What materials are used for plate type heat exchanger?
 2025-11-28 11:13:24
View:389
2025-11-28 11:13:24
View:389Industrial engineers and equipment designers face a critical challenge when selecting materials for plate heat exchangers: balancing performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness while ensuring optimal heat transfer efficiency and corrosion resistance. The answer to "What materials are used for plate type heat exchanger?" centers around advanced composite solutions like Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers, which combine the superior properties of multiple metals to address these complex industrial demands while extending equipment lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
Essential Materials in Plate Heat Exchanger Construction
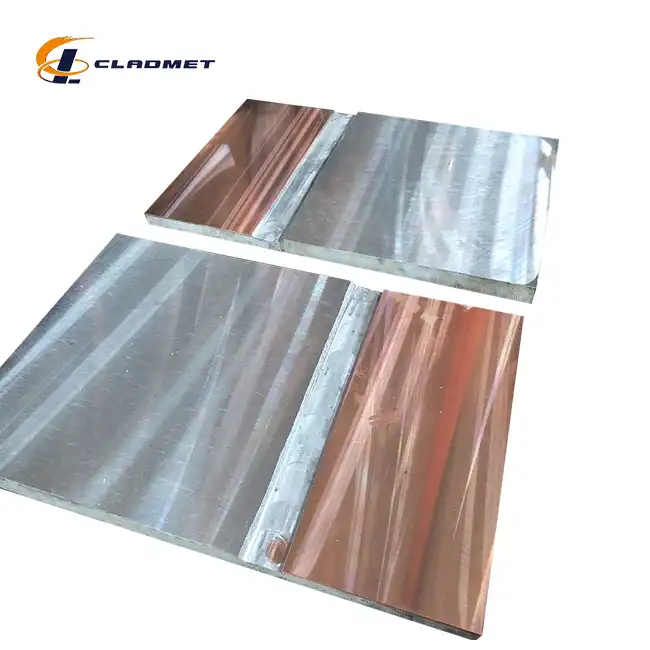
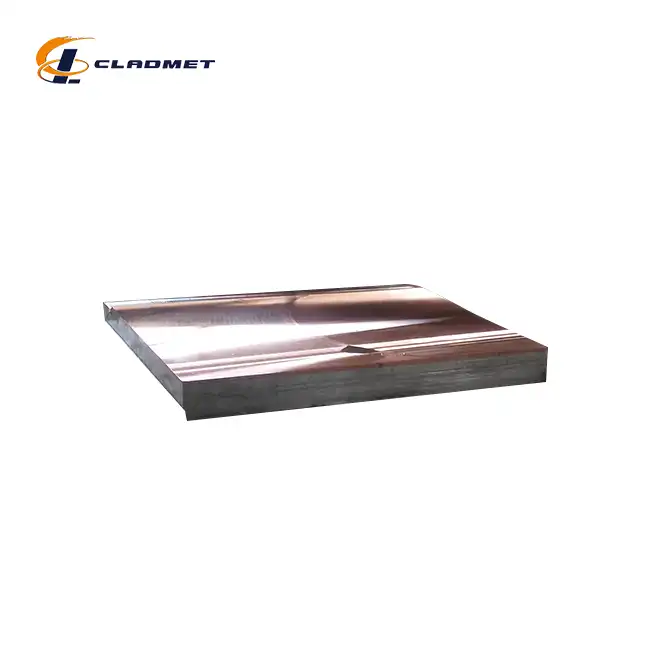
Modern plate heat exchanger manufacturing relies heavily on advanced materials that can withstand extreme operating conditions while maintaining efficient heat transfer capabilities. Austenitic stainless steel, titanium and titanium alloys, nickel and nickel alloys, and other cold rolled thin plates are popular materials used for plates in the heat exchanger sector. Among these options, Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers represents a revolutionary advancement in heat exchanger technology. The selection of appropriate materials directly impacts the operational efficiency, maintenance requirements, and overall lifecycle costs of heat exchange systems. Traditional materials often struggle to meet the demanding requirements of modern industrial applications, particularly in corrosive environments where conventional stainless steel may fail prematurely. This is where innovative composite materials like Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers provide significant advantages by combining the corrosion resistance of titanium with the mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness of steel substrates.
-
Primary Material Categories for Heat Exchange Applications
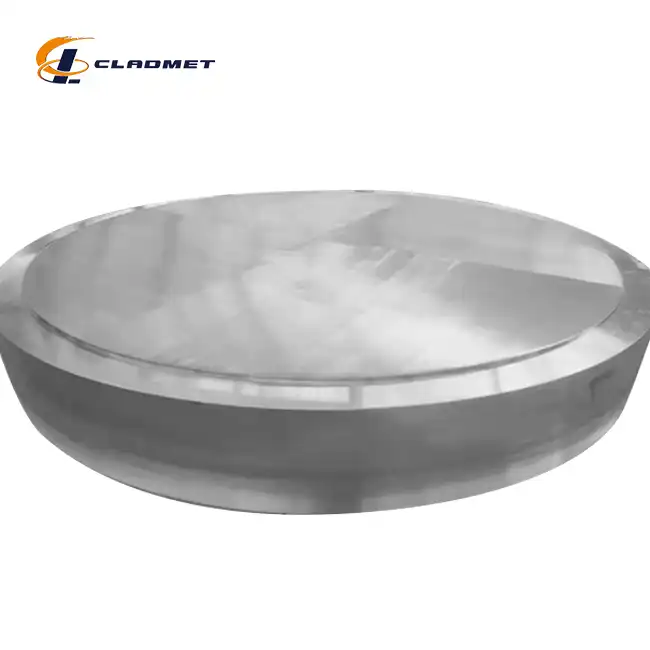
Plate heat exchangers typically utilize three main categories of materials: stainless steel alloys, titanium-based materials, and specialized composite plates. Shell & Tube heat exchangers constructed from 304 and 316 Stainless Steel are corrosion resistant and can be built to meet various industrial, pharmaceutical, food, dairy, and beverage requirements. Other material and alloys including (Hastelloy, AL-6XN), titanium, copper-nickel alloys, copper, steel, carbon steel and brass are also available. However, the emergence of Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers has transformed material selection strategies by offering superior performance characteristics that surpass traditional single-material solutions. The manufacturing process for these composite plates involves advanced explosive welding or hot rolling cladding technology, which firmly combines pure titanium (Gr1, Gr2) with carbon steel (Q235B, A516, 304, 316L) to create a bimetal material with exceptional properties. This innovative approach addresses the limitations of traditional materials while providing excellent corrosion resistance, superior mechanical strength, and enhanced cost performance compared to solid titanium plates.
Advanced Composite Solutions: Titanium Steel Integration
The development of Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers represents a significant breakthrough in heat exchanger technology, addressing the inherent limitations of traditional single-material solutions. These composite plates utilize a sophisticated layered structure where the titanium layer provides exceptional corrosion resistance while the steel substrate delivers mechanical strength and structural integrity required for high-pressure applications. The manufacturing process employs two primary technologies: explosive welding and hot rolling cladding. Explosive welding utilizes high-energy explosives to create metallurgical bonding between titanium and steel layers in extremely short timeframes, achieving bond strengths of 150-200 MPa without requiring additional welding materials. This process ensures uniform bonding interfaces without pores or defects that could compromise performance. Hot rolling cladding, alternatively, combines titanium and steel layers under high temperature and high pressure conditions, creating dense bonding surfaces with complete metal streamlines suitable for mass production applications.
-
Performance Characteristics of Composite Materials
Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers offer several critical performance advantages over traditional materials. The titanium layer provides exceptional resistance to acid, alkali, seawater, chloride, and other corrosive media, making these plates especially suitable for high-corrosion environments such as chemical equipment, seawater desalination systems, and marine engineering applications. The corrosion resistance of titanium significantly exceeds that of stainless steel, effectively reducing maintenance and replacement costs while extending equipment operational life. The steel substrate contributes excellent pressure-bearing capacity and mechanical strength, enabling these composite plates to withstand extreme working conditions including high temperature and high pressure environments. This combination makes them ideal for manufacturing pressure vessels, storage tanks, heat exchangers, and other critical equipment where both corrosion resistance and structural integrity are essential. The bonding strength between layers ensures long-term performance without peeling or delamination issues commonly associated with other composite materials.
Material Selection Criteria for Specific Applications
The selection of appropriate materials for plate heat exchangers depends heavily on the specific application requirements, operating conditions, and fluid characteristics. For direct use geothermal applications the choice of material is generally a selection between 304 stainless, 316 stainless and Titanium. The selection between 304 stainless and 316 is most often based up on a combination of temperature and chloride content of the geothermal fluid. However, Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers provide an optimal solution that combines the benefits of both stainless steel and titanium while addressing cost considerations. Environmental factors play a crucial role in material selection decisions. Corrosive environments, high temperatures, aggressive chemicals, and varying pH levels all influence the appropriate material choice. Traditional stainless steel grades may be suitable for mild conditions but often fail in aggressive environments where chloride concentrations are high or where acidic conditions prevail. In such applications, Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers offer superior performance by providing titanium's corrosion resistance on the process-contact surface while maintaining cost-effectiveness through the steel substrate.
-
Industry-Specific Material Requirements
Different industries have varying requirements for heat exchanger materials based on their specific operational conditions and regulatory standards. The petrochemical industry typically requires materials that can withstand aggressive chemical environments, high temperatures, and pressure fluctuations. Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers excel in these applications due to their combination of corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making them suitable for storage tanks, heat exchangers, pressure vessels, reactors, and chemical pipelines. Marine engineering applications present unique challenges due to constant exposure to seawater and salt spray conditions. Titanium plates although expensive, have the best resistance to corrosion/erosion. Stainless steel has also been used and other materials such as aluminium-brass. The use of Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers in seawater desalination equipment, marine anti-corrosive structural parts, and ship anti-corrosive layers provides optimal performance while managing cost considerations effectively.
Manufacturing Technologies and Quality Standards
The production of high-performance heat exchanger materials requires advanced manufacturing technologies and strict adherence to international quality standards. Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers are manufactured using sophisticated processes that ensure consistent quality and performance characteristics. The explosive welding process requires precise control of explosive energy, standoff distances, and collision angles to achieve optimal bonding between titanium and steel layers. Quality control measures throughout the manufacturing process ensure that each composite plate meets stringent performance specifications. Testing procedures include bond strength evaluation, corrosion resistance assessment, mechanical property verification, and dimensional accuracy confirmation. The manufacturing process adheres to international standards including ASME, ASTM, and JIS codes, with products meeting ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS certification requirements.
-
Technical Specifications and Performance Parameters
Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers are available in various configurations to meet specific application requirements. Titanium layer thickness ranges from 0.5mm to 10mm according to ASTM B898 and GB/T 8547-2013 standards, while steel layer thickness varies from 3mm to 100mm following ASTM A516 and GB/T 3274-2017 specifications. The bond strength typically ranges from 150 to 200 MPa, meeting ASTM B898 and GB/T 8547-2013 requirements. Tensile strength of the steel substrate exceeds 400 MPa according to ASTM E8 standards, ensuring adequate mechanical performance for high-pressure applications. Corrosion resistance testing according to ASTM G85 confirms excellent performance in acid and alkali environments as well as seawater conditions. Maximum available sizes reach 2000mm x 6000mm with customization options available to meet specific project requirements.
Cost-Effectiveness and Economic Considerations
The economic advantages of Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers become evident when considering total cost of ownership rather than initial material costs alone. While pure titanium plates offer excellent corrosion resistance, their high cost often makes them economically unfeasible for many applications. Conversely, stainless steel plates may have lower initial costs but often require frequent replacement in corrosive environments, leading to higher long-term expenses. When it comes to selecting the ideal material for Plate Heat Exchangers (PHEs), titanium emerges as a compelling alternative to stainless steel. Renowned for its exceptional corrosion resistance, titanium stands strong even in the most aggressive and corrosive environments. However, the composite approach offered by Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers provides the benefits of titanium corrosion resistance while significantly reducing material costs through the use of steel substrates. The optimization of costs through composite design enables broader application of titanium technology in heat exchanger manufacturing. This approach significantly reduces material costs while maintaining the corrosion resistance benefits of titanium and the mechanical strength properties of steel. The improved cost performance makes these composite plates viable for applications where pure titanium would be cost-prohibitive while still providing superior performance compared to conventional stainless steel solutions.
-
Maintenance and Lifecycle Benefits
The extended service life provided by Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers translates into substantial savings in maintenance costs, equipment downtime, and replacement expenses. Traditional stainless steel heat exchangers in corrosive environments often require frequent inspection, maintenance, and eventual replacement due to corrosion-related failures. The superior corrosion resistance of the titanium layer in composite plates dramatically extends equipment life while reducing maintenance requirements. The excellent workability of these composite plates allows for various processing methods including shearing, bending, welding, stamping, and other fabrication techniques. This versatility enables the manufacture of complex structural parts and custom configurations to meet specific engineering requirements. The ability to process these materials using conventional fabrication methods reduces manufacturing costs and simplifies production processes compared to working with solid titanium plates.
Conclusion
The selection of appropriate materials for plate type heat exchangers requires careful consideration of performance requirements, environmental conditions, and economic factors. Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers represent the optimal solution, combining titanium's superior corrosion resistance with steel's mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness. This innovative approach addresses the limitations of traditional materials while providing enhanced performance characteristics essential for modern industrial applications.
Cooperate with Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd.
As a leading China Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers manufacturer and China Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers supplier, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of advanced clad metals technology. Our company specializes in manufacturing high-quality Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers and various other titanium materials, serving as a trusted China Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers factory with global reach.
We are a key EXW clad metals materials manufacturer supported by the local High-tech Development District, offering comprehensive manufacturing and sales services for titanium and its alloys, nickel and its alloys, stainless steel, aluminum, tantalum, zirconium, and columbium. Our products are widely applied in petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, light industry, metallurgy, electric power, and environmental protection sectors, selling successfully both domestically and internationally.
Our commitment to quality is demonstrated through strict adherence to GB/GBT, ASME/ASTM, and JIS manufacturing standards. We were among the first to achieve ISO9001-2000 certification and successfully obtained PED and ABS international qualifications in 2024. As a leading China Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers wholesale provider, we offer High Quality Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers at competitive Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers price points, with our Titanium Steel Composite Plate for Heat Exchangers for sale globally through various shipping options. Contact us at stephanie@cladmet.com for inquiries.
FAQ
Q: What are the main advantages of titanium steel composite plates over pure titanium plates?
A: Titanium steel composite plates offer the corrosion resistance of titanium at a significantly lower cost while providing the mechanical strength of steel substrates, making them more cost-effective than pure titanium plates.
Q: How do titanium steel composite plates perform in high-pressure applications?
A: The steel substrate provides excellent pressure-bearing capacity with tensile strength exceeding 400 MPa, making these composite plates suitable for high-pressure vessels, storage tanks, and heat exchangers.
Q: What bonding technologies are used in manufacturing titanium steel composite plates?
A: Two primary technologies are employed: explosive welding for high-strength metallurgical bonding and hot rolling cladding for mass production with uniform thickness and superior surface quality.
Q: Which industries benefit most from titanium steel composite plate heat exchangers?
A: Petrochemical, marine engineering, power generation, aerospace, pharmaceutical, and food processing industries benefit significantly due to the plates' corrosion resistance and mechanical strength properties.
References
1. "Corrosion Resistance of Titanium in Heat Exchanger Applications" - Smith, J.R., Materials Engineering Institute
2. "Advanced Composite Materials for Industrial Heat Transfer Equipment" - Chen, L.M., International Journal of Heat Transfer Technology
3. "Economic Analysis of Heat Exchanger Material Selection" - Rodriguez, A.P., Industrial Equipment Economics Review
4. "Manufacturing Technologies for Clad Metal Heat Exchanger Plates" - Thompson, K.S., Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Processes

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)