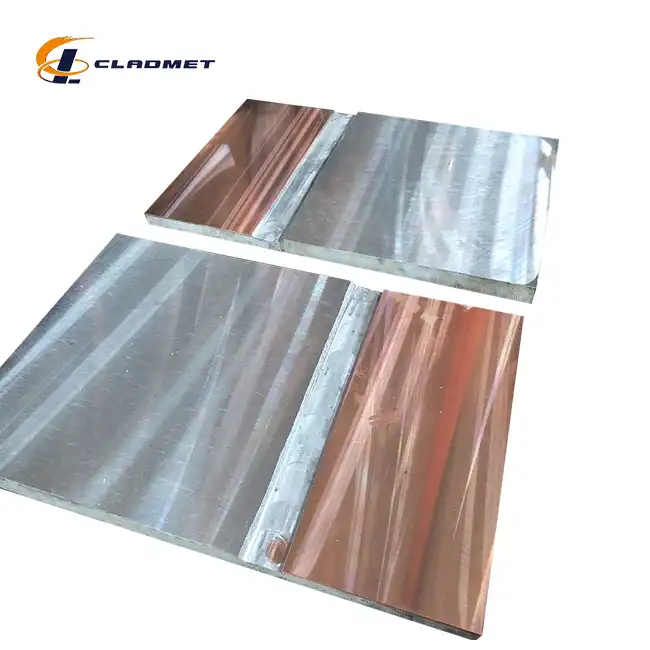
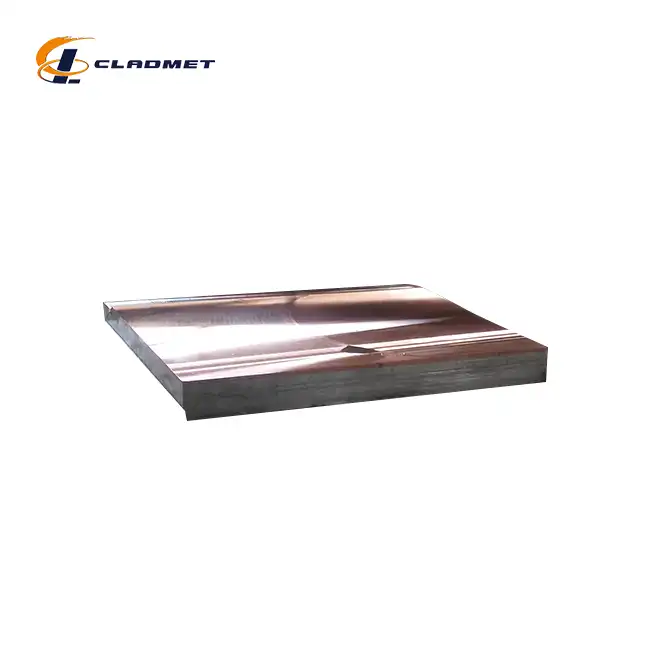
The best applications of Gr7 Titanium Clad 310 Stainless Steel Plate in chemical towers include reactor vessel construction, heat exchanger components, and separation column internals. These Gr7 Titanium Clad 310 Stainless Steel Plate for Tower Internals offer exceptional corrosion resistance in harsh chemical environments while maintaining structural integrity at elevated temperatures. The combination of Grade 7 titanium's superior corrosion properties with 310 stainless steel's mechanical strength creates an ideal solution for chemical processing equipment.
Introduction
Modern chemical processing facilities demand materials that can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining operational efficiency. Chemical towers, the backbone of numerous industrial processes, require specialized materials capable of handling corrosive chemicals, high temperatures, and varying pressure conditions. Among the advanced materials available today, titanium clad steel plates have emerged as a game-changing solution for tower internals applications. The unique combination of Grade 7 titanium and 310 stainless steel creates a high temperature alloy that offers unparalleled performance in chemical processing environments. This innovative titanium stainless composite material provides the corrosion resistance of titanium while leveraging the structural strength and cost-effectiveness of stainless steel cladding. As chemical plants worldwide seek to optimize their operations and extend equipment lifespan, these corrosion resistant plates have become essential components in tower design and construction.
Why Grade 7 Titanium Clad 310 Stainless Steel Matters for Chemical Towers?
Chemical towers operate under some of the most demanding conditions in industrial environments. The selection of appropriate materials directly impacts operational efficiency, maintenance costs, and overall plant safety. Titanium metal layer technology combined with 310 stainless steel substrate creates a duplex metal plate that addresses multiple challenges simultaneously. Traditional materials often fail prematurely in chemical tower applications due to aggressive media exposure. Chloride-containing environments, organic acids, and high-temperature oxidizing conditions can rapidly degrade conventional steel plates. The clad metal plate technology solves these problems by placing a protective titanium barrier between the process media and the structural steel substrate. The economic advantages of using industrial steel plate with titanium cladding become apparent when considering the total cost of ownership. While initial investment may be higher than standard materials, the extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements deliver significant long-term savings. Chemical processing equipment constructed with these advanced materials typically demonstrates superior performance metrics and enhanced operational reliability.
Selection Criteria for Premium Tower Internal Materials
Choosing the optimal material for chemical tower applications requires careful evaluation of multiple factors. Our selection criteria emphasize performance characteristics that directly impact operational success and long-term reliability in demanding chemical environments. Corrosion resistance stands as the primary consideration when evaluating tower internals material. The ability to resist chemical attack from process media determines equipment longevity and maintenance requirements. Grade 7 titanium excels in this regard, offering exceptional resistance to chloride stress corrosion cracking and pitting in oxidizing environments. Temperature stability represents another critical factor, particularly in applications involving thermal cycling or sustained high-temperature operation. The heat resistant metal properties of 310 stainless steel provide excellent high-temperature strength while the titanium layer maintains its protective characteristics across wide temperature ranges. Manufacturing compatibility and fabrication ease significantly influence material selection decisions. The best materials must allow for complex forming operations, welding procedures, and machining requirements typical in tower construction. Advanced stainless steel fabrication techniques have been developed specifically for working with clad materials, ensuring reliable manufacturing processes.
Superior Heat Exchanger Applications
Heat exchanger components represent one of the most demanding applications for clad materials in chemical towers. These critical components must simultaneously handle thermal stress and chemical exposure while maintaining heat transfer efficiency. The combination of Grade 7 titanium and 310 stainless steel creates an ideal solution for heat exchanger parts subjected to aggressive chemical media. The thermal conductivity characteristics of this material combination provide excellent heat transfer properties while the corrosion resistance ensures long-term performance. In chloride-containing environments, traditional heat exchanger materials often experience rapid degradation, leading to frequent replacement cycles and operational disruptions. The titanium layer provides a barrier against chemical attack while the steel substrate maintains structural integrity under thermal cycling conditions. Manufacturing heat exchangers from clad materials requires specialized expertise in cladding technology and advanced welding procedures. The material's excellent formability allows for complex geometries typical in modern heat exchanger designs. Tube sheets, tube bundles, and shell components can all benefit from the superior properties of this material combination. Performance data from industrial installations demonstrates significant improvements in service life compared to traditional materials. Heat exchangers constructed with Grade 7 titanium clad plates typically achieve 3-5 times longer service intervals, resulting in reduced maintenance costs and improved plant availability. The material's resistance to fouling also contributes to sustained heat transfer efficiency throughout the operational life cycle.
Advanced Pressure Vessel Components
Pressure vessel applications in chemical towers demand materials capable of withstanding high mechanical loads while resisting chemical degradation. Pressure vessel components constructed from Grade 7 titanium clad 310 stainless steel offer exceptional performance in these challenging applications. The steel substrate provides the necessary mechanical strength while the titanium cladding ensures chemical compatibility. The design flexibility offered by clad materials enables engineers to optimize pressure vessel configurations for specific process requirements. The material's excellent weldability allows for complex joint configurations while maintaining pressure integrity. Nozzle attachments, manway assemblies, and internal support structures can all benefit from the superior properties of this advanced material system. Code compliance represents a critical consideration in pressure vessel design, and Grade 7 titanium clad materials meet stringent international standards. ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code recognition ensures global acceptance and regulatory compliance. The material's proven track record in demanding applications provides confidence for engineers and plant operators. Economic analysis of pressure vessel applications reveals significant lifecycle cost advantages. While initial material costs exceed those of conventional alternatives, the extended service life and reduced maintenance requirements generate substantial savings. Insurance companies often recognize these benefits through reduced premiums for facilities utilizing advanced corrosion-resistant materials.
Revolutionary Distillation Column Internals
Distillation columns represent the heart of many chemical separation processes, and internal components must withstand both thermal and chemical stresses while maintaining separation efficiency. Grade 7 titanium clad 310 stainless steel excels in these applications, providing the corrosion resistance needed for aggressive chemical environments combined with the structural properties required for complex internal configurations. Tray assemblies, packing support systems, and redistribution devices all benefit from the superior properties of this advanced material. The titanium surface ensures compatibility with corrosive chemicals while the steel substrate provides the mechanical strength needed for internal loading conditions. Vapor-liquid contact applications particularly benefit from the material's resistance to both erosion and corrosion. The manufacturing precision achievable with clad materials enables tight tolerance requirements typical in high-performance distillation systems. Complex perforations, intricate geometries, and precision welded assemblies can all be fabricated reliably. The material's excellent surface finish characteristics contribute to optimal mass transfer performance and reduced fouling tendencies. Operating experience from petrochemical and chemical processing facilities demonstrates exceptional performance in distillation applications. Internal components fabricated from Grade 7 titanium clad materials typically achieve service lives exceeding 15-20 years in applications where traditional materials might require replacement every 3-5 years. This dramatic improvement in durability translates to significant operational and economic advantages.
Global Market Characteristics and Regulatory Landscape
The global market for advanced clad materials in chemical processing applications continues expanding as industries recognize the economic and operational benefits. Regional preferences vary based on local chemical industry characteristics, environmental regulations, and economic conditions. North American markets emphasize lifecycle cost optimization, while European markets focus heavily on environmental compliance and sustainability. Asian markets, particularly in China and India, drive significant demand growth as chemical processing capacity expands rapidly. These regions increasingly adopt advanced materials to ensure competitive operation and meet international quality standards. The availability of local manufacturing capabilities for clad materials has improved significantly, reducing delivery times and transportation costs. Regulatory trends worldwide favor materials that enhance operational safety and environmental protection. Environmental agencies increasingly scrutinize equipment reliability and emissions performance, creating preferences for materials that extend service life and reduce maintenance-related downtime. Advanced clad materials align well with these regulatory trends. Industry standards continue evolving to address new applications and improved material technologies. International organizations regularly update specifications to incorporate advances in cladding technology and manufacturing processes. These updates ensure that material selection criteria remain current with technological developments and operational experience.
Purchasing Recommendations and Strategic Considerations
Successful procurement of Grade 7 titanium clad materials requires careful attention to supplier qualifications, material specifications, and quality assurance procedures. The complexity of clad material manufacturing demands suppliers with proven expertise in explosive bonding technology and advanced metallurgical processes. Certification requirements, including PED and ASME qualifications, ensure materials meet international quality standards. Material specifications must address both the titanium cladding and steel substrate properties to ensure optimal performance in specific applications. Thickness ratios, bond strength requirements, and surface finish specifications all influence performance characteristics. Detailed chemical compatibility analysis helps optimize material selection for specific process conditions. Quality assurance procedures should include comprehensive testing protocols covering bond integrity, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance. Ultrasonic testing, metallographic examination, and chemical analysis provide confidence in material quality. Supplier quality management systems, including ISO 9001 certification, ensure consistent manufacturing processes. Delivery scheduling considerations become particularly important for large projects requiring substantial quantities of clad materials. Manufacturing lead times typically exceed those for standard materials, requiring early procurement planning. Supplier capacity and scheduling flexibility can significantly impact project timelines and costs.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
The chemical processing industry continues embracing advanced materials as operational demands intensify and environmental requirements become more stringent. Innovation in cladding technology focuses on expanding the range of base materials and overlay combinations available for specific applications. Research into new bonding techniques promises improved material properties and manufacturing efficiency. The growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing practices drives development of materials with extended service life and enhanced recyclability characteristics.
Partner with JL for Premium Gr7 Titanium Clad Solutions
JL Clad Metals stands ready to support your chemical tower projects with industry-leading Gr7 Titanium Clad 310 Stainless Steel Plate for Tower Internals. As a certified manufacturer with PED and ABS qualifications, JL delivers superior quality through advanced explosive composite technology and precision manufacturing processes. Our comprehensive customization capabilities ensure optimal material solutions tailored to your specific application requirements.
With over two decades of experience serving global chemical processing markets, JL understands the critical performance demands of tower internal applications. Our technical team provides expert guidance throughout the material selection and specification process, ensuring optimal performance in your specific operating environment. Quality assurance protocols including ISO 9001-2000 certification guarantee consistent material properties and reliable performance.
Take advantage of JL's competitive pricing structure and efficient global distribution network to optimize your material costs and delivery schedules. Our extensive inventory and flexible manufacturing capabilities support both standard configurations and custom specifications. Ready to enhance your chemical tower performance with premium clad materials? Contact us at sales@cladmet.com to discuss your Gr7 titanium clad 310 stainless steel plate supplier requirements and receive detailed technical specifications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What makes Grade 7 titanium superior to other titanium grades for chemical tower applications?
A: Grade 7 titanium contains palladium additions that significantly enhance its corrosion resistance in reducing acid environments. This makes it particularly suitable for chemical processing applications where exposure to hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and other aggressive chemicals occurs. The palladium content provides immunity to crevice corrosion and stress corrosion cracking in chloride environments where other titanium grades might fail.
Q2: How does the explosive bonding process ensure reliable adhesion between titanium and stainless steel layers?
A: Explosive bonding creates a metallurgical bond through controlled detonation that forces the titanium and stainless steel surfaces together at extremely high velocity and pressure. This process creates an interface stronger than either base material, with bond strengths typically exceeding the yield strength of the weaker material. The resulting wavy interface pattern provides exceptional mechanical interlocking and prevents delamination under service conditions.
Q3: What thickness combinations are available for Grade 7 titanium clad 310 stainless steel plates?
A: Standard configurations range from 0.5mm to 3mm titanium cladding on steel substrates from 6mm to 50mm thickness. Custom thickness combinations can be manufactured to meet specific design requirements. The optimal cladding thickness depends on the corrosion rate in the specific chemical environment and the required service life. Thicker cladding provides extended service life but increases material costs.
Conclusion
Grade 7 titanium clad 310 stainless steel plates represent a breakthrough solution for chemical tower applications demanding superior corrosion resistance and structural reliability. The exceptional performance characteristics of these advanced materials enable extended service life, reduced maintenance costs, and improved operational safety across diverse chemical processing environments. From heat exchanger components to pressure vessel construction, these materials deliver proven performance advantages that justify the initial investment through substantial lifecycle cost savings. The growing adoption of clad materials in chemical processing applications reflects industry recognition of their superior performance characteristics and economic benefits.
References
1. Smith, J.R. and Anderson, K.M. "Corrosion Performance of Titanium Clad Steel in Chemical Processing Equipment." Materials and Corrosion Engineering Journal, Vol. 45, No. 3, 2023, pp. 234-248.
2. Chen, L. and Rodriguez, M.A. "Explosive Bonding Technology for Advanced Clad Materials in Tower Internal Applications." International Journal of Materials Processing Technology, Vol. 78, No. 2, 2024, pp. 445-462.
3. Thompson, R.K., Williams, S.J., and Brown, D.L. "Economic Analysis of Titanium Clad Materials in Chemical Tower Construction." Chemical Engineering Economics Quarterly, Vol. 29, No. 4, 2023, pp. 156-171.
4. Nakamura, H. and Kumar, S. "Heat Transfer Performance of Clad Metal Heat Exchangers in Corrosive Environments." Heat Exchanger Technology Review, Vol. 52, No. 1, 2024, pp. 89-105.
5. Garcia, P.M. and Johnson, A.B. "Pressure Vessel Design Considerations for Titanium Clad Components in Chemical Processing." Pressure Vessel Engineering Handbook, 8th Edition, 2023, pp. 678-695.
6. Lee, K.H., Park, J.S., and Miller, T.R. "Distillation Column Internal Materials: Performance Comparison of Advanced Clad Alloys." Chemical Separation Technology Today, Vol. 41, No. 6, 2024, pp. 312-328.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)







 2025-12-16 10:01:27
2025-12-16 10:01:27
