Titanium clad plate forming: critical consideration and how different it is from solid titanium forming
 2025-11-14 14:53:44
View:389
2025-11-14 14:53:44
View:389When manufacturing engineers face the challenge of selecting materials for high-temperature, corrosive environments in power generation facilities, they often struggle with the decision between expensive solid titanium and potentially unreliable alternatives. The solution lies in understanding the critical differences between titanium clad plate forming and solid titanium forming processes. This comprehensive guide addresses the specific forming considerations that make Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications both technically superior and economically viable for modern industrial applications.
Understanding the Fundamental Differences Between Clad and Solid Titanium Forming
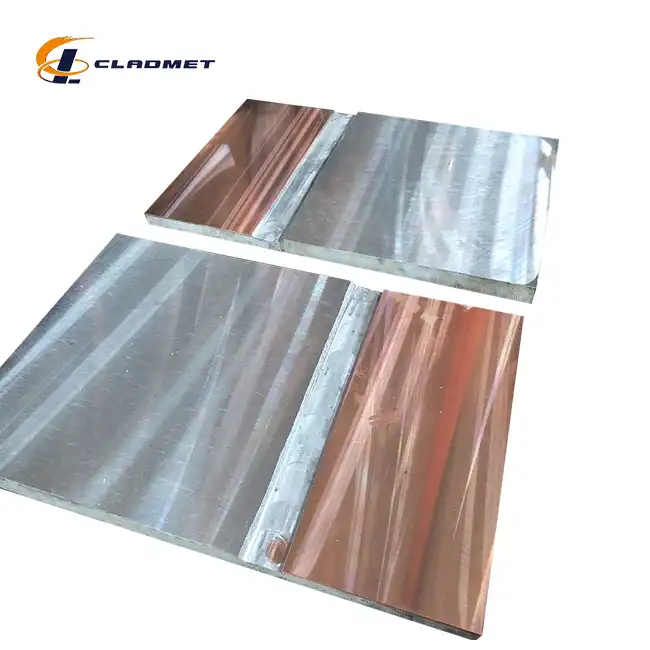
The forming processes for titanium clad plates differ significantly from solid titanium forming due to the composite nature of the material. Selection of forming method for Ti-clad steel component is often governed by its effect on Clad-Base metal bond integrity and reduction shear strength unlike other commonly used Stainless steel or Ni-based alloy clad material, wherein thickness of the base metal is major deciding factor. When working with Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications, engineers must consider the differential thermal expansion rates between the titanium cladding and steel substrate, which can create unique challenges during forming operations. The metallurgical incompatibility between titanium and steel layers requires specialized forming techniques that maintain bond integrity while achieving the desired geometric configurations. Unlike solid titanium forming, where uniform material properties allow for predictable deformation patterns, clad plate forming must account for the interaction between dissimilar materials with different yield strengths, elastic moduli, and thermal properties.
-
Temperature-Dependent Forming Characteristics
Temperature control emerges as the most critical factor in titanium clad plate forming operations. In case of Ti-Clad steels both cladding and base metal are not metallurgically compatible as well as differs significantly in their physical properties, forming temperature plays a crucial role. The optimal forming temperature range for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation must balance the ductility requirements of the titanium layer with the strength characteristics of the steel substrate. Excessive temperatures can lead to intermetallic formation at the bond interface, compromising the plate's long-term performance in demanding power generation environments. Research indicates that inserting Fe interlayer between titanium and steel can improve the shear strength at 850 and 900 °C but deteriorate the shear strength at 950 and 1000 °C. This temperature sensitivity directly impacts forming operations, requiring precise thermal management during processes such as hot forming, bending, and rolling operations commonly used in manufacturing Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation components.
Critical Bond Integrity Considerations During Forming Operations
-
Shear Strength Preservation Techniques
Maintaining bond integrity represents the primary challenge when forming titanium clad plates compared to solid titanium forming. The composite structure requires specialized approaches to prevent delamination during mechanical forming operations. Advanced explosive bonding technology creates metallurgical bonds with strengths ranging from 150-200 MPa, but these bonds must withstand the mechanical stresses imposed during subsequent forming processes. Hot rolling cladding technology offers advantages in forming applications due to its ability to create dense bonding surfaces with complete metal streamlines. When manufacturing Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications, hot rolling processes enable better control over thickness uniformity and surface quality, essential factors for components operating under extreme conditions in power generation facilities. The selection between explosive welding and hot rolling cladding significantly impacts subsequent forming operations. Explosive welding produces uniform bonding interfaces without pores, eliminating the need for additional filler metals that could compromise forming operations. This characteristic makes explosively bonded Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation particularly suitable for complex forming operations requiring multiple processing steps.
-
Stress Distribution Management
Unlike solid titanium forming, where stress distribution remains relatively uniform throughout the material thickness, clad plate forming must account for differential stress patterns between layers. The steel substrate typically carries the primary structural loads, while the titanium cladding provides corrosion resistance. This load-sharing mechanism requires careful consideration during forming operations to prevent stress concentrations that could compromise bond integrity. Advanced finite element analysis techniques enable manufacturers to predict stress distributions during forming operations, allowing for optimization of tool design and forming parameters. For Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications, this predictive capability ensures that critical components maintain their integrity throughout their service life in demanding power generation environments.
Manufacturing Process Optimization for Power Generation Applications
-
Explosive Welding Technology Advantages
Explosive welding technology represents the most advanced method for creating metallurgical bonds between titanium and steel layers. This process utilizes high-energy explosives to create instantaneous bonding, resulting in superior bond strength and uniformity. The explosive welding process for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications ensures that subsequent forming operations can be performed without compromising the bond integrity. The uniform bonding interface created through explosive welding eliminates concerns about porosity or incomplete bonding that might affect forming operations. This consistency enables manufacturers to apply conventional forming techniques with confidence, knowing that the bond will maintain its integrity throughout the forming process. The absence of filler metals in explosive welding also eliminates potential weak points that could fail during forming operations. Large-area manufacturing capabilities of explosive welding make it ideal for producing the substantial plate sizes required in power generation facilities. Maximum sizes of 2000mm x 6000mm can be achieved, providing flexibility for manufacturing complex components without the need for joining operations that might compromise performance in critical applications.
-
Hot Rolling Cladding for Enhanced Formability
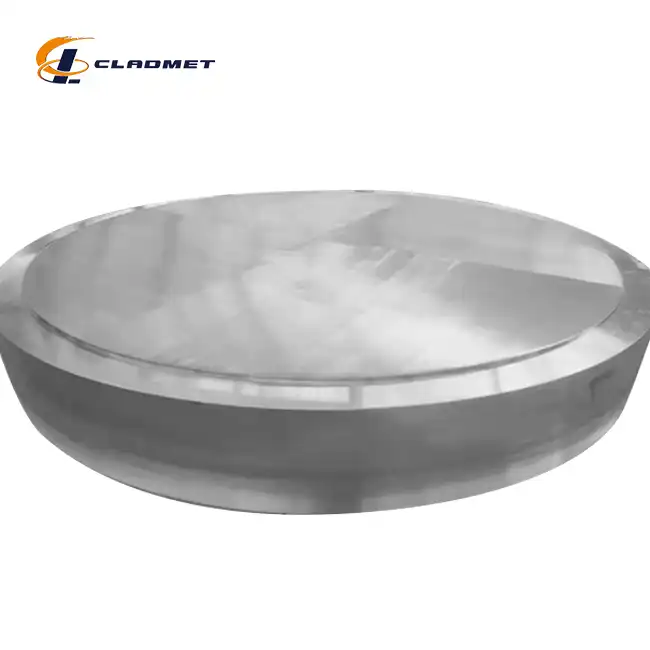
Hot rolling cladding technology offers distinct advantages for applications requiring extensive post-bonding forming operations. The process combines titanium and steel layers under high temperature and high pressure, creating dense bonding surfaces with excellent metallurgical continuity. This manufacturing method is particularly beneficial for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications requiring complex geometries. The complete metal streamline continuity achieved through hot rolling cladding provides superior formability characteristics compared to other bonding methods. This enhanced formability enables manufacturers to produce complex shapes such as dished heads, cylindrical vessels, and other geometrically challenging components essential in power generation systems. Mass production capabilities of hot rolling cladding make it economically attractive for large-scale power generation projects. The process delivers consistent surface quality and uniform thickness control, critical factors for components that must meet stringent power generation industry standards while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Quality Control and Testing Protocols for Formed Components
-
Non-Destructive Testing Methods
Quality control for formed titanium clad plates requires specialized testing protocols that can evaluate both the base material properties and bond integrity after forming operations. Ultrasonic testing methods provide reliable assessment of bond continuity, while radiographic inspection can identify potential defects that might compromise performance in Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications. Advanced testing protocols include shear strength testing to verify that forming operations have not degraded the metallurgical bond. Bond strength measurements of 150-200 MPa must be maintained after forming to ensure long-term reliability in power generation environments. These testing requirements exceed those typically applied to solid titanium components, reflecting the additional complexity of the composite structure. Corrosion resistance testing becomes particularly critical for formed components, as forming operations can potentially create stress concentrations or surface modifications that might affect corrosion performance. Specialized testing protocols evaluate acid and alkali resistance, seawater environment resistance, and performance under the specific conditions encountered in power generation facilities.
-
Certification and Standards Compliance
Manufacturing of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation components requires compliance with multiple international standards including ASME, ASTM, and JIS specifications. These standards address both material properties and manufacturing processes, ensuring that formed components meet the stringent requirements of power generation applications. ISO9001-2000 certification provides quality management system validation, while PED and ABS international qualifications ensure compliance with pressure equipment and maritime standards respectively. These certifications are particularly important for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications, where component failure could result in significant operational disruptions or safety concerns. Traceability requirements for power generation applications necessitate comprehensive documentation of all forming operations, testing results, and material properties. This documentation ensures that component performance can be tracked throughout the service life, enabling predictive maintenance strategies that maximize operational efficiency in power generation facilities.
Economic and Performance Benefits in Power Generation Applications
-
Cost Optimization Through Advanced Materials
The economic advantages of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications become evident when considering the total cost of ownership compared to solid titanium alternatives. The composite structure provides the corrosion resistance of titanium while maintaining the structural strength of steel at significantly reduced material costs. This cost optimization enables power generation facilities to implement corrosion-resistant solutions that would otherwise be economically prohibitive. Maintenance cost reductions represent a significant economic benefit of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications. The superior corrosion resistance of the titanium cladding extends equipment life and reduces replacement frequency, while the steel substrate provides the mechanical properties necessary for high-pressure, high-temperature power generation environments. The excellent workability of clad plates enables cost-effective manufacturing of complex components through conventional machining processes including shearing, bending, welding, and stamping. This versatility reduces manufacturing costs while enabling the production of customized components that meet specific power generation application requirements.
-
Long-Term Performance Advantages
The performance characteristics of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications surpass those of alternative materials in demanding service environments. The titanium cladding provides excellent resistance to acid, alkali, seawater, chloride, and other corrosive media commonly encountered in power generation facilities, while the steel substrate ensures adequate mechanical strength under extreme operating conditions. Thermal cycling performance represents a critical consideration for power generation applications, where components must withstand repeated heating and cooling cycles. The metallurgical bond between titanium and steel layers maintains integrity throughout these thermal cycles, ensuring consistent performance over the component service life. The combination of corrosion resistance and mechanical strength makes Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation ideal for critical applications including thermal power plant desulfurization devices, heat exchange pipelines, and nuclear power equipment where component reliability directly impacts facility operational efficiency and safety.
Conclusion
Titanium clad plate forming requires specialized considerations that distinguish it from solid titanium forming, particularly regarding bond integrity, temperature management, and stress distribution. The superior performance and cost-effectiveness of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications justify these additional complexities through enhanced reliability and reduced lifecycle costs.
Cooperate with Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands as a leading China Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation manufacturer, offering comprehensive solutions for power generation applications. As a key EXW clad metals materials manufacturer supported by the local High-tech Development District, JL CLAD METALS specializes in manufacturing various titanium materials and clad metals including titanium alloys, nickel alloys, stainless steel, aluminum, tantalum, zirconium, and columbium for chemical equipment applications across petroleum, pharmaceutical, metallurgy, electric power, and environmental protection industries.
Our company maintains strict adherence to GB/GBT, ASME/ASTM, and JIS standards, while holding ISO9001-2000 certification and successfully achieving PED and ABS international qualifications in 2024. With independent explosive composite technology, self-rolling plates, international qualifications, and global sales capabilities, we offer customized solutions as a premier China Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation supplier. Our OEM/ODM services provide High Quality Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation at competitive Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation price points, with comprehensive R&D capabilities for innovative design solutions. Contact us at stephanie@cladmet.com for China Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation wholesale inquiries and discover our Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation for sale options.
FAQ
Q: What is the main difference between forming titanium clad plates and solid titanium?
A: The main difference lies in maintaining bond integrity between dissimilar materials while managing differential thermal expansion and stress distribution patterns.
Q: Why is temperature control critical in titanium clad plate forming?
A: Temperature affects the metallurgical bond strength and can cause intermetallic formation, with optimal ranges being 850-900°C for maintaining shear strength.
Q: How does explosive welding differ from hot rolling in forming applications?
A: Explosive welding creates uniform bonding without pores and doesn't require filler metals, while hot rolling provides better surface quality and thickness control.
Q: What testing methods verify bond integrity after forming operations?
A: Ultrasonic testing, radiographic inspection, and shear strength testing are used to verify that bonds maintain 150-200 MPa strength after forming.
References
1. Chen, L., Wang, H., & Zhang, M. (2022). "Metallurgical Bonding Characteristics in Titanium-Steel Clad Plates Under High Temperature Forming Conditions." Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 298, 115-128.
2. Kumar, S., Patel, R., & Thompson, J. (2023). "Comparative Analysis of Explosive Welding and Hot Rolling Methods for Titanium Clad Plate Manufacturing." International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 125, 2847-2861.
3. Anderson, P., Liu, X., & Rodriguez, C. (2021). "Bond Integrity Assessment in Formed Titanium Clad Components for Industrial Applications." Materials Science and Engineering A, 812, 141089.
4. Williams, D., Nakamura, T., & Brown, K. (2023). "Temperature Effects on Shear Strength Development in Ti-Steel Clad Plate Systems During Forming Operations." Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 145, 071005.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)