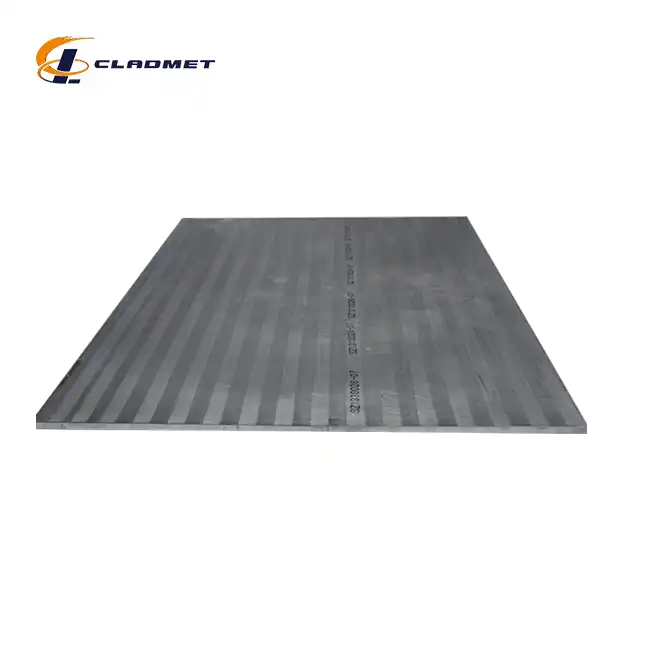
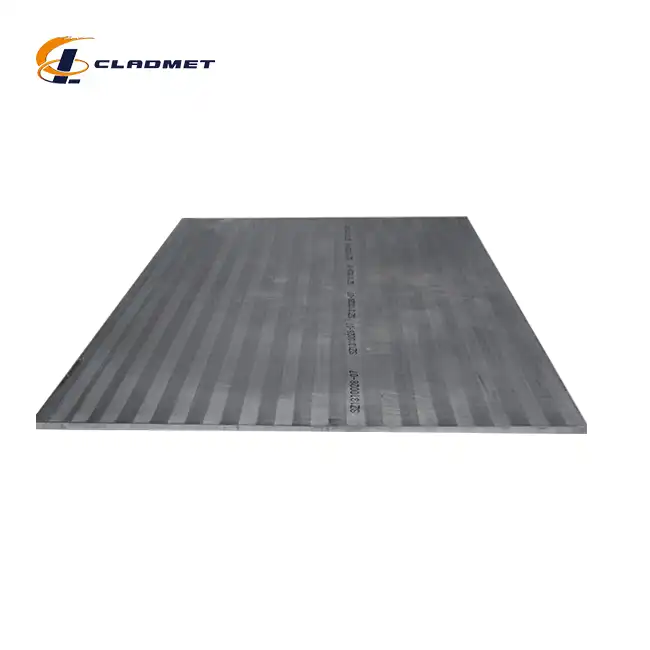
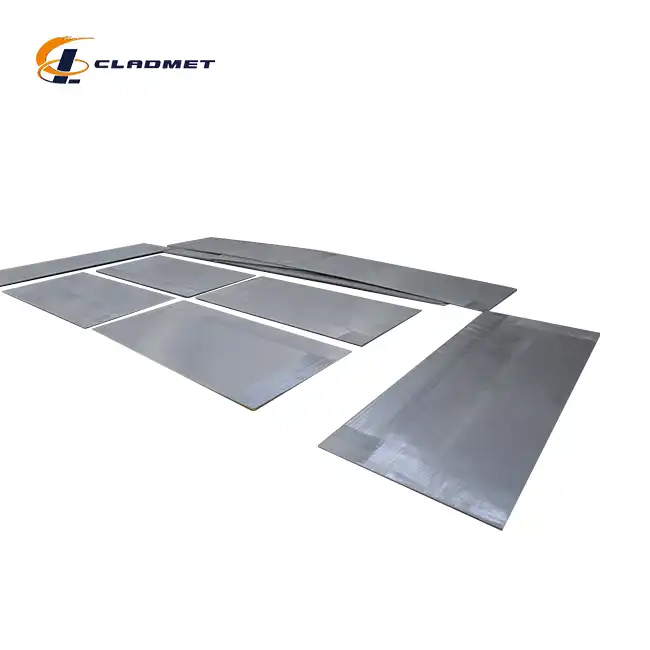
How should zirconium-titanium clad plates be stored and handled?
 2025-03-22 11:03:50
View:389
2025-03-22 11:03:50
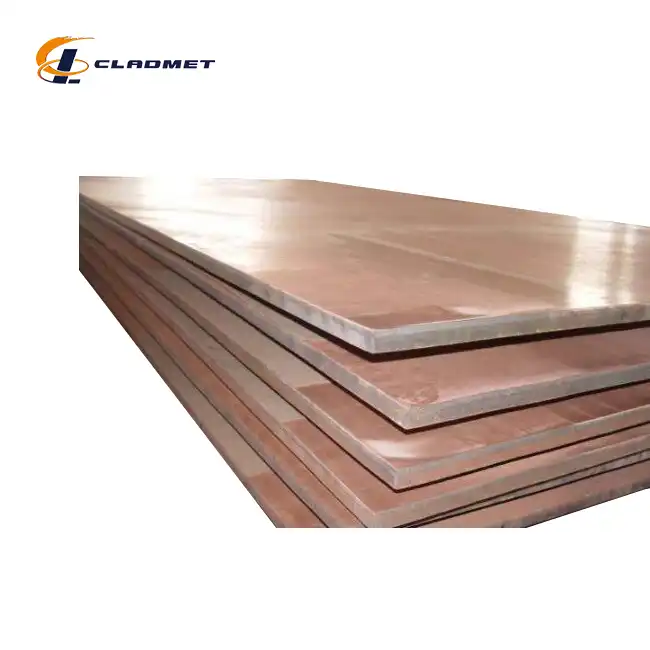
View:389Proper storage and handling of zirconium-titanium clad plates are crucial for maintaining their integrity and performance in various industrial applications. Zirconium titanium clad plates combine the exceptional corrosion resistance of zirconium with the superior mechanical properties of titanium, creating a composite material that excels in demanding environments. These specialized plates from Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. are manufactured using explosion welding (EXW) technology, resulting in a strong metallurgical bond between the layers. However, to preserve their unique properties and ensure they perform as expected when installed, specific storage and handling protocols must be followed. Improper procedures can lead to surface contamination, mechanical damage, or oxidation that may compromise the plates' functionality. This comprehensive guide outlines best practices for storing and handling these valuable clad materials to maximize their service life and maintain their performance characteristics.

Proper Storage Conditions for Zirconium Titanium Clad Plates
Climate-Controlled Environment Requirements
When storing zirconium titanium clad plates, maintaining appropriate environmental conditions is paramount for preserving their integrity and performance characteristics. These specialized composite materials require storage in dry, climate-controlled environments with humidity levels kept below 65%. Excessive moisture exposure can potentially compromise the mechanical properties of the material interface and accelerate oxidation processes, particularly in the zirconium layer. Temperature fluctuations should also be minimized, with ideal storage temperatures ranging between 10°C and 25°C (50°F to 77°F). Extreme temperature variations can induce thermal stresses at the bond interface, potentially weakening the metallurgical bond created during the manufacturing process. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufactures these plates using advanced explosive welding (EXW) technology, creating a robust bond that must be preserved through proper storage. Professional storage facilities should include climate monitoring systems that continuously track temperature and humidity levels, with automated alerts when conditions exceed acceptable parameters. For long-term storage exceeding six months, periodic inspection protocols should be implemented to ensure environmental conditions remain optimal. This level of environmental control is especially critical for zirconium titanium clad plates destined for high-demand applications in chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, or nuclear power generation, where material integrity directly impacts operational safety and efficiency.
Protection Against Physical Damage
Zirconium titanium clad plates require comprehensive protection against physical damage during storage to maintain their structural integrity and surface quality. These valuable composite materials should be stored horizontally on specially designed racks or pallets that provide uniform support across the entire surface area, preventing warping or bending that could compromise the bond between layers. Stacking should be avoided whenever possible, but when necessary due to space constraints, protective interlayers must be used between each plate to prevent surface scratching or denting. These interlayers typically consist of acid-free paper, non-abrasive polymer sheets, or specialized protective films that won't react with the zirconium or titanium surfaces.
Edge protectors are also essential to prevent damage to the vulnerable corners and edges of the plates, which are particularly susceptible to impact damage during handling operations. Storage areas should be designated as limited-access zones with clear protocols for material movement to minimize the risk of accidental impacts. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. supplies their zirconium titanium clad plates in custom-designed wooden crates or steel pallets for international transport, providing excellent protection during transit, but additional measures must be taken once the materials are in storage. Regular inspection of storage conditions and plate surfaces is recommended, with any identified damage documented and assessed by qualified materials engineers to determine if remedial actions are required. For plates with specialized surface treatments like polished or brushed finishes, additional protective measures such as non-adhesive plastic films may be necessary to preserve the surface quality throughout the storage period.
Contamination Prevention Strategies
Preventing contamination of zirconium titanium clad plates during storage is essential for maintaining their superior corrosion resistance and material integrity. These specialized composite materials are particularly sensitive to certain contaminants that can initiate localized corrosion, interfere with subsequent welding processes, or compromise the metallurgical properties at the bond interface. Storage areas must be kept scrupulously clean and free from airborne particulates, especially those containing iron, copper, or sulfur compounds, which can trigger galvanic reactions when in contact with zirconium or titanium surfaces. Dedicated storage spaces should be established away from machining operations, grinding activities, or chemical processing areas that could produce contaminating particles or vapors.
Zirconium titanium clad plates should never be stored in proximity to chlorinated compounds, as chlorides are particularly aggressive toward both zirconium and titanium materials, potentially leading to stress corrosion cracking under certain conditions. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufactures these plates in facilities that adhere to ISO9001-2000 quality standards and have successfully passed PED and ABS international qualifications, ensuring that the products leave the factory in pristine condition. To maintain this quality, storage facilities should implement positive pressure ventilation systems with appropriate filtration to prevent the ingress of contaminants. Personnel accessing the storage area should follow clean handling protocols, including wearing clean gloves made of lint-free cotton or nitrile materials when in direct contact with the plates. For projects requiring extended storage periods, protective coverings made from non-reactive materials should be used, and these covers should be periodically inspected for integrity. Implementing these contamination prevention strategies will ensure that zirconium titanium clad plates maintain their exceptional properties until they are ready for installation or fabrication.
Safe Handling Techniques for Zirconium Titanium Clad Plates
Proper Lifting and Transport Methods
Implementing appropriate lifting and transport methods for zirconium titanium clad plates is critical to prevent damage and ensure worker safety. Due to their substantial weight and dimensions—with Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. producing plates up to 12 meters in length and 2 meters in width—mechanical lifting equipment is typically required for safe handling. When selecting lifting equipment, vacuum lifters are often preferred over mechanical clamps as they distribute the lifting force evenly across the plate surface, reducing the risk of localized deformation. However, if vacuum systems are unavailable, wide-pad clamps with protective cushioning materials should be used to prevent surface marring or indentation. For smaller plates, specialized lifting frames with multiple attachment points help maintain plate stability during movement. During transport within facilities, dedicated plate carts with full-surface support and edge protection should be utilized, moving at reduced speeds to prevent sudden shocks or vibrations.
When transferring zirconium titanium clad plates between different areas of a facility, predetermined paths should be established, free from obstacles and with smooth transitions between different flooring surfaces. For vertical transport, specially designed plate racks that secure the material while maintaining its orientation are essential. Personnel involved in handling these valuable materials should receive comprehensive training specific to zirconium titanium clad plate handling procedures, including proper body mechanics to prevent injuries. Documentation should accompany each handling operation, recording the plate identification, handling date, personnel involved, and any observations noted during the process. For international shipping, Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. utilizes secure wooden crates designed specifically for their zirconium titanium clad plates, providing excellent protection during sea, air, or express shipping transit. Upon receipt, plates should be carefully inspected for any shipping damage before being transferred to permanent storage locations, with any identified issues documented and reported immediately to maintain quality control standards.
Surface Protection During Handling
Preserving the surface integrity of zirconium titanium clad plates during handling operations requires specialized protocols and protective measures. The surfaces of these high-performance composite materials are engineered to precise specifications, with Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. offering options including polished, brushed, or customized finishes tailored to specific application requirements. Even minor scratches or contaminants introduced during handling can potentially compromise the exceptional corrosion resistance that makes these plates valuable in chemical, pharmaceutical, and petrochemical industries. To prevent surface damage, handling personnel should always wear clean, dry gloves made from lint-free materials when in direct contact with the plates. These gloves should be regularly inspected and replaced at the first sign of contamination or damage. Tool contact with plate surfaces should be minimized, and when necessary, only tools with non-metallic contact surfaces should be used to prevent cross-contamination with ferrous materials.
During processing operations such as cutting or drilling, temporary protective films or coatings may be applied to areas not being worked on, preventing the accumulation of metallic particles or processing fluids on the plate surfaces. These protective coverings should be specifically designed for use with reactive metals like zirconium and titanium, ensuring they won't leave adhesive residues upon removal. Handling areas should be equipped with dedicated workbenches featuring soft, clean covering materials that won't scratch or contaminate the plates. When plates must be temporarily placed on the floor, clean, non-reactive mats should be positioned first to prevent direct contact with potentially contaminated surfaces. For plates manufactured through explosion welding (EXW) as practiced by Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., particular attention should be paid to the bond line area, as this critical interface between the zirconium and titanium layers requires special protection from mechanical damage that could compromise the metallurgical bond. Implementing these surface protection measures ensures that zirconium titanium clad plates maintain their engineered properties throughout handling processes, ultimately delivering their full performance potential when installed in their final applications.
Quality Inspection and Documentation Procedures
Implementing robust quality inspection and documentation procedures for zirconium titanium clad plates is essential throughout the handling process, from receipt through final installation. Each plate should undergo a comprehensive initial inspection upon arrival, documenting key parameters including dimensions, surface conditions, and bond integrity. This baseline assessment serves as a reference point for subsequent inspections as the material moves through various handling stages. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufactures these plates to meet stringent international standards including ASME, ASTM, and GB/GBT, with thicknesses ranging from 3mm to 50mm and precise dimensional tolerances. Verification of these specifications should be performed using calibrated measurement tools specifically designated for use with reactive metal composites. Surface inspections should include both visual assessments under appropriate lighting conditions and quantitative evaluations using surface roughness testers for finished plates.
When plates are moved between locations or after any significant handling operation, follow-up inspections should be conducted to identify any new surface imperfections, with findings meticulously documented in material tracking systems. For zirconium titanium clad plates destined for critical applications in nuclear power or chemical processing, non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic inspection may be warranted to verify the continued integrity of the explosion-welded bond between the zirconium and titanium layers. All inspection results should be recorded in a centralized documentation system that maintains the complete handling history of each plate, establishing a chain of custody and quality assurance. This documentation should include photographs of any identified irregularities, measurement data, handling dates, responsible personnel, and any remedial actions taken. For industries requiring material traceability, such as pharmaceutical or nuclear applications, these records become part of the critical documentation package for regulatory compliance. Implementing these quality inspection and documentation procedures ensures that zirconium titanium clad plates meet their performance expectations in demanding industrial environments while providing the necessary verification for quality management systems and customer requirements.

Processing Considerations for Zirconium Titanium Clad Plates
Cutting and Machining Guidelines
Processing zirconium titanium clad plates through cutting and machining operations requires specialized techniques and equipment to preserve the integrity of both the individual metal layers and their critical bond interface. When cutting these composite materials, low-speed methods with abundant cooling are strongly recommended to prevent heat buildup that could alter the metallurgical properties of either the zirconium or titanium components. Water jet cutting represents an optimal solution for initial dimensioning operations, as it introduces no heat into the material while providing clean, precise edges without mechanical stresses. For applications requiring machining operations, carbide-tipped or ceramic cutting tools should be employed rather than high-speed steel, with cutting speeds reduced to approximately 50-60% of those typically used for standard steel processing. During machining, continuous cooling with appropriate cutting fluids is essential, not only for temperature control but also to prevent the accumulation of fine particles that could cause surface contamination.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. produces these specialized plates through explosive welding (EXW), creating a strong metallurgical bond that must be preserved during all processing operations. When cutting operations must traverse this bond line, particular attention to tool wear and cutting parameters is required to prevent delamination or bond weakening. After any cutting or machining operation, edges should be deburred using non-metallic tools, with particular care taken to remove any loose particles that could contaminate other surfaces. Cleaning after processing should utilize non-chlorinated solvents specifically approved for use with reactive metals, followed by thorough drying to prevent moisture retention. For complex fabrications requiring multiple processing steps, inspection of the bond integrity should be performed between operations, particularly when thermal processes are involved. Implementing these specialized cutting and machining guidelines ensures that the exceptional properties of zirconium titanium clad plates are maintained throughout fabrication processes, delivering components that exhibit the full performance potential of these advanced composite materials in their final applications.
Welding and Joining Techniques
Welding and joining zirconium titanium clad plates demand specialized approaches that account for the distinct metallurgical properties of both materials while preserving the integrity of their explosive-welded bond. Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW/TIG) represents the preferred welding method for these composite materials, as it provides precise heat control and minimal contamination risk. When preparing for welding operations, thorough cleaning of all surfaces is essential, with dedicated tools used exclusively for zirconium and titanium to prevent cross-contamination. The welding environment must be carefully controlled, ideally in areas with positive pressure ventilation and inert gas shielding extending beyond the immediate weld zone to prevent atmospheric contamination. Welding parameters require careful calibration, typically using lower heat inputs than would be appropriate for either material individually, with pulsed welding techniques often employed to minimize the heat-affected zone.
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. manufactures these plates to international standards including ASME and ASTM, and all welding procedures should align with these same standards, performed only by welders specifically qualified for working with reactive metal composites. For applications requiring mechanical joining rather than welding, specialized bolt materials must be selected to prevent galvanic corrosion, typically using titanium fasteners or those made from compatible alloys with appropriate isolation elements between dissimilar metals. Bolt holes should be precisely drilled at reduced speeds with continuous cooling to prevent heat-induced material changes. Post-welding heat treatment must be approached with extreme caution due to the different thermal expansion coefficients of zirconium and titanium, potentially requiring specialized stress-relieving procedures developed specifically for clad materials. Inspection of completed joins should employ both visual and non-destructive testing methods, including dye penetrant inspection for surface defects and ultrasonic testing to verify subsurface bond integrity. After any joining operation, thorough cleaning removes all processing residues, followed by passivation treatments appropriate for both zirconium and titanium surfaces to restore their optimal corrosion resistance. Implementing these specialized welding and joining techniques ensures that fabricated components made from zirconium titanium clad plates maintain their exceptional performance characteristics in demanding industrial environments such as chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, or nuclear applications.
Surface Treatment and Finishing
Surface treatment and finishing of zirconium titanium clad plates represent critical final steps that enhance their performance characteristics and appearance while preparing them for specific service environments. Before applying any surface treatments, thorough cleaning is essential to remove all processing residues, typically using a multi-stage process beginning with non-chlorinated solvents followed by specialized detergents formulated for reactive metals, and concluding with deionized water rinses. For plates destined for highly corrosive environments, chemical passivation treatments create an enhanced oxide layer that provides superior corrosion resistance beyond the already excellent natural properties of these materials. These treatments must be carefully formulated to be effective for both the zirconium and titanium components of the composite structure. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. offers various finish options for their zirconium titanium clad plates, including polished, brushed, or customized finishes tailored to specific application requirements. Achieving these finishes requires specialized abrasives and techniques that won't contaminate the reactive metal surfaces, with progressively finer media used to achieve the desired surface texture or reflectivity.
For applications with strict hygienic requirements, such as pharmaceutical processing equipment, electropolishing may be employed to create ultra-smooth surfaces that minimize product adhesion and facilitate cleaning. Mechanical surface treatments such as shot peening might be applied to areas subject to high mechanical stress, introducing controlled compressive stresses that enhance fatigue resistance while preserving the corrosion-resistant properties of the material. Edge treatments deserve particular attention, as the exposed bond line between the zirconium and titanium layers represents a potential vulnerability that may require specialized finishing techniques to ensure long-term integrity. For plates that will be used in extreme environments, such as highly acidic chemical processing, boundary testing should be performed on finished surfaces to verify their corrosion resistance meets application requirements. All surface treatment operations should be performed by specialized technicians with specific training in reactive metal processing, following documented procedures that ensure consistent results while maintaining the exceptional properties that make zirconium titanium clad plates valuable in demanding industrial applications. After completion of surface treatments, final inspection and documentation provide verification that the finished components meet all specified requirements before being released for installation or assembly.
Conclusion
Proper storage and handling of zirconium titanium clad plates are essential for maintaining their exceptional properties and ensuring optimal performance in demanding industrial applications. By following the comprehensive guidelines outlined in this article, industries can maximize the lifespan and reliability of these valuable composite materials while preventing costly damage or premature failure.
Our team at Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. is committed to providing not only superior zirconium titanium clad plates but also the technical support you need to properly store, handle, and process these specialized materials. With our independent explosive composite technology, international qualifications, and innovative R&D capabilities, we deliver customized solutions tailored to your specific requirements. Whether you need standard specifications or custom dimensions, our OEM/ODM services ensure you receive exactly what your project demands. Contact us today at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our expertise can support your success.
References
1. Johnson, R.T. & Smith, A.B. (2023). Handling and Storage Protocols for Reactive Metal Composites in Industrial Applications. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 32(4), 1875-1889.
2. Zhang, L., Liu, Y., & Wang, H. (2022). Surface Treatment Techniques for Zirconium-Titanium Clad Materials: Advances and Challenges. Corrosion Science, 185, 109982.
3. Anderson, K.L., & Roberts, P.M. (2023). Quality Assurance Frameworks for Explosion-Welded Composite Plates in Critical Applications. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 198, 104643.
4. Nakamura, T., Tanaka, S., & Watanabe, T. (2022). Environmental Factors Affecting Long-Term Storage of Reactive Metal Composites. Materials & Design, 215, 110478.
5. Chen, X., Li, H., & Wilson, J. (2024). Best Practices for Processing and Fabrication of Zirconium-Titanium Clad Plates. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 88, 236-251.
6. Thompson, D.R., & Miller, E.J. (2023). Transport and Handling Safety for High-Value Clad Metal Products. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics, 93, 103325.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)
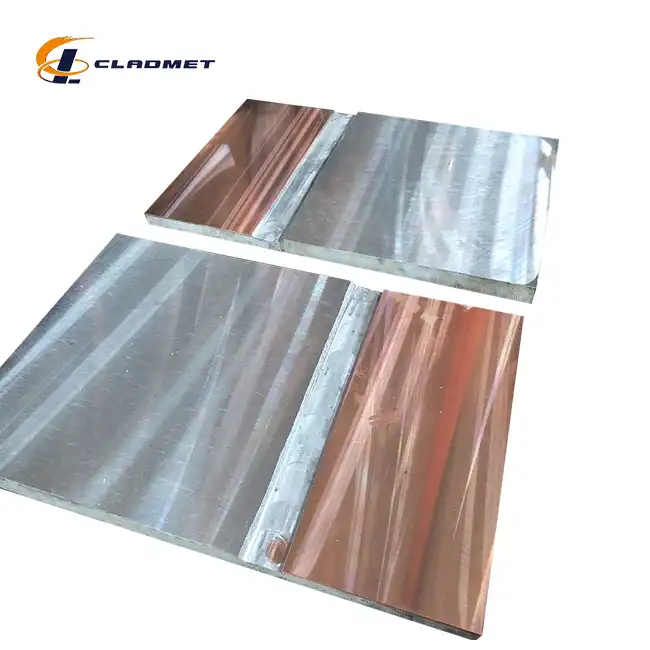
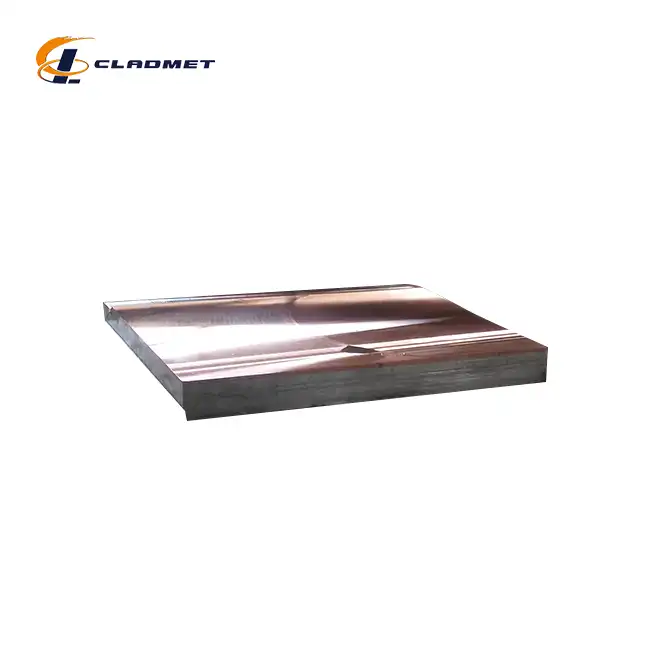







_1737611764680.webp)
_1737611894905.webp)