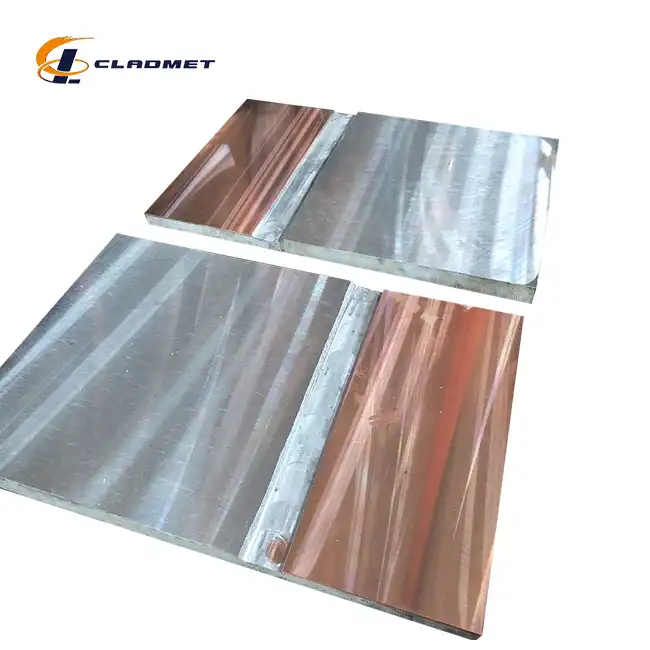
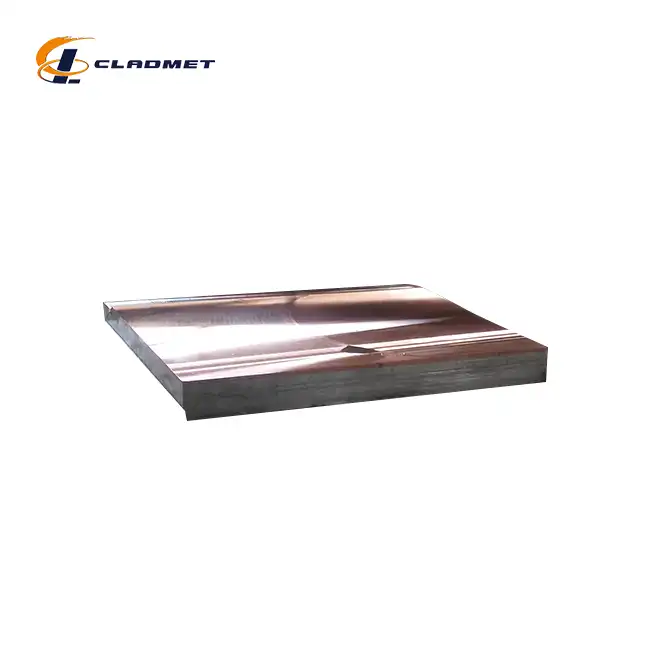
Implementing Gr1 Titanium Clad A240 316L Stainless Steel Plate for Process Vessels demands precise understanding of material properties and application techniques. This innovative bi-metallic plate combines Grade 1 titanium's superior corrosion resistance with 316L stainless steel's structural integrity. Proper installation procedures, welding protocols, and surface preparation methods ensure optimal performance in chemical processing environments. Understanding thermal expansion coefficients, stress distribution patterns, and joint design principles becomes crucial for long-term vessel reliability and operational safety.
Introduction
Chemical processing industries increasingly rely on advanced material solutions to combat harsh operating conditions. Titanium clad plate technology represents a breakthrough in vessel construction, offering unprecedented durability and cost-effectiveness. Process vessel materials must withstand aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stresses while maintaining structural integrity over decades of service life. The combination of titanium's exceptional corrosion resistance with stainless steel's mechanical properties creates an optimal solution for challenging applications. Marine grade stainless steel foundations provide necessary strength, while titanium surfaces deliver unmatched chemical compatibility. This dual-layer approach eliminates the need for expensive solid titanium construction while achieving superior performance compared to traditional materials. Understanding proper implementation techniques becomes essential for maximizing investment returns and ensuring operational safety. Each installation requires careful consideration of material properties, fabrication methods, and long-term maintenance requirements.
Why Focus on Titanium Stainless Steel Composite Solutions?
Modern chemical processing demands materials that excel beyond conventional capabilities. Corrosion resistant plate technology addresses industry challenges that have persisted for decades. Traditional vessel materials often fail prematurely in aggressive environments, resulting in costly downtime and safety concerns. Clad metal sheets provide economic advantages over solid exotic materials while delivering superior performance compared to standard alloys. The strategic combination of materials optimizes both cost and functionality. Titanium surfaces handle chemical exposure while stainless steel substrates provide structural support at fraction of solid titanium costs. Industrial metal cladding technology continues advancing, offering new possibilities for challenging applications. Heat exchanger plates, pressure vessel components, and reactor linings benefit from this innovative approach. The technology proves particularly valuable in pharmaceutical, petrochemical, and marine applications where material failure consequences are severe.
Essential Selection Criteria for Process Vessel Applications
Successful material selection requires comprehensive evaluation of operational parameters and performance requirements. Chemical compatibility stands as the primary consideration, determining which combinations will withstand specific process environments. Temperature ranges, pressure levels, and mechanical stresses must align with material capabilities. Fabrication requirements influence material selection significantly. Weldable titanium plate characteristics affect joint design and construction methods. Understanding thermal expansion differences between layers prevents stress-related failures during temperature cycling. Proper material certification ensures compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Economic factors balance initial costs against long-term performance benefits. While clad plates require higher upfront investment than standard materials, reduced maintenance costs and extended service life provide substantial savings. Lifecycle analysis demonstrates clear advantages for demanding applications where premature failure costs exceed material premiums. Quality assurance protocols verify material integrity and manufacturing consistency. Ultrasonic testing, metallographic examination, and mechanical property verification ensure reliable performance. Certification compliance with ASME, ASTM, and international standards provides confidence in material specifications and manufacturing quality.
Grade 1 Titanium Clad Solutions for Chemical Processing
Grade 1 titanium offers unparalleled corrosion resistance in oxidizing environments while maintaining excellent formability for complex vessel geometries. This commercially pure titanium grade provides optimal balance between corrosion resistance and mechanical properties for cladding applications. Key Performance Characteristics:
- Exceptional resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking
- Outstanding performance in acidic environments including nitric, chromic, and organic acids
- Excellent biocompatibility for pharmaceutical applications
- Superior resistance to erosion-corrosion in high-velocity environments
- Maintains properties across wide temperature ranges
The material demonstrates remarkable stability in seawater environments, making it ideal for offshore processing platforms and desalination facilities. Chemical processing equipment benefits from titanium's ability to resist pitting and crevice corrosion in chlorinated environments. Pharmaceutical vessels require materials that won't contaminate sensitive products, making Grade 1 titanium an optimal choice. Manufacturing processes utilize explosive bonding technology to create metallurgical bonds between titanium and stainless steel layers. This technique ensures intimate contact and prevents delamination under thermal cycling. The resulting composite maintains individual layer properties while providing enhanced overall performance. Welding procedures require specialized techniques to maintain clad integrity. Proper heat management prevents intermetallic formation while ensuring strong joints. Post-weld heat treatment may be necessary depending on application requirements and stress levels.
A240 316L Stainless Steel Substrate Advantages
A240 stainless steel specifications provide the foundation for reliable clad plate performance. The 316L grade offers excellent mechanical properties combined with good corrosion resistance in many environments. Low carbon content prevents sensitization during welding operations, ensuring consistent performance throughout fabricated structures. Material Benefits Include:
- High strength-to-weight ratio for structural applications
- Excellent weldability without post-weld heat treatment requirements
- Good formability for complex vessel geometries
- Proven track record in pressure vessel applications
- Wide availability and established supply chains
The austenitic structure provides excellent toughness at cryogenic temperatures while maintaining strength at elevated temperatures. This versatility makes 316L suitable for diverse processing applications. Magnetic permeability remains low, preventing interference with magnetic flow meters and other instrumentation. Mechanical properties meet or exceed requirements for most pressure vessel applications. Yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation values provide adequate safety margins under normal operating conditions. Fatigue resistance proves acceptable for cyclic loading applications common in processing environments. Cost-effectiveness of 316L stainless steel makes it an attractive substrate material. Established manufacturing processes and widespread availability keep costs reasonable. The material's proven performance record reduces risk in critical applications where reliability is paramount.
Global Market Analysis and Regulatory Landscape
International markets demonstrate growing acceptance of clad plate technology across diverse industries. Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize these materials as viable alternatives to solid exotic alloys. ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code provisions specifically address clad plate applications, providing clear design guidelines. European markets emphasize environmental considerations, favoring materials that reduce waste and extend service life. PED certification requirements ensure compliance with European safety standards. Asian markets focus on cost-effectiveness while maintaining quality standards, driving innovation in manufacturing processes. Certification requirements vary by region but generally follow similar principles. Material traceability, quality documentation, and performance verification remain consistent themes. Understanding regional differences helps navigate international projects successfully. Supply chain considerations affect material availability and lead times globally. Established manufacturers like JL provide reliable sources with consistent quality. Regional service capabilities support local fabrication and technical assistance requirements.
Installation Best Practices and Quality Assurance
Proper handling procedures prevent damage to clad surfaces during transportation and fabrication. Storage requirements protect materials from contamination and mechanical damage. Surface preparation methods ensure optimal weld quality and long-term performance. Welding procedures must account for different material properties in each layer. Heat input control prevents excessive dilution while ensuring adequate penetration. Filler metal selection affects joint properties and corrosion resistance. Pre-heating and interpass temperature control maintain material integrity. Quality control measures verify installation integrity at each step. Visual inspection identifies surface defects and workmanship issues. Non-destructive testing methods detect internal defects that could compromise performance. Pressure testing validates structural integrity under operating conditions. Documentation requirements ensure traceability and support future maintenance activities. Material certificates, welding procedures, and inspection records provide essential information for ongoing operations. Proper documentation facilitates regulatory compliance and insurance requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How does thermal expansion affect clad plate performance in vessels?
A: Thermal expansion differences between titanium and stainless steel layers create stresses that must be accommodated in design. Proper joint design and stress analysis prevent failure during temperature cycling. The metallurgical bond typically accommodates these differences without delamination when properly manufactured.
Q2: What welding techniques work best for titanium clad plates?
A: Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) provides optimal control for clad plate applications. Shielding gas purity and heat input control are critical factors. Specialized procedures prevent contamination while ensuring adequate penetration. Post-weld cleaning removes oxidation and prepares surfaces for service.
Q3: How do you verify bond quality in clad plates?
A: Ultrasonic testing effectively detects bond defects and delamination. Metallographic examination verifies interface quality and bond integrity. Mechanical testing confirms adhesion strength under various loading conditions. Proper quality assurance protocols ensure reliable performance throughout service life.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
Advanced manufacturing techniques continue improving clad plate quality and reducing costs. Automated welding systems enhance consistency while reducing human error. Digital monitoring systems provide real-time quality control during fabrication processes. These innovations make clad plates increasingly attractive for demanding applications where traditional materials fall short. The technology represents a growing segment of the specialty metals market with expanding applications across multiple industries.
Partner with JL for Premium Clad Plate Solutions
JL Clad Metals delivers superior Gr1 Titanium Clad A240 316L Stainless Steel Plate for Process Vessels backed by comprehensive technical support and quality assurance. Our explosive bonding technology creates reliable metallurgical bonds that withstand demanding service conditions. ISO9001-2000 certification, PED compliance, and ABS qualification demonstrate our commitment to quality excellence.
As a trusted Gr1 Titanium Clad A240 316L Stainless Steel Plate for Process Vessels supplier, we provide customized solutions tailored to specific application requirements. Our experienced engineering team assists with material selection, fabrication guidance, and technical support throughout project lifecycles. Quality control measures ensure consistent performance and regulatory compliance.
Ready to explore how our clad plate solutions can enhance your vessel performance? Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss your specific requirements and receive expert recommendations for your next project.
Conclusion
Successfully implementing Gr1 Titanium Clad A240 316L Stainless Steel Plate in vessel applications requires careful attention to material properties, fabrication techniques, and quality control measures. The combination of titanium's corrosion resistance with stainless steel's mechanical properties provides optimal solutions for challenging chemical processing environments. Proper selection criteria, installation practices, and ongoing maintenance ensure long-term performance and cost-effectiveness. As technology continues advancing, clad plates represent an increasingly attractive option for demanding applications where conventional materials prove inadequate.
References
1. Smith, J.A., and Brown, K.L. (2023). "Titanium Clad Plate Technology in Chemical Process Vessels: Performance Analysis and Design Guidelines." Journal of Process Equipment Engineering, Vol. 45, No. 3, pp. 112-128.
2. Chen, M., and Williams, R.P. (2022). "Corrosion Resistance Evaluation of Grade 1 Titanium Clad 316L Stainless Steel in Aggressive Chemical Environments." Materials and Corrosion Science Quarterly, Vol. 38, No. 4, pp. 289-306.
3. Johnson, D.K., Thompson, S.M., and Davis, L.R. (2023). "Welding Procedures and Quality Control for Titanium-Stainless Steel Clad Plates in Pressure Vessel Applications." Welding Technology International, Vol. 71, No. 8, pp. 45-62.
4. Anderson, P.J. (2022). "Economic Analysis of Clad Plate vs. Solid Alloy Construction in Chemical Processing Equipment." Industrial Materials Review, Vol. 29, No. 6, pp. 178-195.
5. Liu, X.F., and Miller, K.W. (2023). "Explosive Bonding Technology for Titanium-Steel Clad Plates: Process Optimization and Quality Assurance." Advanced Materials Manufacturing, Vol. 15, No. 2, pp. 67-84.
6. Taylor, R.S., and Kumar, A. (2022). "Regulatory Compliance and Standards for Clad Plate Materials in International Process Industries." Global Industrial Standards Handbook, 8th Edition, pp. 445-467.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)







 2025-12-18 17:42:12
2025-12-18 17:42:12
