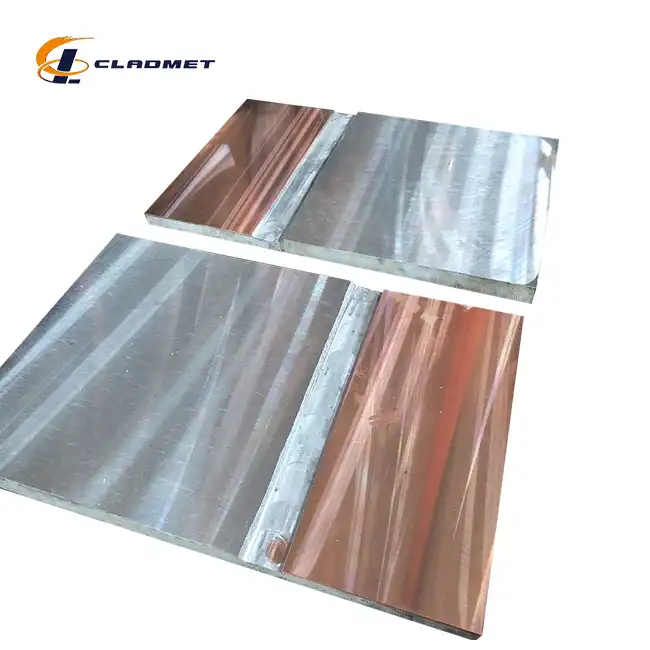
How Titanium Steel Clad Plate are Made: A Step-by-Step Guide
 2025-11-14 14:53:44
View:389
2025-11-14 14:53:44
View:389In today's demanding industrial landscape, power generation facilities face critical challenges with equipment corrosion, high maintenance costs, and premature component failure. Understanding how Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation are manufactured becomes essential for engineers and procurement specialists seeking cost-effective solutions that deliver superior corrosion resistance and structural integrity. This comprehensive guide reveals the intricate manufacturing processes behind these advanced composite materials, providing valuable insights into the technologies that combine titanium's exceptional corrosion resistance with steel's mechanical strength, ultimately solving the persistent problems plaguing power generation infrastructure.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Titanium Steel Clad Plate Manufacturing for Power Generation
The manufacturing of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation represents one of the most sophisticated metallurgical processes in modern industrial applications. This advanced composite material creation involves the precise bonding of pure titanium layers (typically Gr1 or Gr2) with high-quality steel substrates such as carbon steel Q235B, A516, or stainless steel grades 304 and 316L. The manufacturing process requires exceptional precision and control to ensure the resulting composite material maintains the corrosion resistance properties of titanium while preserving the mechanical strength characteristics of steel. The foundation of successful titanium steel clad plate manufacturing lies in understanding the metallurgical compatibility between dissimilar metals. Engineers must carefully consider factors such as thermal expansion coefficients, crystal structures, and chemical compatibility to achieve optimal bonding. The manufacturing process begins with rigorous material selection and quality control measures, where both titanium and steel components undergo comprehensive testing for chemical composition, mechanical properties, and surface quality standards according to ASTM, ASME, and JIS specifications.
-
Material Preparation and Quality Control Standards
The initial phase of manufacturing Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation involves meticulous preparation of both titanium and steel components. Raw materials undergo extensive inspection procedures to verify chemical composition, dimensional accuracy, and surface integrity. Titanium plates typically range from 0.5mm to 10mm in thickness and must meet stringent purity standards specified in ASTM B898 and GB/T 8547-2013 requirements. Steel substrates, ranging from 3mm to 100mm thickness, must comply with ASTM A516 and GB/T 3274-2017 standards to ensure optimal bonding performance. Surface preparation represents a critical aspect of the manufacturing process, as the quality of the bond interface directly impacts the final product's performance characteristics. Both titanium and steel surfaces undergo specialized cleaning procedures including degreasing, mechanical abrasion, and chemical etching to remove oxides, contaminants, and surface irregularities. This preparation phase ensures maximum surface area contact and promotes the formation of strong metallurgical bonds during the subsequent bonding processes. Quality control measures implemented during material preparation include dimensional verification, surface roughness measurement, and chemical analysis to confirm material specifications. Advanced testing equipment such as ultrasonic thickness gauges, surface profilometers, and spectroscopic analyzers ensure that all materials meet the exacting standards required for power generation applications where reliability and longevity are paramount considerations.
Advanced Bonding Technologies in Titanium Steel Clad Plate Production
The bonding phase represents the most critical aspect of manufacturing Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation, where two primary technologies dominate the industry: explosive welding and hot rolling cladding. Each method offers distinct advantages and is selected based on specific application requirements, production volumes, and desired material properties. Understanding these technologies is essential for appreciating the complexity and precision required to create these advanced composite materials.
-
Explosive Welding Technology for Superior Bond Strength
Explosive welding stands as the premier technology for creating Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation with exceptional bond strength and reliability. This sophisticated process utilizes controlled detonation of high-energy explosives to accelerate the titanium plate toward the steel substrate at velocities exceeding 500 meters per second. The tremendous impact energy creates an instantaneous metallurgical bond at the interface, typically achieving bond strengths between 150-200 MPa without requiring additional filler materials or extended heating cycles. The explosive welding process begins with precise positioning of the titanium and steel plates with a predetermined standoff distance, typically ranging from 2-10mm depending on material thickness and desired bonding characteristics. High-energy explosives are then uniformly distributed across the titanium surface, with the explosive load carefully calculated to provide optimal acceleration while preventing damage to the base materials. The detonation propagates in a controlled manner, creating a collision angle that promotes the formation of a wavy interface pattern characteristic of high-quality explosive welds. Temperature generation during explosive welding is localized and instantaneous, reaching several thousand degrees Celsius at the bond interface for microseconds. This extreme thermal condition, combined with tremendous pressure, creates a unique metallurgical phenomenon where both materials undergo plastic deformation and atomic-level diffusion, resulting in an intermetallic bond that often exceeds the strength of the parent materials. The process produces uniform bonding across large surface areas, making it ideal for manufacturing Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications requiring maximum reliability and performance.
-
Hot Rolling Cladding Process for Mass Production
Hot rolling cladding represents an alternative manufacturing approach for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation, particularly suitable for high-volume production requirements and applications where consistent thickness control is paramount. This process involves heating the titanium and steel components to elevated temperatures, typically between 900-1200°C, followed by simultaneous rolling through precision mill stands that apply tremendous pressure to achieve metallurgical bonding. The hot rolling process begins with careful preparation of the material stack, where the titanium plate is positioned on the steel substrate with precise alignment and temperature control. The assembled materials are heated in specialized furnaces equipped with protective atmospheres to prevent oxidation and contamination during the heating phase. Temperature uniformity is critical throughout the process, as variations can result in uneven bonding or material property degradation that could compromise performance in power generation applications. Rolling mill operations for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation require exceptional precision and control, with multiple passes through successively smaller roll gaps to achieve the desired final thickness and bonding characteristics. Each rolling pass applies tremendous pressure, typically exceeding 1000 tons, while maintaining precise temperature control to ensure optimal metallurgical bonding conditions. The rolling process creates a dense, uniform bond interface with excellent metal flow characteristics that result in superior mechanical properties and corrosion resistance performance.
Quality Control and Testing Procedures for Power Generation Applications
Manufacturing Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation demands rigorous quality control and testing procedures to ensure compliance with international standards and performance specifications. The testing protocol encompasses multiple phases including in-process monitoring, intermediate inspections, and final product verification to guarantee that every plate meets the exacting requirements of power generation applications where failure is not an option.
-
Bond Strength and Integrity Verification
Bond strength testing represents the most critical aspect of quality control for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation manufacturing. Standard testing procedures include shear strength tests, tensile bond tests, and peel resistance evaluations performed according to ASTM B898 and GB/T 8547-2013 specifications. These tests verify that the metallurgical bond achieves the required 150-200 MPa strength range and maintains integrity under various loading conditions typical of power generation environments. Ultrasonic testing techniques provide non-destructive evaluation of bond quality throughout the entire plate area, detecting potential delamination, voids, or weak bonding regions that could compromise performance. Advanced ultrasonic equipment capable of detecting bond line discontinuities as small as 0.1mm ensures comprehensive quality verification without damaging the finished product. This testing is particularly crucial for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation applications where structural integrity directly impacts safety and operational reliability.
-
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Testing
Corrosion resistance testing forms another essential component of the quality control process for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation. Standardized corrosion tests according to ASTM G85 specifications evaluate the material's performance in various aggressive environments typical of power generation facilities, including acid exposure, chloride environments, and high-temperature oxidation conditions. Accelerated corrosion testing protocols simulate years of service exposure in controlled laboratory conditions, providing valuable data on expected service life and performance characteristics. These tests are particularly important for power generation applications where equipment operates in harsh environments with exposure to combustion byproducts, cooling water systems, and various chemical treatments that could potentially compromise material integrity over time.
Applications and Performance Benefits in Power Generation Systems
Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation offers exceptional performance benefits across numerous power generation applications, from thermal power plants to nuclear facilities and renewable energy systems. The unique combination of titanium's corrosion resistance and steel's structural strength makes these composite materials ideal for critical components that must withstand harsh operating environments while maintaining long-term reliability and performance.
-
Thermal Power Plant Applications and Benefits
In thermal power plants, Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation finds extensive application in desulfurization equipment, heat exchangers, and cooling water systems where exposure to corrosive flue gases and water treatment chemicals poses significant challenges to conventional materials. The titanium cladding provides superior resistance to sulfuric acid, chlorides, and other aggressive chemicals commonly encountered in these environments, while the steel substrate maintains the structural integrity required for pressure vessel applications. Heat exchanger applications particularly benefit from the thermal conductivity characteristics of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation, where the composite construction allows for efficient heat transfer while providing long-term corrosion protection. The titanium surface maintains its heat transfer efficiency throughout the service life, unlike conventional materials that may develop fouling or corrosion products that reduce thermal performance over time. Flue gas desulfurization systems represent another critical application where Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation provides exceptional value through its resistance to wet scrubber environments containing sulfuric acid, chlorides, and other aggressive chemicals. The composite construction allows for the design of large-scale equipment with complex geometries while maintaining corrosion protection and structural integrity throughout extended service periods.
-
Nuclear Power and Advanced Energy Systems
Nuclear power applications present some of the most demanding requirements for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation, where radiation resistance, chemical compatibility, and long-term structural integrity are paramount considerations. The titanium cladding provides excellent resistance to radiation-induced corrosion while maintaining dimensional stability under neutron bombardment conditions typical of nuclear reactor environments. Cooling system components in nuclear facilities benefit significantly from the corrosion resistance properties of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation, particularly in seawater cooling applications where traditional materials suffer from chloride-induced corrosion and biofouling. The smooth titanium surface resists marine organism attachment while providing superior corrosion protection in high-chloride environments.
Conclusion
The manufacturing of Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation represents a sophisticated metallurgical achievement that combines advanced bonding technologies with rigorous quality control to create composite materials offering exceptional performance in demanding power generation applications. Through explosive welding and hot rolling processes, manufacturers can produce reliable, cost-effective solutions that address the critical challenges of corrosion, durability, and maintenance in modern power generation facilities.
Cooperate with Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd.
As a leading China Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation manufacturer and China Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation supplier, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands at the forefront of advanced metallurgical technology. Our company specializes in manufacturing various titanium materials and clad metals, serving petroleum, chemical, pharmaceutical, power generation, and environmental protection industries worldwide. With ISO9001-2000 certification and successful PED and ABS international qualifications achieved in 2024, we maintain the highest quality standards.
Our independent explosive composite technology and self-rolling plate capabilities position us as your preferred China Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation wholesale partner. We offer comprehensive OEM/ODM services with customized solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you need High Quality Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation or competitive Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation price options, our experienced team delivers precision-engineered solutions that meet international standards including ASME, ASTM, and JIS specifications.
Contact our expert team at stephanie@cladmet.com for Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Power Generation for sale inquiries and discover how our innovative manufacturing capabilities can solve your most challenging power generation material requirements. Save this guide for future reference and reach out whenever you need professional consultation on advanced clad metal solutions.
FAQ
Q: What are the main bonding methods used to manufacture titanium steel clad plates?
A: The two primary methods are explosive welding and hot rolling cladding. Explosive welding uses controlled detonation to create metallurgical bonds with 150-200 MPa strength, while hot rolling applies high temperature and pressure for mass production with uniform thickness.
Q: What thickness ranges are available for titanium and steel layers in clad plates?
A: Titanium layers typically range from 0.5mm to 10mm thickness according to ASTM B898 standards, while steel substrates range from 3mm to 100mm thickness per ASTM A516 specifications, with maximum plate dimensions up to 2000mm x 6000mm.
Q: How is bond quality verified during the manufacturing process?
A: Bond quality is verified through multiple testing methods including shear strength tests achieving 150-200 MPa, ultrasonic testing for delamination detection, tensile bond tests per ASTM B898, and corrosion resistance testing according to ASTM G85 standards.
Q: What industries commonly use titanium steel clad plates for power generation applications?
A: Primary applications include thermal power plants for desulfurization equipment, nuclear power facilities for cooling systems, renewable energy systems, heat exchangers, pressure vessels, and marine power generation where corrosion resistance is critical.
References
1. "Manufacturing Methods and Applications of Titanium Clad Steel Plates" - Gallianz (Anhui) New Materials Co., Ltd., Technical Publication on Advanced Metallurgical Processes
2. "Titanium Clad Steel and Process for Making" - US Patent 4023936A, United States Patent Office, Metallurgical Bonding Technologies
3. "ASTM B898 Standard Specification for Reactive and Refractory Metal Clad Plate" - American Society for Testing and Materials, International Standards Organization
4. "JIS G 3601 Titanium Clad Steel Plate" - Japanese Industrial Standards Committee, Japan Standards Association, Technical Specifications for Clad Materials

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)