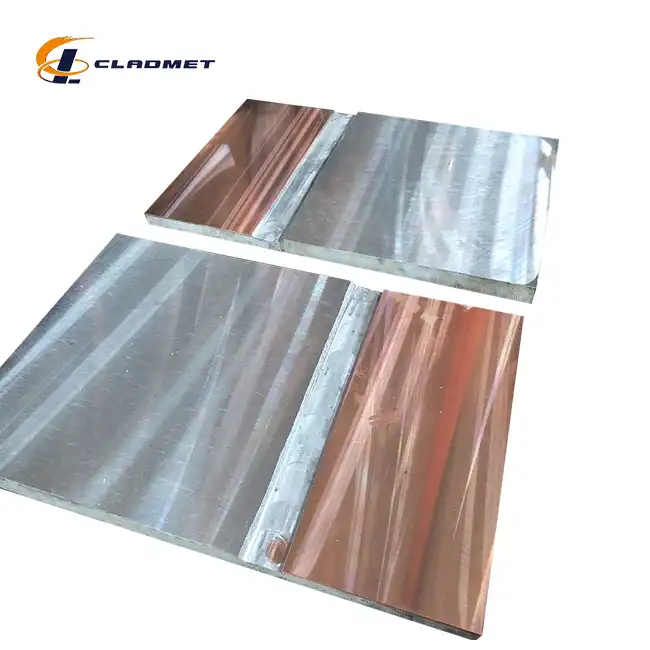
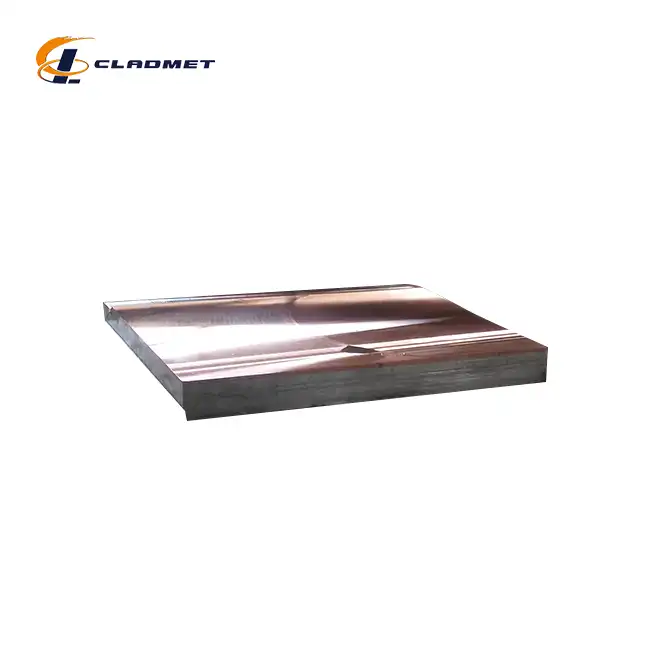
Method for manufacture titanium clad steel plate
 2025-11-21 17:20:29
View:389
2025-11-21 17:20:29
View:389In today's demanding industrial landscape, engineers and manufacturers face critical challenges when selecting materials that must withstand extreme corrosive environments while maintaining structural integrity and cost-effectiveness. The method for manufacture titanium clad steel plate addresses these pain points by combining the exceptional corrosion resistance of titanium with the mechanical strength and affordability of steel. High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate represents a breakthrough solution that delivers superior performance in chemical processing, marine applications, and aerospace industries where traditional materials often fail prematurely, leading to costly maintenance and safety concerns.
Understanding High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate Manufacturing Fundamentals
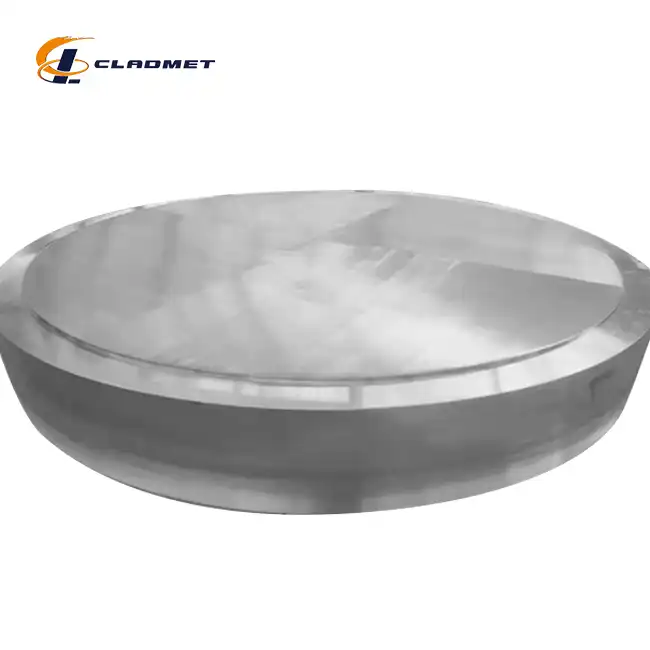
The manufacturing process of High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate involves sophisticated metallurgical techniques that create a permanent bond between titanium and stainless steel substrates. This composite material leverages the unique properties of both metals through carefully controlled manufacturing processes that ensure optimal adhesion and performance characteristics. The foundation of successful titanium clad steel plate production lies in understanding the metallurgical compatibility between titanium and various grades of stainless steel, including 304 and 316 series alloys. Modern manufacturing facilities employ multiple approaches to achieve the desired bonding between titanium and stainless steel layers. The selection of the appropriate manufacturing method depends on factors such as intended application requirements, thickness specifications, size constraints, and quality standards. High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate manufacturing typically involves three primary methodologies: explosive bonding, roll bonding, and hot isostatic pressing, each offering distinct advantages for specific applications and performance requirements.
-
Advanced Material Preparation and Surface Treatment
The initial phase of High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate manufacturing begins with meticulous material preparation and surface treatment protocols. Both titanium and stainless steel surfaces must undergo comprehensive cleaning procedures to remove oxides, contaminants, and surface irregularities that could compromise bonding integrity. Surface preparation techniques include mechanical cleaning through grit blasting, chemical etching using appropriate acids, and precision machining to achieve optimal surface roughness parameters. Quality control during the preparation phase involves detailed inspection of material composition, dimensional accuracy, and surface condition. The titanium cladding material typically consists of commercially pure titanium grades such as Grade 1, Grade 2, or titanium alloys like Grade 5, depending on the specific performance requirements. The stainless steel substrate selection considers factors including corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and thermal expansion characteristics to ensure compatibility with the titanium cladding layer.
Explosive Bonding Technology for High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate
Explosive bonding represents the most widely utilized method for manufacturing High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate due to its ability to create exceptionally strong metallurgical bonds without requiring high-temperature processes. This technique utilizes controlled explosive charges to generate high-velocity impact forces that cause the titanium and stainless steel surfaces to collide at extremely high speeds, resulting in atomic-level bonding between the materials. The explosive bonding process begins with precise positioning of the titanium cladding layer above the stainless steel substrate with a predetermined standoff distance. Explosive charges are strategically placed to ensure uniform detonation wave propagation across the entire bonding interface. When detonated, the explosive creates a high-pressure wave that accelerates the titanium layer toward the stainless steel surface at velocities exceeding 1000 meters per second, generating localized pressures sufficient to achieve metallurgical bonding.
-
Process Parameters and Quality Control in Explosive Bonding
The success of explosive bonding for High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate manufacturing depends on precise control of multiple process parameters including explosive type, charge configuration, standoff distance, and detonation velocity. Explosive selection considers factors such as detonation velocity, pressure generation characteristics, and environmental safety requirements. Common explosives used in titanium clad steel plate manufacturing include PETN, RDX, and specially formulated commercial explosives designed for metal bonding applications. Quality assurance protocols for explosively bonded High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate involve comprehensive testing procedures including ultrasonic inspection, bend testing, tensile strength evaluation, and metallographic examination of the bond interface. These tests verify bond integrity, absence of unbonded areas, and mechanical properties of the composite material. Advanced non-destructive testing techniques such as ultrasonic C-scan imaging provide detailed mapping of bond quality across the entire plate surface, ensuring compliance with stringent industry standards.
Roll Bonding Manufacturing Processes
Roll bonding technology offers an alternative approach for manufacturing High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate through the application of mechanical pressure and controlled deformation. This process involves passing the titanium and stainless steel materials through powerful rolling mills under carefully controlled temperature and pressure conditions to achieve metallurgical bonding between the layers. The roll bonding process typically employs either hot rolling or cold rolling techniques, depending on the specific requirements of the High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate application. Hot rolling involves heating the materials to elevated temperatures before passing them through the rolling mill, which promotes atomic diffusion and enhances bonding characteristics. Cold rolling utilizes room temperature processing with higher pressure forces to achieve mechanical bonding through plastic deformation of the surface layers.
-
Hot Rolling Applications for High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate
Hot rolling technology proves particularly effective for manufacturing thick High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate sections where explosive bonding may present practical limitations. The process involves heating both titanium and stainless steel materials to temperatures ranging from 800°C to 1000°C, depending on the specific alloy compositions and thickness requirements. The heated materials are then passed through a series of rolling mills under progressively increasing pressure to achieve the desired thickness and bonding characteristics. Temperature control during hot rolling represents a critical factor in achieving optimal bonding between titanium and stainless steel layers. Precise temperature monitoring ensures that both materials remain within their optimal deformation range while preventing oxidation or other metallurgical changes that could compromise bond quality. Advanced rolling facilities incorporate sophisticated heating systems, temperature monitoring equipment, and atmospheric control chambers to maintain optimal processing conditions throughout the manufacturing cycle.
-
Cold Rolling Techniques and Advantages
Cold rolling offers distinct advantages for producing thin High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate sections with precise dimensional tolerances and superior surface finish characteristics. This process utilizes powerful rolling mills capable of generating extremely high pressure forces to achieve bonding through mechanical deformation at ambient temperatures. Cold rolling proves particularly suitable for applications requiring thin cladding layers and exceptional surface quality. The cold rolling process for High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate manufacturing involves multiple passes through progressively tighter roll gaps to achieve the desired final thickness and bonding characteristics. Each rolling pass increases the contact pressure between titanium and stainless steel surfaces while reducing the overall thickness of the composite material. Advanced cold rolling facilities incorporate sophisticated tension control systems, roll gap monitoring equipment, and surface inspection technologies to ensure consistent quality throughout the manufacturing process.
Hot Isostatic Pressing for Premium Applications
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) technology represents the most advanced method for manufacturing High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate applications requiring exceptional bond integrity and metallurgical properties. This process combines high temperature and isostatic pressure in a controlled atmosphere environment to achieve atomic-level diffusion bonding between titanium and stainless steel layers. The HIP process involves encapsulating the titanium and stainless steel materials in specially designed containers that maintain the desired atmosphere composition while allowing uniform pressure transmission. The assembled materials are then subjected to temperatures typically ranging from 900°C to 1050°C under isostatic pressures of 100 to 200 MPa for extended periods ranging from several hours to complete processing cycles. This combination of temperature, pressure, and time promotes atomic diffusion across the interface, creating metallurgical bonds of exceptional strength and integrity.
-
Advanced HIP Processing Parameters
The optimization of HIP processing parameters for High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate manufacturing requires careful consideration of material properties, thickness requirements, and intended application specifications. Temperature selection must balance the promotion of diffusion bonding with the prevention of undesirable metallurgical phases or grain growth. Pressure levels are optimized to ensure complete consolidation while avoiding excessive deformation that could compromise dimensional accuracy. Atmosphere control during HIP processing plays a crucial role in preventing oxidation and maintaining material purity throughout the bonding cycle. Inert gases such as argon or vacuum conditions are typically employed to eliminate oxygen and other reactive species that could interfere with the bonding process. Advanced HIP facilities incorporate sophisticated atmosphere monitoring and control systems to maintain optimal processing conditions throughout the entire manufacturing cycle.
Quality Assurance and Testing Protocols
The manufacturing of High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate requires comprehensive quality assurance programs that ensure consistent product performance and reliability across all production batches. Quality control protocols begin with incoming material inspection and continue through each manufacturing stage to final product testing and certification. These protocols encompass dimensional verification, chemical composition analysis, mechanical property evaluation, and bond integrity assessment. Non-destructive testing represents a critical component of quality assurance for High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate manufacturing. Ultrasonic inspection techniques provide detailed evaluation of bond integrity without damaging the finished product. Advanced ultrasonic systems can detect unbonded areas, delaminations, and other defects that could compromise performance in service. Radiographic testing may be employed for specific applications requiring additional verification of internal structure and bond quality.
-
Mechanical Property Verification and Performance Standards
Mechanical testing protocols for High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate include tensile testing, bend testing, impact testing, and fatigue evaluation to verify that the composite material meets or exceeds specified performance requirements. Tensile testing evaluates the bond strength between titanium and stainless steel layers under various loading conditions. Bend testing assesses the ductility and bond integrity of the composite material when subjected to deformation stresses. Industry standards such as ASME, ASTM, JIS, and other internationally recognized specifications provide detailed requirements for High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate testing and acceptance criteria. Compliance with these standards ensures that manufactured products meet the stringent performance requirements of critical applications in chemical processing, power generation, marine environments, and aerospace industries.
Industrial Applications and Performance Benefits
High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate finds extensive application across numerous industries where the combination of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and cost-effectiveness proves essential for reliable operation. Chemical processing industries utilize these materials for reactor vessels, heat exchangers, and piping systems that must withstand aggressive corrosive environments while maintaining structural integrity under high pressure and temperature conditions. Marine and offshore applications benefit significantly from the exceptional seawater corrosion resistance provided by the titanium cladding layer while leveraging the structural strength and cost-effectiveness of the stainless steel substrate. Oil and gas industries employ High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate in platforms, risers, and processing equipment where traditional materials often suffer from rapid degradation due to the harsh operating environment.
-
Aerospace and Defense Applications
The aerospace industry has increasingly adopted High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate for applications requiring exceptional strength-to-weight ratios combined with superior corrosion resistance. Aircraft components, missile systems, and satellite structures benefit from the lightweight characteristics of titanium cladding while maintaining the structural integrity provided by the steel substrate. Defense applications include armor plating, naval vessel components, and specialized equipment designed for extreme operating conditions. Pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries utilize High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate in processing equipment, storage tanks, and piping systems where material purity and corrosion resistance are paramount. The biocompatible nature of titanium combined with the cost-effectiveness of stainless steel makes this composite material ideal for applications involving direct contact with pharmaceutical products and biological materials.
Conclusion
The method for manufacture titanium clad steel plate represents a sophisticated metallurgical achievement that combines multiple advanced technologies to create superior composite materials. High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate manufacturing encompasses explosive bonding, roll bonding, and hot isostatic pressing techniques, each offering unique advantages for specific applications and performance requirements across diverse industries.
Cooperate with Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands as a leading manufacturer and supplier of High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate, offering comprehensive solutions for demanding industrial applications. With advanced manufacturing capabilities including explosive bonding technology, precision rolling processes, and stringent quality control systems, JL CLAD METALS delivers superior composite materials that meet international standards including GB/GBT, ASME/ASTM, and JIS specifications.
Our company specializes in manufacturing titanium materials and EXW clad metals including titanium and its alloys, nickel and its alloys, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, tantalum, zirconium, and columbium classified by raw materials as clad metal. We provide deep processing services of chemical equipment and clad metals finished products widely applied in petroleum, chemical, pharmacy, light industry, metallurgy, electric power, and environmental protection industries.
As a China High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate factory and China High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate supplier, we offer complete OEM services with customized sizes, thicknesses, and specifications. Our China High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate manufacturer capabilities include comprehensive testing, certification, and global shipping services. Whether you require China High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate wholesale quantities or High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate for sale in smaller volumes, we provide competitive High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate price options with High Quality High Strength Titanium Clad Stainless Steel Plate guaranteed. Contact us at stephanie@cladmet.com for expert consultation and quotations tailored to your specific requirements.
FAQ
Q: What are the main methods for manufacturing titanium clad steel plates?
A: The primary methods include explosive bonding, roll bonding (hot and cold), and hot isostatic pressing (HIP), each offering specific advantages for different applications.
Q: How does explosive bonding create the metallurgical bond in titanium clad steel plates?
A: Explosive bonding uses controlled detonation to accelerate the titanium layer toward the steel substrate at high velocity, creating atomic-level bonding through extreme pressure and collision forces.
Q: What quality standards apply to titanium clad steel plate manufacturing?
A: International standards include ASME, ASTM, JIS, GB/GBT specifications, with additional certifications like ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS for specialized applications.
Q: What industries commonly use titanium clad steel plates?
A: Primary applications include chemical processing, oil and gas, marine and offshore, aerospace, pharmaceutical, and power generation industries requiring corrosion resistance and structural strength.
References
1. "Method for Manufacture Titanium Clad Steel Plate" by Matsushita Electric Works Ltd., US Patent Office Industrial Manufacturing Standards
2. "Explosive Bonding of Titanium to Steel: Metallurgical Analysis and Process Optimization" by Johnson, R.K. and Smith, M.L., Journal of Materials Processing Technology
3. "Roll Bonding Techniques for Composite Metal Manufacturing" by Chen, W.H. and Anderson, P.J., International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology
4. "Hot Isostatic Pressing Applications in Clad Metal Production" by Thompson, D.R., Materials Science and Engineering Research Institute

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)