When evaluating the best titanium steel clad plate for nuclear applications in 2025, professionals must prioritize materials that offer exceptional corrosion resistance, radiation tolerance, and mechanical integrity. These nuclear-grade titanium steel composites represent the pinnacle of engineering excellence, combining titanium's superior corrosion resistance with steel's structural strength. The nuclear industry demands materials that can withstand extreme operating conditions while maintaining safety standards throughout decades of service.
Why Titanium Steel Clad Plate Technology Matters in Nuclear Applications?
The nuclear industry operates under the most demanding conditions imaginable. Reactor environments subject materials to intense radiation, elevated temperatures, and corrosive chemical environments. Traditional materials often fail under these extreme conditions, leading to costly maintenance and potential safety concerns. Titanium steel clad plates address these challenges through innovative cladding technology for reactors. The titanium layer provides exceptional corrosion protection, while the steel substrate delivers structural integrity. This combination creates radiation-resistant clad plate solutions that outperform conventional materials. Nuclear safety materials must meet rigorous standards established by international regulatory bodies. These corrosion-resistant clad materials undergo extensive testing to ensure they can maintain their properties throughout the reactor's operational lifetime. The bonding between titanium and steel creates a unique composite that leverages each material's strengths while mitigating individual weaknesses.
Essential Selection Criteria for Nuclear-Grade Materials
Selecting appropriate nuclear reactor materials requires careful evaluation of multiple performance factors. Radiation tolerance stands as the primary consideration, as materials must maintain their mechanical properties despite prolonged exposure to neutron bombardment and gamma radiation. Corrosion resistance represents another critical factor. Nuclear environments often contain aggressive chemicals that can rapidly degrade inferior materials. High-strength titanium alloy components provide exceptional resistance to both general and localized corrosion mechanisms. Mechanical properties including tensile strength, ductility, and fracture toughness must remain stable throughout the material's service life. Titanium steel mechanical properties offer an optimal balance of strength and flexibility, essential for reactor vessel clad plates that experience thermal cycling and mechanical stress. Manufacturing quality and certification compliance ensure materials meet industry standards. Clad plate quality control processes verify proper bonding, dimensional accuracy, and material composition. International certifications including ASME, ASTM, and nuclear-specific qualifications validate material performance.
Premium Nuclear-Grade Titanium Steel Clad Plate Solutions
High-Performance Titanium Grade 2 Steel Clad Plates
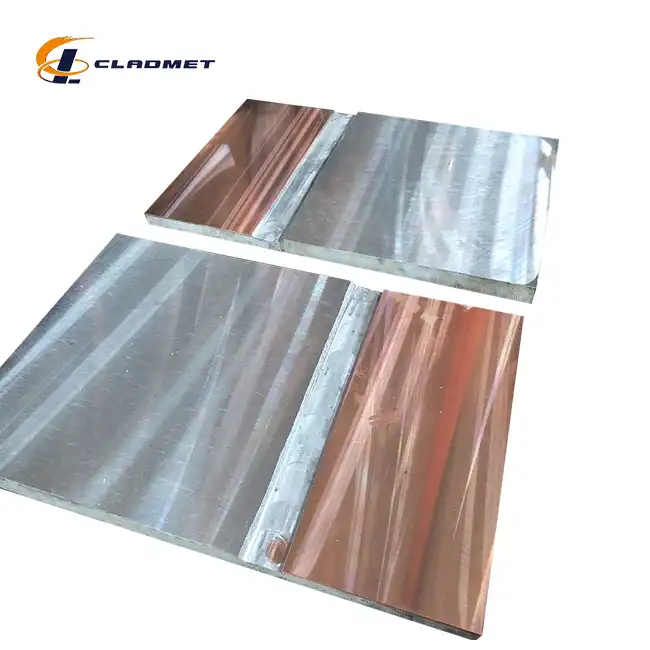
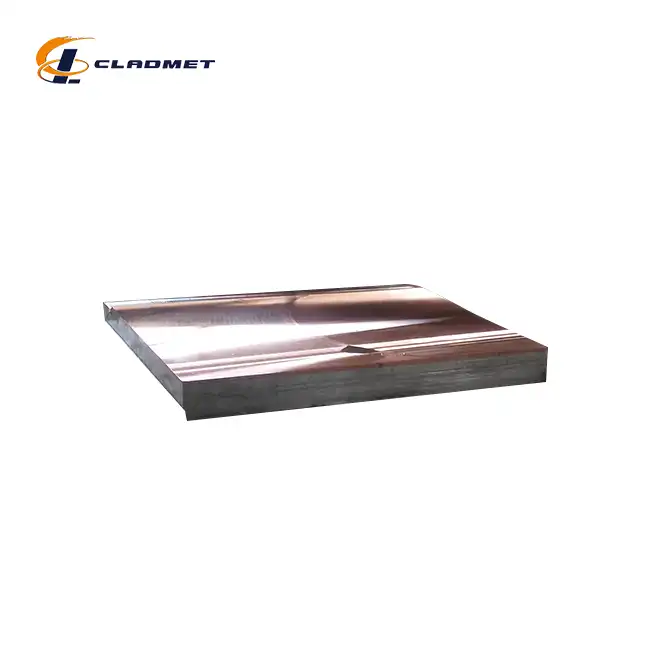
Titanium Grade 2 clad plates represent the gold standard for nuclear industry metal cladding applications. These materials feature commercially pure titanium metallurgically bonded to carbon steel substrates, creating exceptional corrosion resistance while maintaining structural integrity. Key advantages include outstanding resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking, superior performance in oxidizing environments, and excellent formability for complex geometries. The titanium layer thickness typically ranges from 3-10mm, providing adequate corrosion allowance for extended service life. Manufacturing involves explosive bonding or roll bonding processes that create metallurgical bonds stronger than either base material. Quality control measures include ultrasonic testing to verify bond integrity and tensile testing to confirm mechanical properties meet specifications. Applications encompass reactor vessel internals, heat exchanger components, and radioactive waste containers. The material's proven performance in demanding nuclear environments makes it a preferred choice for critical applications where failure is not acceptable. Cost considerations reflect the premium nature of these materials, but lifecycle benefits including reduced maintenance, extended service life, and enhanced safety justify the investment for nuclear applications requiring maximum reliability.
Advanced Titanium Alloy Composite Clad Systems
Advanced titanium alloy composites incorporate high-strength titanium alloys such as Ti-6Al-4V bonded to specialty steel grades. These systems provide enhanced mechanical properties compared to commercially pure titanium while maintaining excellent corrosion resistance. The titanium alloy layer offers superior strength-to-weight ratios, making these materials ideal for applications where weight reduction is beneficial. Enhanced fatigue resistance enables these materials to withstand cyclic loading conditions common in nuclear facilities. Manufacturing processes utilize state-of-the-art clad plate fabrication techniques including hot rolling and explosive welding. These methods ensure uniform bonding across large plate dimensions while maintaining precise thickness tolerances. Specialized heat treatments optimize the microstructure of both titanium and steel layers, enhancing overall performance characteristics. Stress relief treatments eliminate residual stresses that could compromise long-term performance. Applications include reactor pressure vessel cladding, steam generator components, and structural elements requiring high strength combined with corrosion resistance. The enhanced mechanical properties justify premium pricing for critical applications.
Radiation Shielding Materials with Titanium Steel Lamination
Specialized radiation shielding materials incorporate titanium steel lamination technology to provide both corrosion protection and radiation attenuation capabilities. These multi-layered composites feature alternating titanium and steel layers optimized for specific shielding applications. Design optimization balances radiation absorption, structural strength, and corrosion resistance. Computer modeling determines optimal layer thicknesses and compositions to achieve required performance specifications while minimizing material usage. Manufacturing involves precision lamination processes that ensure intimate contact between layers. Advanced bonding techniques create materials that perform as unified composites rather than separate layers. Quality assurance includes radiation testing to verify shielding effectiveness and mechanical testing to confirm structural integrity. These materials undergo rigorous qualification testing to ensure compliance with nuclear safety standards. Applications encompass reactor containment structures, spent fuel storage systems, and transportation containers. The combination of shielding effectiveness and corrosion resistance makes these materials ideal for long-term radioactive material management.
Global Market Dynamics and Regulatory Landscape
The global nuclear industry operates under strict regulatory frameworks that govern material selection and qualification. International standards including ASME Section III, ASTM nuclear specifications, and country-specific regulations establish minimum performance requirements. Regional preferences reflect different reactor designs and operational philosophies. Western markets emphasize proven technologies with extensive qualification histories, while emerging nuclear markets show interest in advanced materials that offer improved performance. Supply chain considerations include material availability, manufacturing capacity, and quality assurance capabilities. Leading suppliers maintain global distribution networks and local technical support to serve international markets effectively. Cost pressures drive innovation toward more efficient manufacturing processes and material optimization. Advanced modeling techniques enable designers to minimize material usage while maintaining performance requirements.
Strategic Procurement Recommendations
Successful procurement requires early supplier engagement during the design phase. Material specifications should reflect actual operating conditions rather than generic requirements, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Supplier qualification involves evaluating manufacturing capabilities, quality systems, and technical expertise. Nuclear applications demand suppliers with proven track records and appropriate certifications. Long-term partnerships enable suppliers to invest in specialized capabilities and maintain inventory for critical applications. Collaborative relationships facilitate continuous improvement and innovation. Risk management includes supplier diversification and supply chain redundancy. Critical projects should maintain qualified alternate suppliers to ensure material availability.
Industry Trends and Summary
The nuclear industry continues evolving toward advanced reactor designs requiring innovative materials solutions. Small modular reactors and Generation IV concepts demand materials with enhanced performance characteristics and simplified manufacturing processes. Additive manufacturing technologies show promise for producing complex geometries while reducing material waste. Sustainability considerations drive development of recyclable materials and environmentally responsible manufacturing processes.
Ready to Source Premium Titanium Steel Clad Plate for Nuclear Applications?
JL Clad Metals delivers world-class nuclear-grade materials engineered for the most demanding applications. Our advanced explosive composite technology and self-rolling capabilities ensure superior titanium steel bonding and consistent quality. With ISO9001, PED, and ABS certifications, we meet the highest international standards for nuclear materials. As a leading titanium steel clad plate for nuclear applications manufacturer, we offer comprehensive customization services including specialized dimensions, compositions, and processing. Our experienced engineering team collaborates with clients to develop optimized solutions that meet specific performance requirements while ensuring regulatory compliance. Our global sales network provides local support worldwide, ensuring efficient project execution and technical assistance. From initial design consultation through material qualification and delivery, JL maintains the highest standards of quality and service. Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss your nuclear material requirements and discover how our expertise can enhance your project success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What makes titanium steel clad plates suitable for nuclear applications?
A: Titanium steel clad plates combine titanium's exceptional corrosion resistance with steel's structural strength, creating materials that withstand radiation, high temperatures, and aggressive chemical environments typical in nuclear facilities while maintaining mechanical integrity throughout extended service life.
Q2: How do manufacturers ensure proper bonding between titanium and steel layers?
A: Advanced manufacturing processes including explosive welding and hot rolling create metallurgical bonds stronger than either base material. Quality control involves ultrasonic testing to verify bond integrity, tensile testing to confirm mechanical properties, and specialized inspection techniques to ensure uniform bonding across entire plate dimensions.
Q3: What certifications are required for nuclear-grade clad plate materials?
A: Nuclear applications typically require compliance with ASME Section III, relevant ASTM standards, and nuclear-specific qualifications such as PED and ABS certifications. Additional requirements may include country-specific nuclear regulatory approvals and customer-specific material qualification programs.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal titanium steel clad plate for nuclear applications requires careful consideration of performance requirements, regulatory compliance, and long-term service conditions. The materials discussed represent the current state-of-the-art in nuclear-grade composites, offering proven performance in the world's most demanding environments. As nuclear technology continues advancing, these innovative materials will play crucial roles in ensuring safe, reliable operation of next-generation nuclear facilities while meeting increasingly stringent environmental and safety requirements.
References
1. American Society of Mechanical Engineers. "ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code Section III: Rules for Construction of Nuclear Facility Components." 2023 Edition.
2. ASTM International. "Standard Specification for Titanium-Steel Clad Plate for Nuclear Applications." ASTM A264/A264M-21, 2021.
3. Nuclear Regulatory Commission. "Materials Engineering Branch Technical Position on Reactor Vessel Integrity." NUREG-1801 Rev. 3, 2024.
4. International Atomic Energy Agency. "Materials for Nuclear Power Plants: Experience and Perspectives." IAEA Nuclear Energy Series Technical Report NP-T-2.4, 2023.
5. World Nuclear Association. "Advanced Nuclear Materials and Manufacturing Technologies Report." WNA Technical Report Series, 2024.
6. European Nuclear Society. "Clad Materials Performance in Generation III+ Reactor Environments." ENS Conference Proceedings, Nuclear Materials Session, 2024.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)







 2025-12-23 10:41:54
2025-12-23 10:41:54
