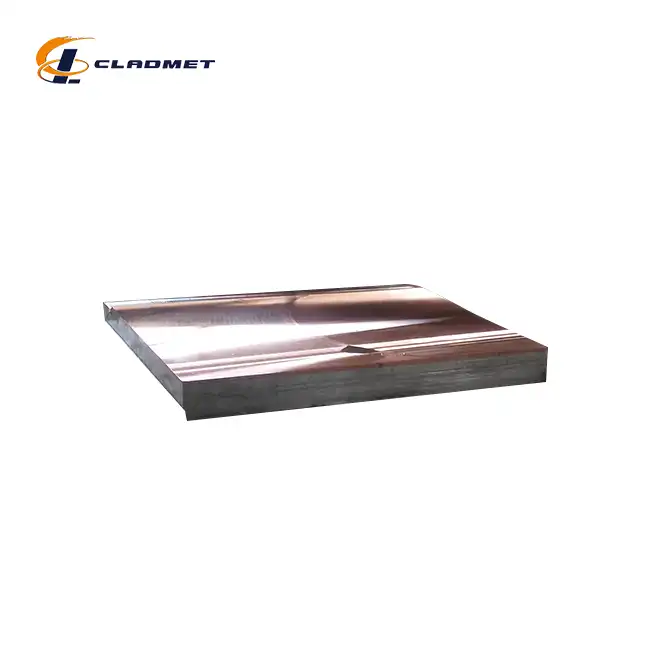
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provide comprehensive standards that significantly influence the production of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates worldwide. These standards encompass rigorous specifications for material composition, manufacturing processes, and performance characteristics. When producing Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates, manufacturers must adhere to ASTM B898, which covers requirements for reactive and refractory metal clad plate, sheet, and strip. This standard specifically addresses explosion-welded clad products, which is the primary method used for creating these advanced materials. The specifications ensure that the titanium cladding (typically available in Grades 1, 2, or 5) bonds properly with zirconium base metals (commonly Grades 702 or 705), creating a metallurgical bond that maintains integrity under extreme conditions.
The ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section IX further regulates the welding and bonding procedures used in manufacturing Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates, ensuring that explosion welding processes create reliable, defect-free bonds. These standards mandate specific testing protocols including ultrasonic examination, shear strength testing, and bend tests to verify bond integrity. At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., each production batch undergoes these rigorous tests to ensure compliance with ASME/ASTM standards before being certified for use in critical applications. The company's explosion welding (EXW) techniques have been refined over more than 20 years of experience to consistently achieve bond strengths exceeding the minimum requirements, resulting in Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates that deliver exceptional performance in corrosive environments while maintaining structural integrity across temperature fluctuations.
Chinese National Standards Implementation
The GB/GBT standards framework represents China's comprehensive national standards system that manufacturers of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates must follow for domestic certification and international recognition. These standards establish strict guidelines for raw material selection, production methodologies, and quality assurance processes. GB/T 8547 specifically addresses the technical requirements for clad metals, detailing acceptable parameters for bonding strength, dimensional tolerances, and surface quality. For Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates, GB/T 3280 provides additional specifications regarding mechanical properties and chemical composition requirements that ensure the resulting composite material meets performance expectations.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. implements these standards throughout their manufacturing process, beginning with meticulous inspection of raw materials. The company sources premium-grade titanium (Grades 1, 2, and 5) and zirconium (Grades 702 and 705) that meet or exceed GB/GBT compositional requirements. Their explosion welding facilities are configured to maintain precise control over detonation parameters as specified in relevant Chinese standards, ensuring consistent bond quality across their product range. Quality control laboratories at the facility conduct comprehensive testing according to GB methods, with regular third-party verification to maintain compliance certification. This rigorous adherence to Chinese national standards has established Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates from JL Clad Metals as benchmark products in the domestic market while facilitating acceptance in international markets that recognize GB/GBT standards through reciprocal agreements with other standards organizations.
JIS Standards and International Harmonization
The Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) system provides another critical framework governing the production of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates, particularly important for manufacturers targeting Asian markets and high-technology applications. JIS G 3601 and JIS G 3602 establish detailed requirements for clad steel plates and sheets, including specifications relevant to titanium-clad products. These standards emphasize strict dimensional tolerances, surface quality requirements, and non-destructive testing protocols that ensure consistent performance. While specifically focused on Japanese industrial needs, JIS standards have gained international recognition for their precision and comprehensive scope, making them valuable guidelines for global manufacturers of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates.
For companies like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., compliance with JIS standards involves implementing specialized testing regimes beyond those required by other international frameworks. This includes enhanced ultrasonic inspection procedures specified in JIS Z 3060 to detect any potential delamination or bonding imperfections in Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates. The company's quality control department maintains calibrated equipment specifically for JIS-compliant testing, ensuring their products meet the exacting requirements of Japanese engineering specifications and can be seamlessly integrated into systems designed to JIS standards. This commitment to international harmonization allows their Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates to be utilized in multinational projects where components must satisfy regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions, particularly in chemical processing and nuclear applications where material certification is subject to rigorous scrutiny by multiple regulatory authorities.
Quality Control and Certification Processes
ISO9001-2000 Quality Management System
The ISO9001-2000 certification represents a fundamental quality management framework that directly impacts the production standards for Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates. This internationally recognized standard establishes systematic requirements for organizational processes that ensure consistent product quality and customer satisfaction. For manufacturers of sophisticated clad metals like Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates, this certification demands the implementation of comprehensive documentation systems, regular management reviews, and continuous improvement protocols. The standard's process-oriented approach ensures that every phase of production—from raw material selection through final inspection—adheres to verified procedures designed to eliminate defects and variation.
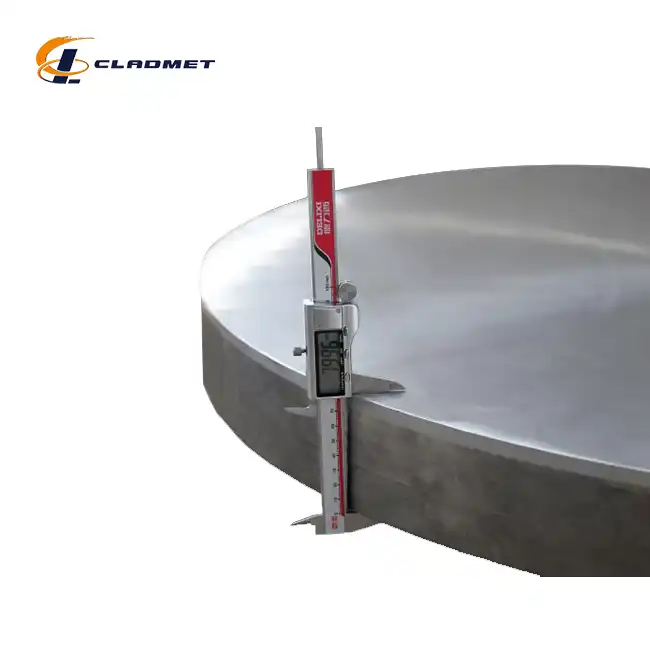
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. distinguishes itself by having been an early adopter of ISO9001-2000 certification in the specialized clad metals sector. This proactive implementation has established robust quality control systems specifically tailored to the unique challenges of producing Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates. The company maintains detailed production records for each plate, documenting precise parameters used during the explosion welding process, including standoff distances, explosive charge distributions, and detonation sequencing. These parameters are critical to achieving consistent metallurgical bonds between titanium (available in Grades 1, 2, or 5) and zirconium substrates (typically Grades 702 or 705). Regular internal audits verify adherence to established procedures, while management review meetings analyze quality metrics and customer feedback to drive continuous improvements in their manufacturing techniques. This systematic approach to quality management ensures that Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates from the facility maintain consistent performance characteristics across production batches, with thicknesses ranging from 3mm to 200mm and dimensions extending to 6000mm in length and 2500mm in width.
PED and ABS International Qualifications
The Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) and American Bureau of Shipping (ABS) certifications represent critical international qualifications that significantly elevate the standards governing Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates production, particularly for applications in pressure vessels and marine environments. These certifications involve rigorous third-party assessment of manufacturing processes, material properties, and quality control systems to ensure compliance with international safety standards. The PED certification, essential for European market access, focuses on pressure containment capabilities and requires extensive mechanical testing of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates, including burst pressure tests, cyclic loading evaluations, and creep resistance assessments under various temperature conditions.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. achieved these prestigious certifications in 2024, following comprehensive audits of their production facilities and quality management systems. The qualification process for these Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates involved submitting production samples for independent laboratory testing to verify conformance with specified mechanical and chemical properties. The company's explosion welding (EXW) technology underwent particular scrutiny to confirm consistent bond integrity across varying plate dimensions and material combinations. Their successful certification validates that their manufacturing processes consistently produce Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates that meet the stringent safety requirements for critical applications in petrochemical processing, offshore installations, and high-pressure chemical reactors. This achievement positions their products for specification in international projects requiring certified materials that satisfy multiple regulatory frameworks, providing customers with documented assurance that these specialized clad metals will perform reliably in demanding operating environments.
Testing Methodologies and Acceptance Criteria
The evaluation of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates requires specialized testing methodologies and clearly defined acceptance criteria to ensure compliance with international standards. These comprehensive testing protocols verify both the integrity of the metallurgical bond and the performance characteristics of the composite material. Ultrasonic testing, conducted in accordance with ASTM A578/A578M, serves as the primary non-destructive examination method for detecting delamination or bonding defects across the entire surface area of these specialized plates. Shear strength testing, performed according to ASTM A264, quantifies the mechanical strength of the bond between titanium and zirconium layers, with acceptance typically requiring minimum values exceeding 140 MPa depending on the specific application requirements.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. implements these rigorous testing methodologies throughout their production process, maintaining advanced testing equipment calibrated to international standards. Their quality control laboratories perform bond integrity verification through specialized bend tests where samples are bent to predetermined angles without evidence of separation between the titanium cladding and zirconium base. For Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates destined for corrosive environments, the company conducts additional electrochemical testing to verify corrosion resistance, often exceeding standard requirements by performing extended exposure tests in simulated service environments. Dimensional inspections verify thickness uniformity across the entire plate surface, ensuring the cladding layer maintains consistent thickness between 2mm and 10mm as specified in customer requirements. The company's documented testing procedures establish clear acceptance criteria for each test, with non-conforming materials subjected to root cause analysis and corrective action procedures in accordance with their ISO9001-2000 quality management system. This comprehensive testing regime ensures that every Titanium Clad Zirconium Plate leaving their facility meets or exceeds the performance standards required for critical applications in chemical processing, nuclear power generation, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.

Manufacturing Technologies and Material Performance
Explosion Welding (EXW) Specifications
Explosion Welding (EXW) represents the primary manufacturing technology for producing high-quality Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates, with specific technical specifications governed by international standards to ensure consistent product integrity. This sophisticated process utilizes controlled detonation energy to create a metallurgical bond between dissimilar metals at the atomic level, with the resulting wave-like interface providing exceptional mechanical strength and thermal stability. The ASTM B898 standard establishes detailed specifications for explosive bonding parameters, including standoff distance requirements, explosive charge density calculations, and detonation velocity controls that directly influence bond quality in Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates.
At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., the explosion welding process follows precisely engineered protocols developed through decades of specialized experience. The company's EXW facilities incorporate advanced material preparation systems that ensure pristine surface conditions necessary for optimal bonding, with titanium and zirconium plates undergoing rigorous cleaning processes to remove any contaminants that could compromise bond integrity. Their proprietary charge placement techniques ensure uniform impact energy distribution across plates measuring up to 6000mm in length and 2500mm in width, maintaining consistent bond characteristics throughout the entire surface area. The collision velocities are carefully controlled to generate the optimal kinetic energy for creating the characteristic wavy interface between titanium and zirconium layers that enhances mechanical interlocking while preventing excessive heat that could alter material properties. This precision in explosion welding parameters allows Baoji JL to produce Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates with exceptional bond strength exceeding industry standards, verified through systematic destructive testing of production samples. The company's continuous refinement of their EXW methodology has resulted in bonding techniques specifically optimized for the unique metallurgical characteristics of titanium (available in Grades 1, 2, and 5) and zirconium (typically Grades 702 and 705), ensuring maximum performance in challenging industrial applications.
Material Selection and Compatibility Factors
The production of high-performance Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates begins with meticulous material selection governed by standards that ensure chemical and mechanical compatibility between the constituent metals. International specifications, including ASTM B265 for titanium and ASTM B551 for zirconium, establish strict compositional requirements that manufacturers must verify through certified material testing. These standards define acceptable ranges for alloying elements, impurity limits, and mechanical properties that directly impact the performance of the finished clad product. The selection process must account for the differential thermal expansion coefficients between titanium and zirconium to prevent stress development during temperature fluctuations in service applications.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. implements rigorous material selection protocols that exceed basic standard requirements to ensure optimal compatibility in their Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates. Their procurement specifications require material certifications documenting chemical composition analysis for each heat of raw material, with internal verification testing to confirm supplied information. The company selects specific grades of titanium (typically Grades 1, 2, or 5) and zirconium (usually Grades 702 or 705) based on the intended application environment, carefully matching corrosion resistance properties to customer requirements. Material preparation involves specialized surface treatments to optimize bonding conditions, with precise control of surface roughness parameters that enhance mechanical interlocking during the explosion welding process. Titanium's exceptional resistance to chloride environments combines perfectly with zirconium's outstanding performance in strong acids, creating composite plates with unmatched chemical versatility. This thoughtful material selection process produces Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates with optimal performance characteristics, including high strength-to-weight ratios, superior thermal stability, and extraordinary resistance to a wide spectrum of corrosive media encountered in chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and nuclear power generation applications.
Performance Standards and Application Requirements
The performance standards governing Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates are directly linked to the demanding application requirements across multiple industries, with specific benchmarks established by engineering codes and industry-specific regulations. ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section VIII, Division 1 provides comprehensive requirements for clad materials used in pressure vessels, stipulating minimum mechanical properties, corrosion allowances, and design methodologies specific to bimetallic constructions. For nuclear applications, additional requirements from ASME Section III establish stricter controls on material traceability, manufacturing documentation, and non-destructive examination coverage for Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates used in critical components.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. designs their Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates to meet and exceed these stringent performance standards through carefully controlled manufacturing processes. Their products demonstrate exceptional mechanical integrity with shear strengths consistently exceeding 200 MPa at the bond interface, surpassing minimum requirements specified in ASTM standards. The corrosion resistance properties of these specialized plates are verified through electrochemical testing according to ASTM G48 for pitting resistance and ASTM G28 for intergranular corrosion susceptibility, with results documented in material test reports accompanying each shipment. The thermal stability of their Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates allows for operation across temperature ranges from cryogenic conditions up to 550°C without bond degradation, making them ideal for applications involving thermal cycling. The company's manufacturing capabilities accommodate customized thickness ratios between titanium cladding (ranging from 2mm to 10mm) and zirconium base metal to optimize performance for specific operating conditions, with total plate thicknesses available from 3mm to 200mm. This combination of standardized testing and application-specific customization ensures that Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates from Baoji JL deliver reliable performance in the most demanding industrial environments, from aggressive chemical processing to high-purity pharmaceutical production systems where material compatibility directly impacts product quality and safety.
Conclusion
The production of Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates is governed by comprehensive international standards including ASME/ASTM, GB/GBT, and JIS, with additional certifications like ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS ensuring consistent quality and performance. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. distinguishes itself through rigorous compliance with these standards while implementing advanced explosion welding technologies that produce superior metallurgical bonds for demanding industrial applications.
Looking to enhance your industrial capabilities with premium Titanium Clad Zirconium Plates that meet the highest international standards? Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. offers unmatched expertise in custom clad metal solutions, backed by independent explosive composite technology, international qualifications, and innovative R&D capabilities. Whether you need standard specifications or custom designs, our team is ready to collaborate on your specific requirements. Contact us today at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our advanced clad metal solutions can optimize your operations and extend equipment lifespan in challenging environments.
References
1. American Society for Testing and Materials. (2023). ASTM B898: Standard Specification for Reactive and Refractory Metal Clad Plate, Sheet, and Strip. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA.
2. Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. (2022). JIS G 3601: Clad Steel Plates and Sheets. Japanese Standards Association, Tokyo, Japan.
3. International Organization for Standardization. (2020). ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management Systems - Requirements. ISO Central Secretariat, Geneva, Switzerland.
4. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. (2023). ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section IX: Welding, Brazing, and Fusing Qualifications. ASME, New York, NY.
5. Standardization Administration of China. (2022). GB/T 8547: Technical Requirements for Clad Metals. Standards Press of China, Beijing, China.
6. European Committee for Standardization. (2021). Pressure Equipment Directive (PED) 2014/68/EU Technical Requirements for Pressure Equipment Manufacturing. CEN, Brussels, Belgium.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)