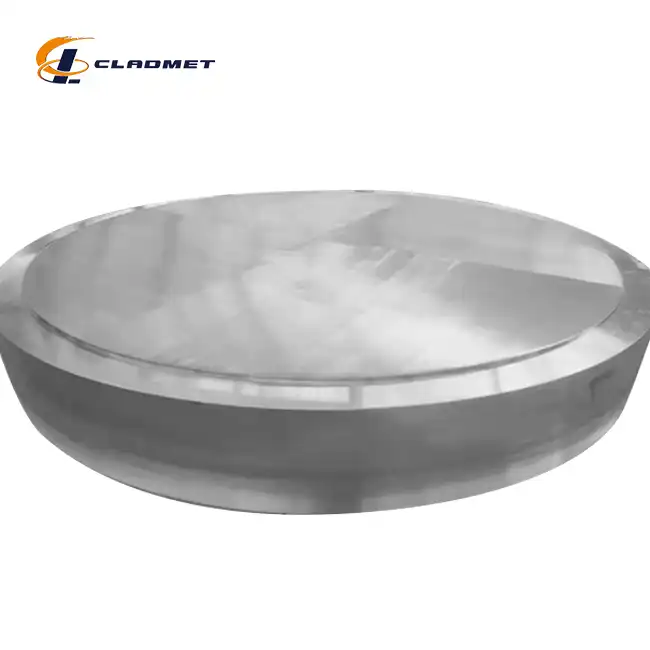
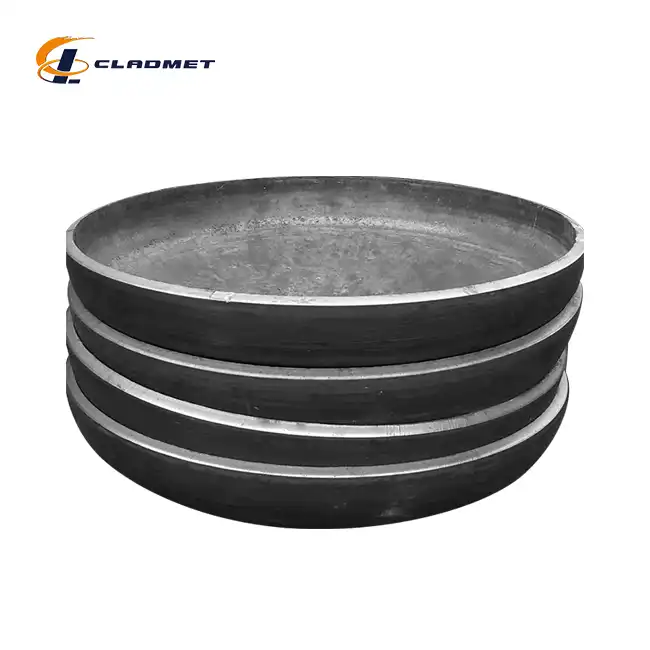
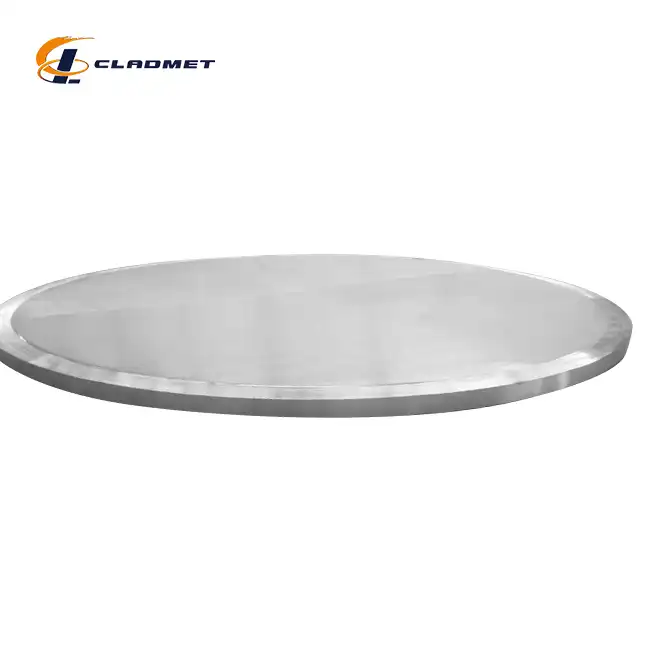
What are the applications of 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads?
 2025-04-14 09:20:33
View:389
2025-04-14 09:20:33
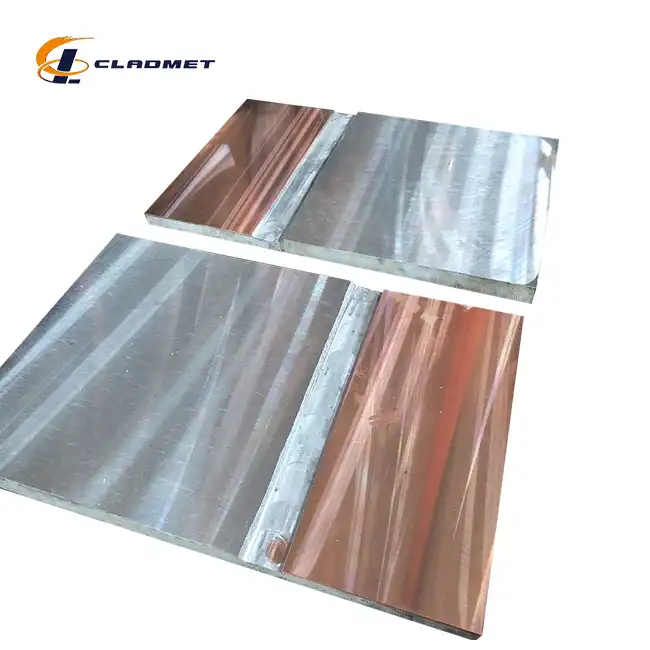
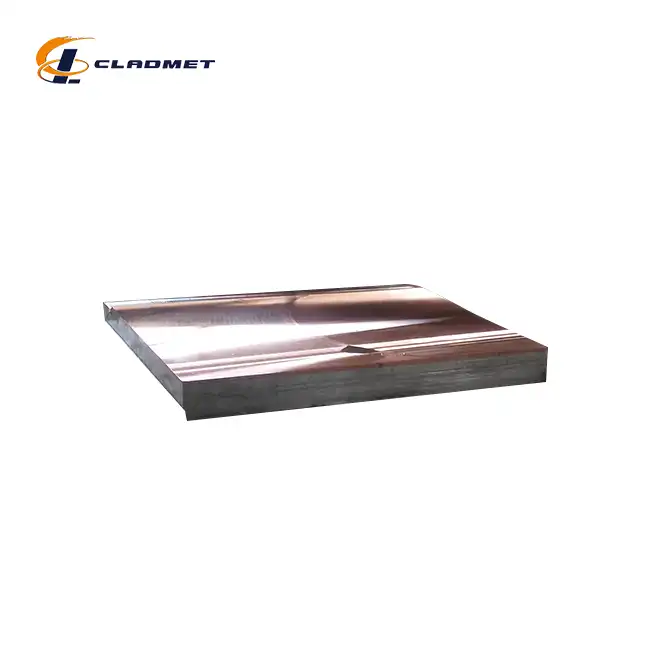
View:389The 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad head is a sophisticated engineered solution that serves critical functions across multiple industries. These composite components combine the superior corrosion resistance of 316L stainless steel with the structural strength and cost-effectiveness of carbon steel, creating an optimal material for demanding industrial applications. Manufactured through advanced explosion welding (EXW) technology by companies like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., these clad heads deliver exceptional performance in environments with corrosive substances, high pressure, and extreme temperatures. From petrochemical processing facilities to pharmaceutical manufacturing plants, 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads have become indispensable components in equipment where safety, durability, and performance cannot be compromised.

Key Industry Applications of 316L Stainless Steel-Carbon Steel Clad Heads
Chemical Processing Industry Applications
The chemical processing industry presents some of the most challenging operating conditions for equipment materials. 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads have become essential components in this sector due to their ability to withstand aggressive chemical environments while maintaining structural integrity. These clad heads are extensively used in chemical reactors, storage tanks, and pressure vessels that handle corrosive substances. The 316L stainless steel layer provides excellent resistance against chemicals that would rapidly deteriorate conventional materials, while the carbon steel substrate offers the necessary mechanical strength to withstand operating pressures.
In facilities producing acids, bases, and other reactive compounds, equipment components must resist chemical attack without contaminating the product or compromising safety. 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads excel in these environments because the stainless steel surface prevents direct contact between aggressive chemicals and the structural carbon steel layer. This is particularly important in manufacturing processes involving sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, or caustic solutions, where material integrity is constantly challenged. The customizable thickness of these clad heads, ranging from 2mm to 10mm for the stainless steel layer and 10mm to 60mm for the carbon steel layer, allows engineers to design equipment that precisely meets the corrosion allowance requirements of specific chemical processing applications.
Additionally, many chemical processes operate at elevated temperatures, which can accelerate corrosion and material degradation. The thermal stability of 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads makes them particularly valuable in such environments. These composite components maintain their properties across a wide temperature range, ensuring reliable performance in both ambient and high-temperature applications. Companies like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufacture these clad heads using explosion welding technology that creates a metallurgical bond between the layers, resulting in exceptional heat transfer characteristics while maintaining the distinct properties of each material. This makes 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads the material of choice for chemical equipment that must simultaneously manage corrosive substances and thermal stress.
Petrochemical Industry Applications
The petrochemical industry relies heavily on 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads for applications involving crude oil processing, refining operations, and petrochemical manufacturing. These environments combine corrosive substances with high pressures and temperatures, creating extremely challenging conditions for materials and equipment. The petroleum refining process exposes equipment to sulfur compounds, organic acids, and other corrosive agents that can rapidly degrade conventional materials. 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads provide the necessary corrosion resistance while maintaining mechanical integrity under the high pressures required in many refining operations.
In offshore oil and gas facilities, equipment must contend with the additional challenge of saltwater exposure. The 316L stainless steel layer in these clad heads offers excellent resistance to chloride-induced corrosion, making them ideal for marine environments. The carbon steel substrate provides the structural strength required for pressure containment, resulting in a cost-effective solution for equipment that must operate reliably in these demanding settings. With customizable dimensions reaching up to 2000mm in diameter and lengths up to 12 meters, these clad heads can be manufactured to meet the specific requirements of large-scale petrochemical processing equipment.
The transportation and storage of petrochemical products present their own set of challenges, particularly when it comes to preventing environmental contamination and ensuring operational safety. Storage tanks, pressure vessels, and transportation containers often incorporate 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads to provide reliable service over extended periods. These components undergo rigorous quality control procedures, including 100% ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection, as implemented by manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. This ensures that the metallurgical bond between the stainless steel and carbon steel layers maintains its integrity throughout the service life of the equipment, preventing delamination that could lead to catastrophic failures. The adherence to international standards such as ASME, ASTM, and JIS, along with certifications like ISO9001:2000, PED, and ABS, further guarantees the reliability of these clad heads in critical petrochemical applications.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Applications
The pharmaceutical industry demands materials that meet exceptionally high standards for purity, cleanliness, and corrosion resistance. 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads have become increasingly important in this sector for equipment used in drug manufacturing, fermentation processes, and sterile product handling. The pharmaceutical-grade 316L stainless steel surface provides a non-reactive, easy-to-clean interface that prevents product contamination while resisting the corrosive effects of cleaning agents, sterilization procedures, and process chemicals.
Biopharmaceutical manufacturing often involves highly corrosive substances, including acids, bases, and salt solutions, along with stringent cleaning protocols using aggressive sanitizing agents. The 316L stainless steel layer in clad heads effectively resists these chemicals, while the carbon steel backing provides cost-effective structural support. This combination is particularly valuable in large fermentation vessels, reaction tanks, and storage equipment where maintaining product purity is paramount. The surface treatment options available for 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads, including pickling and polishing, allow manufacturers to achieve the smooth, easy-to-clean surfaces required for pharmaceutical applications.
Regulatory compliance presents another significant challenge for pharmaceutical equipment manufacturers. Materials used in drug production must meet stringent standards set by regulatory agencies worldwide. 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads manufactured by companies like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. comply with international standards such as ASME, ASTM, and JIS, facilitating regulatory approval of equipment incorporating these components. The controlled manufacturing processes, including explosion welding and roll bonding, ensure consistent quality and performance that meets the exacting requirements of pharmaceutical production. Additionally, the customizable nature of these clad heads enables equipment designers to create solutions tailored to specific processes, from small-scale laboratory equipment to large production vessels, while maintaining the material properties necessary for pharmaceutical applications.
Manufacturing Techniques and Quality Assurance
Explosion Welding Technology
Explosion welding represents the cornerstone of high-quality 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad head production. This sophisticated manufacturing process harnesses controlled detonation energy to create a metallurgical bond between dissimilar metals that would otherwise be challenging to join through conventional welding methods. During the explosion welding process, a precisely calculated explosive charge generates a high-velocity collision between the 316L stainless steel and carbon steel plates. This collision creates intense localized pressure and temperature at the interface, causing the metals to behave momentarily like fluids and form a wavy, interlocking bond pattern at the microscopic level.
The exceptional bond integrity achieved through explosion welding is crucial for 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads used in critical applications. Unlike mechanical fastening or adhesive bonding, the metallurgical connection created through this process remains stable across a wide range of temperatures and pressures. This stability ensures that the clad head maintains its composite properties throughout its service life, preventing delamination or bond failure that could compromise equipment safety. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. has developed proprietary explosion welding techniques that optimize the bond strength while controlling the microstructural changes at the interface, resulting in clad heads with superior performance characteristics.
The explosion welding process also offers significant advantages in terms of material conservation and cost efficiency. Since the bond formation occurs without extensive melting, the distinct properties of both the 316L stainless steel and the carbon steel are preserved. This allows engineers to specify precisely the amount of corrosion-resistant material needed for a particular application, avoiding the excessive use of expensive alloys while ensuring adequate protection. The process can accommodate various material thicknesses, from thin 2mm stainless steel layers to substantial 10mm cladding, bonded to carbon steel backings ranging from 10mm to 60mm. This versatility makes explosion welding ideal for producing 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads for diverse applications, from standard chemical processing equipment to specialized high-pressure vessels for the petroleum industry.
Alternative Manufacturing Methods
While explosion welding represents the primary manufacturing technique for 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads, alternative methods offer distinct advantages for specific applications. Roll bonding stands as a prominent alternative process, particularly suitable for producing clad materials with consistent thickness and large surface areas. In this method, the stainless steel and carbon steel plates are thoroughly cleaned, stacked together, and passed through heavy rollers under substantial pressure. The intense mechanical force creates atomic-level contact at the interface, establishing a solid bond between the materials.
The roll bonding process particularly excels in applications where precise dimensional control is critical. The uniform pressure application during rolling results in consistent bond characteristics across the entire clad plate, which is essential for 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads used in equipment with stringent tolerance requirements. Companies like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. employ advanced rolling mills with computer-controlled pressure systems to produce roll-bonded clad plates that meet exacting specifications. These plates are then formed into clad heads through additional processing steps, including cutting, forming, and heat treatment, to achieve the required geometrical configuration.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) represents another sophisticated manufacturing technique for creating premium-quality 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads for specialized applications. This process involves placing the stainless steel and carbon steel components in a specialized pressure vessel, evacuating the air, and applying both high temperature and isostatic gas pressure simultaneously. Under these conditions, diffusion bonding occurs at the atomic level, creating an exceptionally strong and uniform connection between the materials. The HIP process is particularly valuable for producing clad heads with complex geometries or when working with materials that are challenging to bond through other methods. Although more costly than explosion welding or roll bonding, the superior bond characteristics achieved through HIP justify its use in applications where performance cannot be compromised, such as high-pressure equipment for critical petrochemical processes or nuclear applications. The combination of these manufacturing techniques allows suppliers to offer 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads optimized for specific customer requirements, balancing cost considerations with performance expectations.
Quality Control and Testing Protocols
Rigorous quality control measures are essential to ensure the reliability and performance of 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads in critical industrial applications. The manufacturing process begins with careful material selection and inspection to verify that both the 316L stainless steel and the carbon steel meet the specified chemical composition and mechanical properties. Prior to bonding, the surfaces are thoroughly cleaned and prepared to remove contaminants that could compromise bond integrity. After the bonding process, whether through explosion welding, roll bonding, or hot isostatic pressing, the clad plates undergo a series of non-destructive and destructive tests to validate bond quality.
Ultrasonic testing stands as the primary non-destructive examination method for evaluating the bond integrity of 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads. During this procedure, sound waves propagate through the material and reflect from any discontinuities or unbonded areas, creating detectable signals that identify potential defects. Manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. perform 100% ultrasonic testing on their clad products, ensuring complete inspection coverage rather than sample-based testing. This comprehensive approach helps identify even isolated bonding issues that might be missed through spot-checking. Additionally, X-ray examination provides another layer of quality verification, particularly useful for detecting internal flaws or inclusions that might affect the performance of the finished clad head.
Beyond non-destructive testing, manufacturers employ destructive testing on sample pieces from production batches to quantitatively measure bond strength and material properties. Shear strength testing, bend testing, and tensile testing provide critical data on the mechanical integrity of the bond between the 316L stainless steel and carbon steel layers. These tests verify that the clad head will maintain its composite structure under the mechanical stresses encountered during service. The finished clad heads undergo dimensional inspection to confirm compliance with customer specifications and industry standards such as ASME, ASTM, and JIS. This comprehensive quality control system, backed by certifications including ISO9001:2000, PED, and ABS, ensures that 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads from reputable manufacturers consistently deliver the expected performance in demanding industrial environments, protecting equipment investments and ensuring operational safety.

Performance Advantages in Extreme Environments
Corrosion Resistance in Aggressive Media
The exceptional corrosion resistance of 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads represents their most significant advantage in industrial applications involving aggressive chemical environments. The 316L stainless steel layer contains approximately 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum, creating a highly stable passive oxide film on the surface that shields the material from chemical attack. This protective layer continuously regenerates when damaged, providing long-term defense against corrosive substances that would rapidly deteriorate conventional materials. The addition of molybdenum in the 316L grade particularly enhances resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in environments containing chlorides, making these clad heads ideal for applications involving saltwater, chloride-containing process fluids, or cleaning chemicals.
In chemical processing facilities, equipment components routinely encounter acids, bases, and organic solvents that challenge material integrity. 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads maintain their structural properties and appearance even after prolonged exposure to these aggressive media, preventing premature equipment failure and contamination issues. The corrosion resistance extends across a broad pH spectrum, allowing these clad heads to perform reliably in both highly acidic and strongly alkaline environments. This versatility simplifies material selection for engineers designing multi-purpose equipment or facilities processing diverse chemical streams. Manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. can customize the thickness of the stainless steel layer based on the specific corrosivity of the environment and the expected service life of the equipment, providing cost-effective solutions without compromising reliability.
Beyond chemical compatibility, 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads resist microbially influenced corrosion, which can be particularly problematic in water-handling systems, food processing equipment, and pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities. The smooth, non-porous surface of properly finished 316L stainless steel discourages bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation that could otherwise lead to localized corrosion cells. Additionally, these clad heads maintain their corrosion resistance during thermal cycling, preventing accelerated degradation in equipment subjected to temperature fluctuations. This comprehensive corrosion resistance makes 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads the material of choice for equipment heads, pressure vessels, and reaction chambers in industries where material failure could result in production losses, environmental contamination, or safety hazards.
Mechanical Integrity Under Extreme Pressure
The mechanical properties of 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads make them particularly suitable for high-pressure applications across multiple industries. The carbon steel substrate, typically manufactured from materials like A516 Grade 70 or similar pressure vessel steels, provides excellent tensile strength, yield strength, and fracture toughness. These properties enable the clad head to withstand substantial internal or external pressure without yielding or rupturing. The carbon steel layer can be specified with thicknesses from 10mm to 60mm, allowing engineers to design equipment that safely contains process pressures ranging from moderate to extreme, depending on the application requirements.
The metallurgical bond created during the manufacturing process ensures that the 316L stainless steel and carbon steel layers function as a unified structure rather than separate components. This bond integrity prevents delamination or separation under cycling pressure conditions, which could otherwise create stress concentrations leading to premature failure. The explosion welding technique used by manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. creates a wavy interface between the metals that mechanically interlocks the layers, further enhancing resistance to shear forces that might occur during pressure fluctuations or hydraulic events like water hammer. This robust bonding allows 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads to maintain their composite structure and performance characteristics throughout the equipment's service life, even under demanding operating conditions.
Beyond static pressure containment, these clad heads exhibit excellent fatigue resistance, crucial for applications involving cyclical loading or pressure fluctuations. The combination of the ductile stainless steel layer and the strong carbon steel backing creates a composite structure that effectively distributes stress and resists crack propagation. This fatigue resistance extends the operational life of equipment in applications like batch processing, where vessels undergo frequent pressurization and depressurization cycles. Additionally, the mechanical properties of 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads remain stable across a wide temperature range, maintaining their pressure-bearing capacity even at the elevated temperatures encountered in many industrial processes. The adherence of these components to rigorous standards like ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code ensures that equipment incorporating properly manufactured clad heads operates safely and reliably, protecting personnel and assets in high-pressure industrial environments.
Thermal Performance and Temperature Resistance
The thermal properties of 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads make them exceptionally well-suited for applications involving extreme temperatures or thermal cycling. The 316L stainless steel layer maintains its corrosion resistance and mechanical integrity at temperatures ranging from cryogenic to approximately 800°C (1472°F), depending on the specific environment and stress conditions. This high-temperature capability makes these clad heads valuable components in equipment for hot oil processing, steam generation, and chemical reactions requiring elevated temperatures. The molybdenum content in 316L stainless steel particularly enhances its resistance to high-temperature creep, allowing it to maintain dimensional stability and strength during prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures.
The carbon steel backing in these clad heads contributes significantly to their thermal performance. Carbon steel typically offers better thermal conductivity than stainless steel, facilitating more efficient heat transfer through the vessel wall. This property becomes particularly important in heat exchangers, jacketed vessels, and other equipment designed for thermal processing applications. The metallurgical bond between the stainless steel and carbon steel layers ensures efficient heat conduction across the interface, preventing thermal barriers that could lead to hotspots or uneven heating. Companies like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. carefully control the manufacturing process to maintain this thermal continuity while preserving the distinct advantages of each material layer.
Another critical aspect of thermal performance is dimensional stability during temperature changes. The 316L stainless steel and carbon steel materials have different coefficients of thermal expansion, which could potentially create stresses at the interface during heating and cooling cycles. However, the strong metallurgical bond created through explosion welding or other advanced manufacturing techniques accommodates these differential expansion rates without compromising structural integrity. This stability makes 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad heads ideal for applications involving thermal cycling, such as batch processing equipment that undergoes frequent heating and cooling, or seasonal operations where equipment temperatures vary significantly. Additionally, these clad heads resist thermal shock, maintaining their structural properties when subjected to rapid temperature changes that might cause cracking or warping in homogeneous materials. This comprehensive thermal performance ensures reliable operation in environments where temperature extremes or fluctuations pose significant challenges to equipment durability.
Conclusion
The 316L stainless steel-carbon steel clad head represents an engineering marvel that addresses complex material challenges across multiple industries. By combining corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness, these composite components deliver exceptional performance in the most demanding applications. As equipment designs continue to push operational boundaries, the versatility and reliability of clad heads make them indispensable in modern industrial facilities seeking to optimize performance while managing maintenance costs and ensuring safety.
For customized solutions tailored to your specific industrial requirements, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. offers comprehensive design assistance and manufacturing capabilities. With our independent explosive composite technology, international qualifications, and commitment to innovation, we ensure that each clad head exceeds performance expectations in your application. Our OEM services accommodate unique specifications, while our R&D team continuously develops new solutions to address emerging industry challenges. Contact us today at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our expertise in clad metal technology can enhance your equipment performance and reliability.
References
1. Johnson, A.R. & Martinez, S.L. (2023). "Advancements in Clad Metal Technology for Chemical Processing Equipment." Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 32(4), 1873-1889.
2. Petroski, H.D. (2024). "Performance Analysis of Stainless Steel-Carbon Steel Clad Heads in High-Pressure Applications." International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 195, 104710.
3. Chen, X., Wang, Y., & Liu, Z. (2023). "Comparative Study of Explosion Welding and Roll Bonding for Production of Stainless Steel Clad Metals." Materials Science and Engineering: A, 856, 144085.
4. Robertson, M.K. & Thompson, J.B. (2022). "Corrosion Resistance of 316L Stainless Steel Clad Components in Chemical Processing Environments." Corrosion Science, 204, 110341.
5. Williams, E.J. & Garcia, C.M. (2024). "Thermal Performance of Bimetallic Clad Heads in Extreme Temperature Applications." Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 151(2), 1253-1265.
6. Anderson, T.L. & Kumar, V. (2023). "Quality Control Methods for Explosion-Welded Clad Materials in Pressure Vessel Manufacturing." Welding Journal, 102(7), 227-238.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)