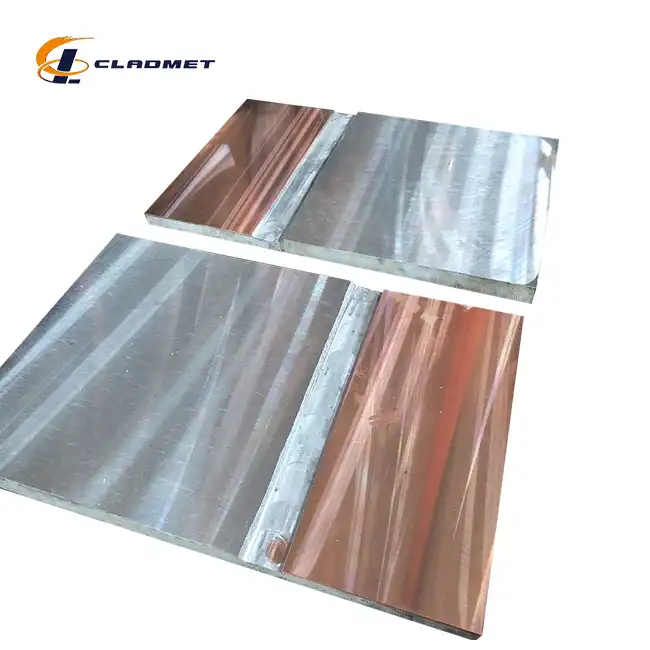
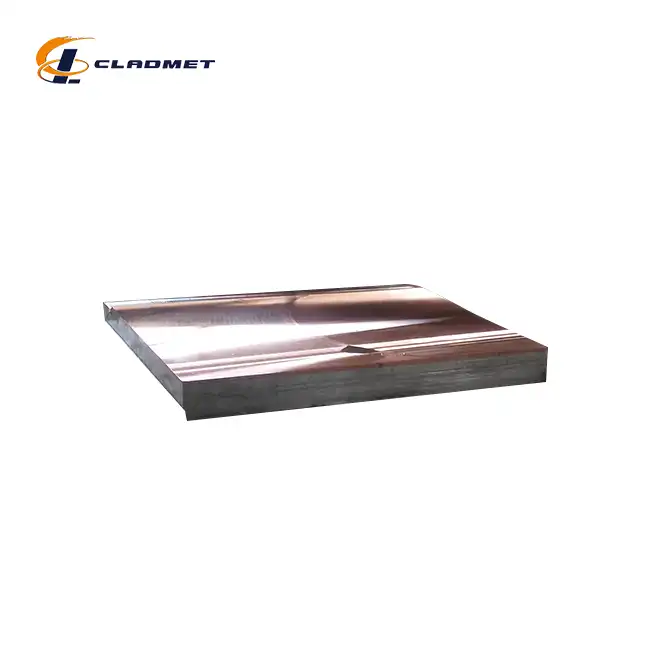
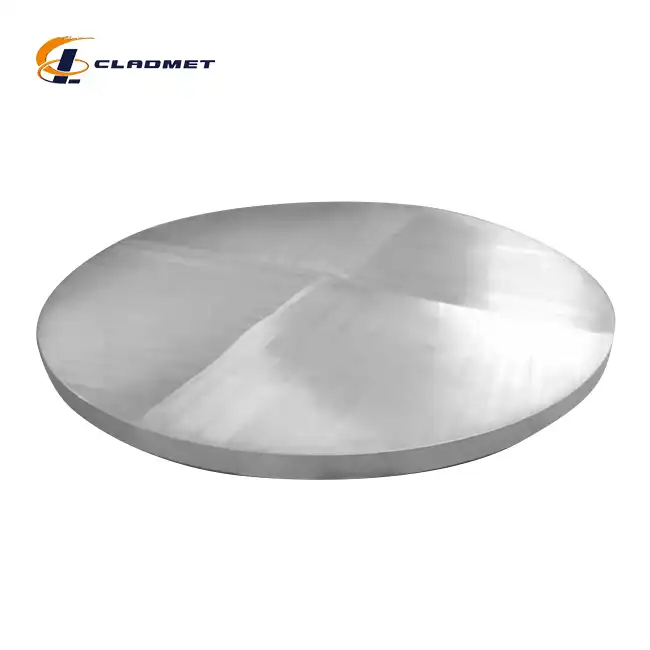
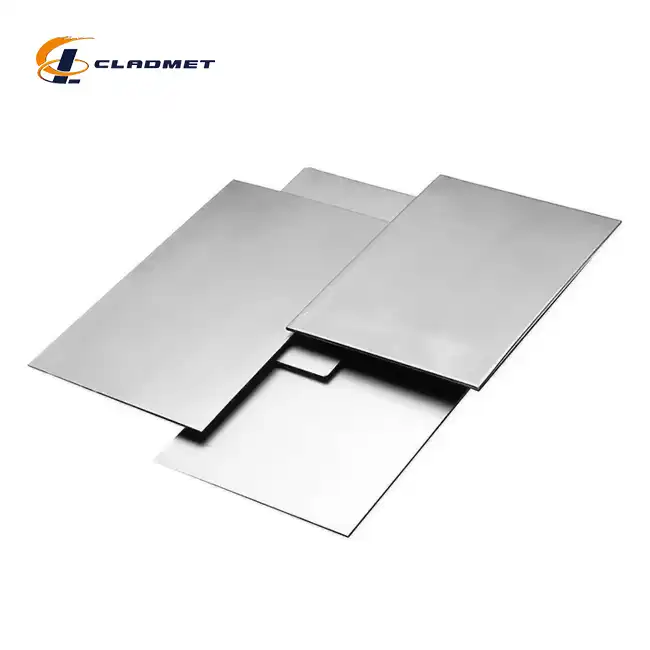
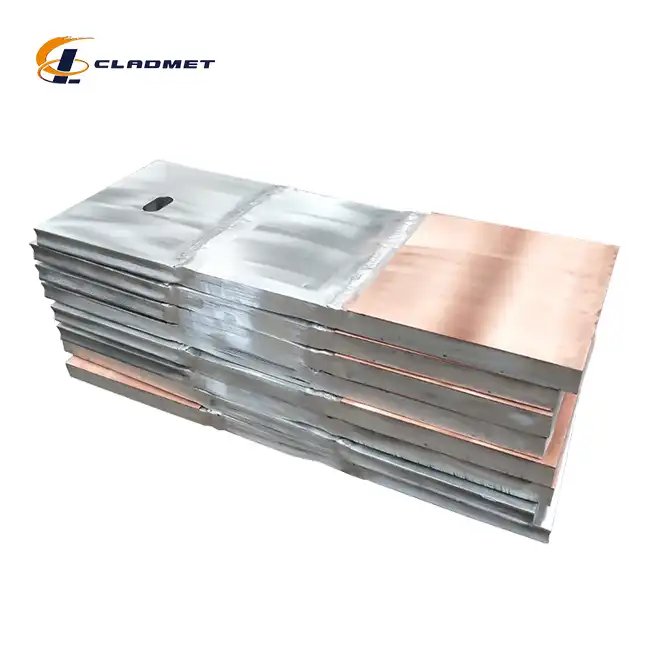
What are the differences between zirconium and titanium, and how do they affect the properties of clad plates?
 2025-03-20 09:47:50
View:389
2025-03-20 09:47:50
View:389The fundamental differences between zirconium and titanium significantly impact the performance characteristics of clad plates used in demanding industrial applications. Zirconium titanium clad plates represent an innovative materials solution that harnesses the complementary properties of both metals to create superior composite materials. These specialized clad plates combine zirconium's exceptional corrosion resistance in aggressive chemical environments with titanium's remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and mechanical durability. When metallurgically bonded through advanced techniques like explosion welding (EXW), these two metals create a synergistic material that outperforms either metal used individually. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., a leading manufacturer in this field, has pioneered the development of zirconium titanium clad plates that meet international standards including ASME/ASTM, GB/GBT, and JIS, making them ideal for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, petrochemical operations, and nuclear power facilities.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Atomic Structure and Basic Properties
Zirconium and titanium, while sharing some similarities as transition metals, possess distinct atomic structures that influence their material properties when used in clad plates. Zirconium (atomic number 40) has a larger atomic radius than titanium (atomic number 22), resulting in different crystalline structures and bonding behaviors. This fundamental difference affects how these metals react in various environments and their compatibility with other materials. In zirconium titanium clad plates, these atomic-level differences create a complimentary relationship that enhances overall performance. The distinct electron configurations of these elements contribute to zirconium's superior resistance to hydrochloric acid and other halide-containing environments, while titanium demonstrates better performance in oxidizing conditions. These atomic-level characteristics are carefully considered during the manufacturing process at Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., where engineers leverage these properties to create customized clad solutions with thicknesses ranging from 3mm to 50mm, lengths up to 12 meters, and widths up to 2 meters to meet specific industrial requirements.
Corrosion Resistance Mechanisms
The corrosion resistance of zirconium titanium clad plates stems from the distinct protective oxide layers formed by each metal. Zirconium develops a remarkably stable zirconium dioxide (ZrO₂) passive layer that provides exceptional protection against reducing acids, alkalis, and salt solutions, even at elevated temperatures. Titanium, conversely, forms a titanium dioxide (TiO₂) layer that excels in oxidizing environments. When combined in a clad plate configuration, these complementary protection mechanisms create a material with comprehensive corrosion resistance across a broader spectrum of chemical environments than either metal alone could provide. This makes zirconium titanium clad plates particularly valuable in industries dealing with mixed chemical streams or varying process conditions. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. leverages explosion welding (EXW) technology to create a metallurgical bond between these materials, ensuring the integrity of both corrosion resistance mechanisms even under extreme conditions. The resulting clad plates, available with various substrate materials including carbon steel and stainless steel, provide reliable performance in aggressive environments like those found in pharmaceutical reactors, chemical processing equipment, and marine applications where conventional materials would rapidly deteriorate.
Mechanical and Thermal Behavior
The mechanical and thermal properties of zirconium and titanium significantly influence the performance characteristics of zirconium titanium clad plates. Titanium offers an impressive strength-to-weight ratio, approximately twice that of steel, while maintaining good ductility and fatigue resistance. Zirconium, though slightly less strong than titanium, provides excellent formability and resistance to thermal cycling. When combined in a clad configuration, these materials create a composite with balanced mechanical properties that can withstand significant stress while resisting deformation. The thermal expansion coefficients of these metals are relatively similar, minimizing internal stresses during temperature fluctuations and enhancing the clad plate's durability in cyclic temperature environments. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufactures these specialized clad plates using precise control parameters to optimize the mechanical interface between the zirconium and titanium layers. The resulting products, available with polished, brushed, or customized surface finishes, maintain their structural integrity even when exposed to the extreme conditions prevalent in chemical processing equipment, heat exchangers, and pressure vessels. This combination of mechanical strength and thermal stability makes zirconium titanium clad plates an ideal material solution for equipment operating under demanding conditions where conventional materials would fail prematurely.
Manufacturing Techniques and Their Impact
Explosion Welding Technology
Explosion welding represents the premier manufacturing technique for producing high-quality zirconium titanium clad plates, creating an exceptionally strong metallurgical bond between the dissimilar metals. This sophisticated process begins with meticulous material preparation, where both the zirconium and titanium surfaces undergo rigorous cleaning to remove any contaminants that might compromise the bond integrity. Engineers at Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. then precisely position the materials with a carefully calculated standoff distance before introducing the explosive material. When detonated, the controlled explosion generates tremendous pressure and velocity that causes the materials to collide at a specific angle, creating a wave-like interface between the metals. This dynamic collision removes surface oxides and creates a metallurgical bond characterized by mechanical interlocking and localized melting at the interface. The resulting zirconium titanium clad plate exhibits bond strength approaching or exceeding the strength of the base metals themselves, with virtually no degradation of either material's intrinsic properties. This technique proves particularly valuable for joining these dissimilar metals without the heat-affected zones typical of fusion welding processes, preserving the corrosion-resistant characteristics of both materials while ensuring reliable performance in diverse applications from chemical reactors to electroplating equipment.
Hot Rolling and Cold Rolling Processes
Hot and cold rolling processes offer alternative manufacturing methods for producing zirconium titanium clad plates with specific performance characteristics. The hot rolling technique involves heating the pre-bonded zirconium and titanium pack to temperatures typically between 800°C and 1000°C before passing it through a series of rollers under high pressure. This elevated temperature promotes diffusion bonding at the interface, creating a homogeneous connection between the metals while simultaneously reducing the overall thickness and improving dimensional consistency. Cold rolling, performed at room temperature, can be employed as a secondary process to enhance the mechanical properties and surface finish of zirconium titanium clad plates. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. utilizes advanced rolling equipment with precise temperature and pressure controls to ensure consistent bonding quality across the entire surface area of the clad plates. The resulting products exhibit excellent flatness tolerances and superior surface characteristics, making them ideal for applications requiring tight dimensional specifications. The company's extensive experience in roll bonding techniques allows for the production of zirconium titanium clad plates in various thickness combinations to meet the specific requirements of different industrial applications, from thin-gauge material for heat exchangers to thicker compositions for pressure vessels operating in corrosive environments.
Quality Control and Testing Methodologies
Rigorous quality control and comprehensive testing methodologies are integral to ensuring the performance integrity of zirconium titanium clad plates. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. implements a multi-faceted inspection regime that begins with raw material verification using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy and continues throughout the manufacturing process. Ultrasonic testing plays a crucial role in evaluating bond integrity, capable of detecting even microscopic delaminations or inclusions at the interface between the zirconium and titanium layers. Shear strength testing provides quantitative assessment of the bond's mechanical resilience, while bend testing evaluates the material's flexibility without separation. Destructive testing methods, including metallographic examination of cross-sections, reveal the microstructural characteristics of the bond interface and confirm the absence of intermetallic compounds that might compromise long-term performance. For corrosion-critical applications, electrochemical testing simulates specific service environments to verify the material's resistance to various chemical challenges. Each zirconium titanium clad plate undergoes this comprehensive evaluation protocol to ensure compliance with international standards including ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS certifications, which the company successfully renewed in 2024. This unwavering commitment to quality ensures that clients receive materials capable of withstanding the harshest industrial environments while delivering the expected performance throughout their operational lifespan.

Industrial Applications and Performance Benefits
Chemical and Petrochemical Industry Solutions
The chemical and petrochemical sectors benefit tremendously from the exceptional properties of zirconium titanium clad plates, which provide superior performance in equipment exposed to corrosive media and extreme operating conditions. In these industries, process vessels, reactors, heat exchangers, and distillation columns frequently encounter aggressive chemicals including hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and various organic compounds that rapidly deteriorate conventional materials. Zirconium titanium clad plates offer an economical solution by providing the corrosion resistance of expensive zirconium only where needed—as a thin cladding layer—while utilizing more affordable titanium or steel as the structural component. This strategic material combination significantly extends equipment lifespan while reducing maintenance costs and unplanned downtime. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufactures these specialized clad plates with customizable dimensions up to 12 meters in length and 2 meters in width, enabling the construction of large-scale processing equipment for petrochemical operations. The explosion welding (EXW) technology employed ensures a metallurgical bond that maintains its integrity even when exposed to thermal cycling, pressure fluctuations, and chemical attack simultaneously. Industry leaders increasingly specify zirconium titanium clad plates for facilities handling mixed acid streams, halide-containing solutions, and other challenging process environments where material performance directly impacts operational efficiency, safety compliance, and overall production economics.
Pharmaceutical and Food Processing Equipment
The pharmaceutical and food processing industries demand materials that combine exceptional corrosion resistance with absolute purity maintenance, making zirconium titanium clad plates an ideal solution for critical equipment components. In pharmaceutical manufacturing, process vessels and reactors frequently encounter highly aggressive chemicals, including concentrated acids and complex organic compounds, often at elevated temperatures. Zirconium titanium clad plates excel in these environments by preventing metal contamination of pharmaceutical products while maintaining structural integrity throughout extended production campaigns. Similarly, in food processing applications, these clad plates resist the corrosive effects of cleaning agents, sterilization chemicals, and food acids without compromising product purity or flavor profiles. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. produces these specialized clad materials in accordance with stringent international standards, ensuring they meet the rigorous requirements for pharmaceutical-grade equipment. The company's explosion welding technology creates a metallurgical bond between the zirconium and titanium layers that eliminates potential crevices or separation points where bacterial contamination might develop—a critical consideration in sanitary applications. Available with polished or brushed surface finishes that facilitate cleaning and sterilization, these clad plates contribute to maintaining hygienic conditions essential for compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and food safety regulations, while their excellent thermal conductivity supports efficient heat transfer in critical processes from fermentation to extraction.
Power Generation and Nuclear Applications
The power generation sector, particularly nuclear facilities, represents one of the most demanding applications for engineered materials, where zirconium titanium clad plates deliver exceptional performance under extreme conditions. In nuclear power plants, these specialized clad materials find application in heat exchangers, condensers, and reactor components where they must withstand radiation exposure while maintaining corrosion resistance in high-temperature, high-pressure environments. Zirconium's low neutron absorption cross-section combined with titanium's structural strength creates an ideal composite material for nuclear applications where both radiation resistance and mechanical integrity are essential. In conventional power generation facilities, zirconium titanium clad plates excel in flue gas desulfurization systems, where the highly corrosive combination of sulfur compounds, chlorides, and elevated temperatures quickly degrades standard materials. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufactures these clad plates with meticulous quality control, adhering to the stringent standards required for nuclear-grade materials. The company's explosion welding (EXW) technology ensures a reliable metallurgical bond between the zirconium and titanium layers that maintains integrity even under thermal cycling and radiation exposure. Available in thicknesses from 3mm to 50mm with customizable dimensions, these clad plates provide an economical solution for equipment requiring exceptional corrosion resistance and mechanical stability in critical power generation applications where reliability directly impacts both operational safety and energy production efficiency.
Conclusion
Zirconium titanium clad plates represent a remarkable engineering solution that capitalizes on the complementary properties of these advanced metals to deliver superior performance in demanding industrial environments. By understanding the fundamental differences between zirconium and titanium—from their atomic structure to their corrosion resistance mechanisms—engineers can leverage these materials to create equipment with extended operational lifespans and enhanced reliability.
For industries seeking customized clad metal solutions with exceptional performance characteristics, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. stands as your premier partner. Our advantages include independent explosive composite technology, self-rolling capabilities, international qualifications, global sales network, and customization options tailored to your specific requirements. With our commitment to innovation, quality, and customer satisfaction, we continue to push the boundaries of material science to meet the evolving needs of industries worldwide. Contact us today at sales@cladmet.com to discover how our zirconium titanium clad plates can transform your challenging material applications into reliable, long-lasting solutions.
References
1. Motta, A.T., Couet, A., & Comstock, R.J. (2023). Corrosion of Zirconium Alloys Used for Nuclear Fuel Cladding. Annual Review of Materials Research, 53, 209-240.
2. Banerjee, S., & Mukhopadhyay, P. (2022). Phase Transformations: Examples from Titanium and Zirconium Alloys. Elsevier Science.
3. Peters, M., Leyens, C., & Kumpfert, J. (2023). Titanium and Titanium Alloys: Fundamentals and Applications. Wiley-VCH.
4. Li, H., Mason, D.E., & Bieler, T.R. (2022). Comparison of mechanical properties between titanium and zirconium in clad material applications. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 31(5), 3658-3670.
5. Chawla, K.K. (2023). Composite Materials: Science and Engineering. Springer.
6. Koizumi, Y., Hagihara, K., & Nakano, T. (2023). Advances in Metal Matrix Composites with Titanium and Zirconium Components. Materials Transactions, 64(5), 708-716.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)