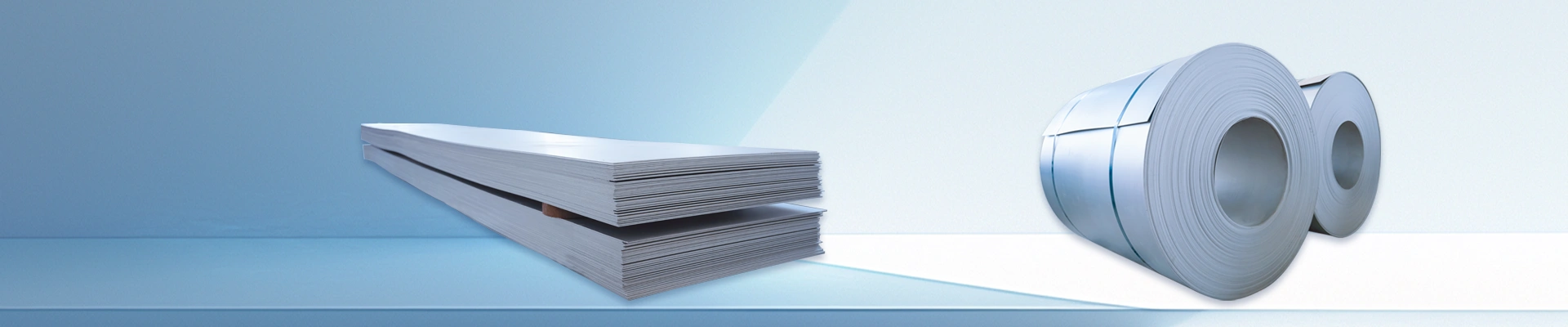
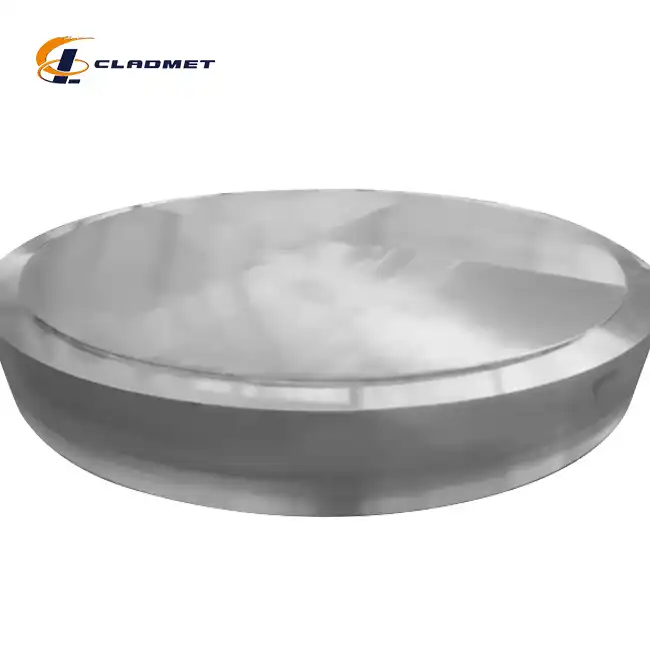
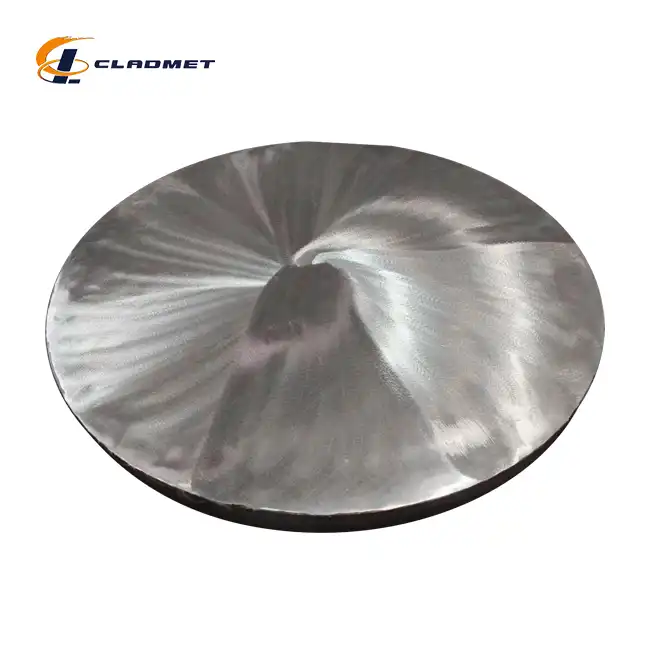
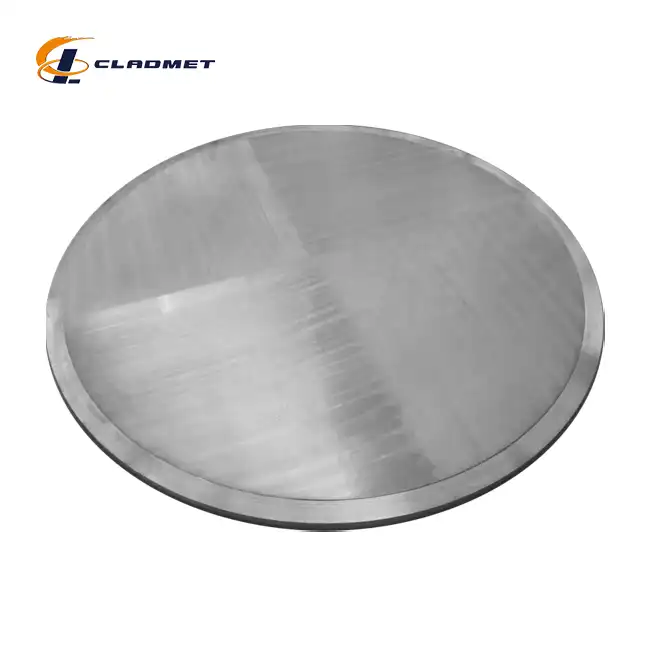
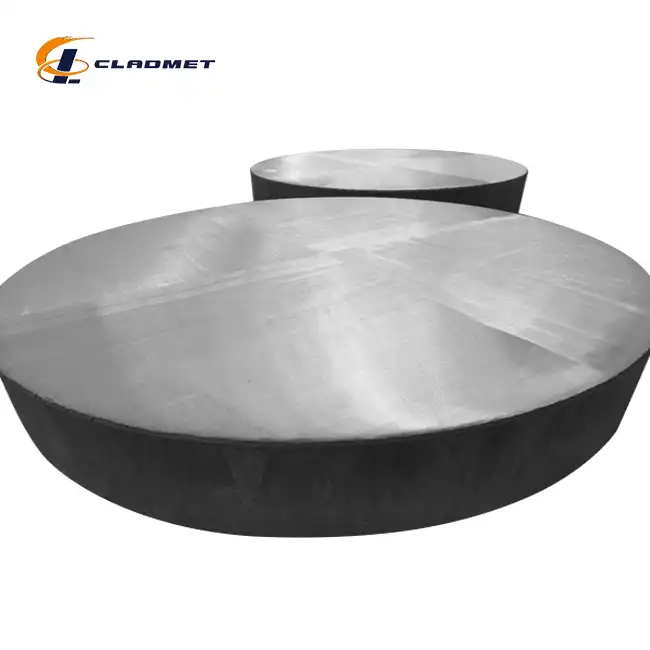
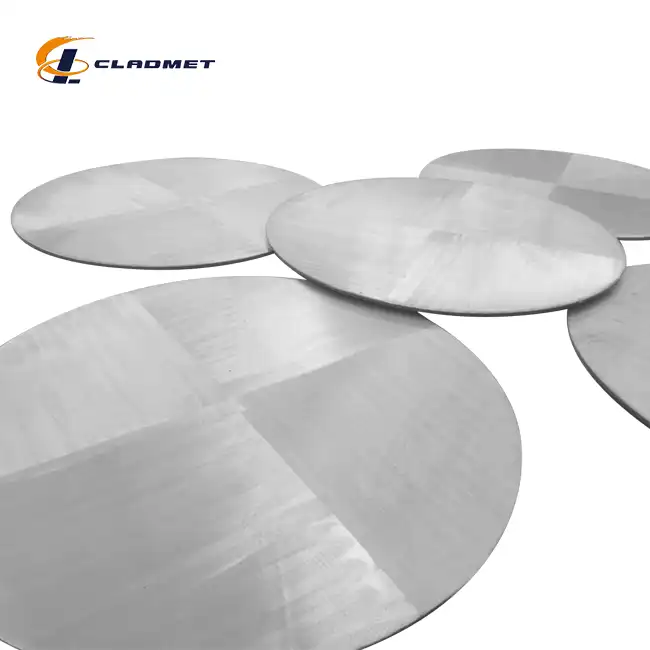
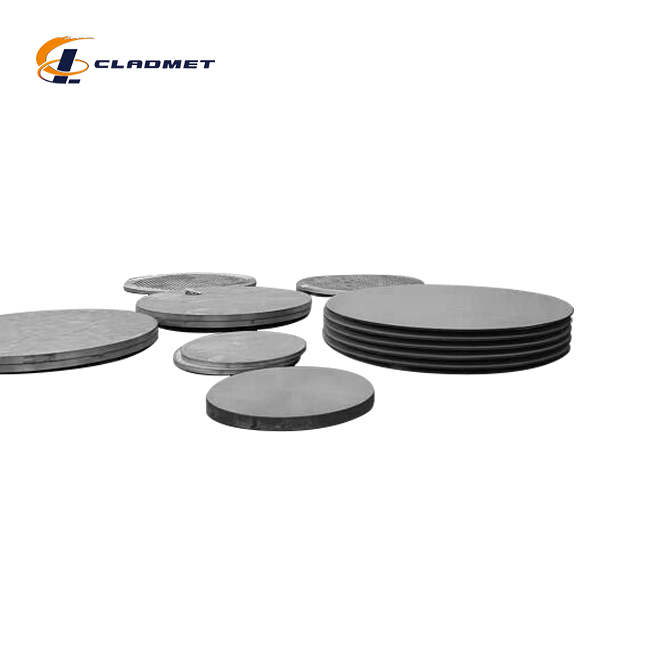
clad steel sheets
Available Sizes:Standard and custom sizes available upon request
Product Applications:Used in electroplating, chemical, and marine industries
Processing Technology:Explosive bonding and hot-rolled processing techniques
Quality Control and Testing: Strict testing ensures adherence to ISO9001-2000, PED, ABS standards
Product Implementation Standards:ASME, ASTM, JIS certified
Delivery:Available via sea, air, and express shipping
Packaging:Secure wooden crates for international transport
Product Introduction
Clad steel plates are advanced composite materials that combine two or more different metals, offering enhanced performance for a range of industrial applications. These plates are produced through either roll-bonding or explosion-bonding, which fuses the materials at a molecular level. This combination creates a material that boasts superior strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance compared to single-metal plates. Widely used in the oil and gas, chemical, nuclear, aerospace, and marine engineering industries, the steel plates provide a durable and cost-effective solution to various industrial challenges.
Product Specifications
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Base Material | Carbon Steel, Low Alloy Steel, or Stainless Steel (e.g., Q235B, Q345B, A516 Gr.70, etc.) |
| Cladding Material | Stainless Steel, Titanium, Copper, Nickel Alloy, Aluminum, or Customized Materials |
| Thickness Range | Total: 6 mm - 200 mm (e.g., 2 mm Cladding + 8 mm Base) |
| Clad Layer Thickness | 1 mm - 20 mm (customizable) |
| Base Layer Thickness | 5 mm - 180 mm (customizable) |
| Width Range | Up to 4000 mm |
| Length Range | Up to 12000 mm |
| Bonding Technology | Explosion Bonding, Hot Rolling, or Explosion + Rolling |
| Bonding Strength | ≥ 140 MPa |
| Shear Strength | ≥ 105 MPa |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior resistance based on cladding material (e.g., acid, alkali, marine) |
| Heat Resistance | High-temperature tolerance depending on cladding material |
| Application Industries | Chemical, Oil & Gas, Power Generation, Marine, Desalination, Aerospace, etc. |
| Standards Compliance | ASTM B898, ASME SB-898, GB/T 8165, and other relevant standards |
| Surface Finish | Polished, Sandblasted, or as per customer requirements |
| Customizations Available | Thickness Ratio, Size, Material Combination, and More |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Manufacturing Techniques
Clad steel sheets are produced by bonding a layer of one material, typically a corrosion-resistant metal, to the surface of a more cost-effective and durable base steel. This composite material combines the best properties of both metals, offering strength, durability, and resistance to harsh environments. Several advanced bonding techniques are employed to ensure a strong and lasting bond between the layers, including:
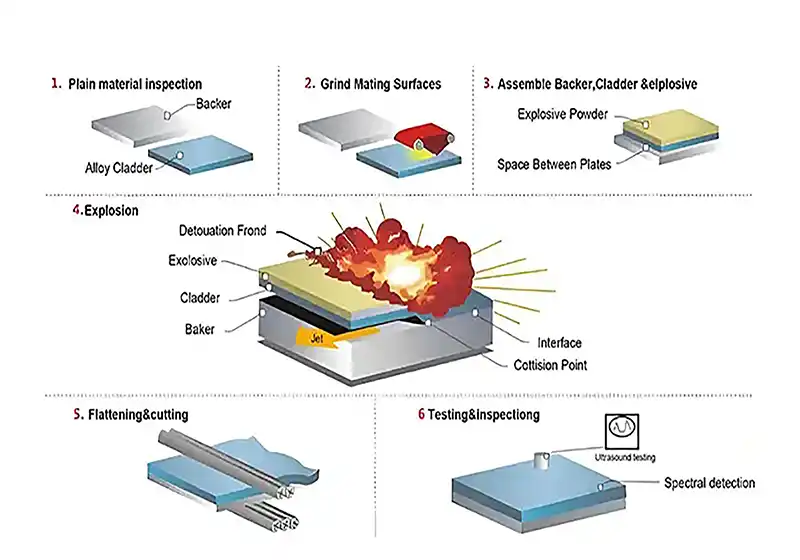
Explosive Bonding
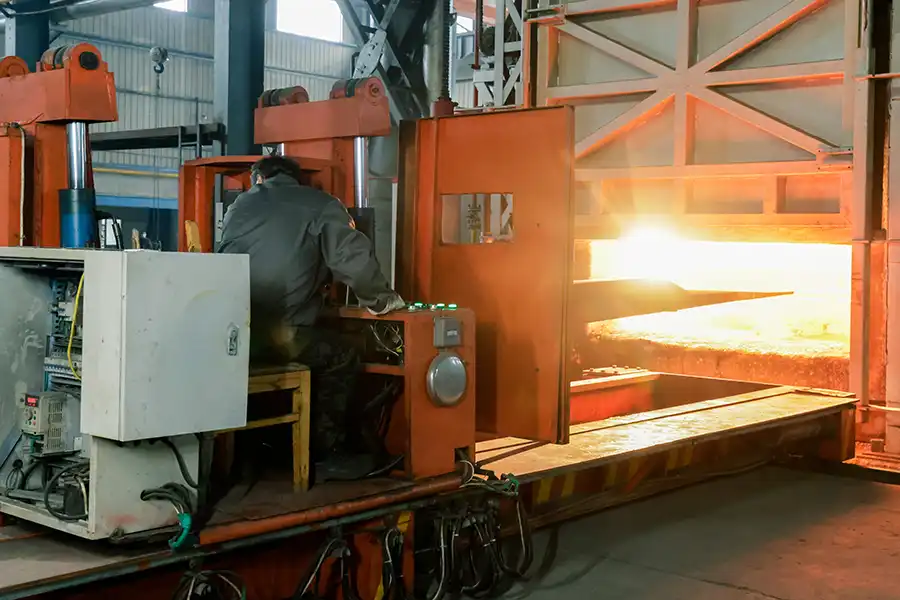
Explosive bonding is an energy-intensive process that uses controlled explosions to create a strong, metallurgical bond between the base steel and the cladding material. The explosive force drives the materials into a high-speed collision, ensuring that they fuse without the need for melting.
Pre-Bonding Setup: The base material and the cladding are carefully cleaned and positioned to align them properly before the explosive charge is placed.
Detonation: An explosive charge is detonated between the two materials, causing them to collide at high velocity.
Bond Formation: The force of the explosion ensures the materials form a robust, seamless bond.
This method is ideal for creating clad steel sheets that need to withstand high stresses, aggressive chemicals, or extreme environments, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications like heat exchangers and pressure vessels.
Roll Bonding
Roll bonding is a cold-rolling process where the steel and cladding are passed through a series of rollers under high pressure. This pressure is sufficient to bond the two layers together, producing a solid, cohesive sheet.
Cleaning and Preparation: Both the steel and cladding are thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants that could interfere with the bonding.
Roller Application: The materials are passed through rollers, applying extreme pressure to join them permanently. Multiple passes through the rollers may be necessary to ensure a complete bond.
Uniform Bond: The result is a smooth, uniform layer of cladding fused securely to the steel substrate.
Roll bonding is commonly used for producing large sheets and plates, particularly for industries that require a strong bond but do not need the extreme strength offered by explosive welding.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing involves placing the steel and cladding in a high-pressure, high-temperature environment. This method uses both heat and pressure to achieve a diffusion bond between the materials, providing a high-quality, durable product.
Enclosing and Sealing: The steel and cladding are carefully arranged in a sealed container before the HIP process begins.
Pressurization and Heating: The container is exposed to high heat and pressure, causing the materials to fuse at the atomic level.
Bond Integrity: The resulting bond is exceptionally strong, with excellent resistance to fatigue and wear.
HIP is ideal for manufacturing high-performance clad steel sheets for critical applications such as aerospace components, industrial machinery, and high-pressure vessels.
Key Benefits and Features
Superior Corrosion Resistance: The cladding material, often stainless steel or another corrosion-resistant metal, offers excellent protection against rust, chemicals, and environmental degradation. This makes clad steel sheets ideal for applications in harsh environments, including offshore structures and chemical processing plants.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties: The combination of the base steel’s strength with the cladding’s protective properties provides a material that is both durable and resistant to mechanical wear, making these sheets suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Cost-Effective: By combining a relatively inexpensive base material with a corrosion-resistant cladding, clad steel sheets offer an economical solution that doesn't compromise on performance, significantly lowering the overall cost of materials.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance: The cladding layer offers enhanced resistance to heat and chemicals, making these sheets suitable for applications involving exposure to high temperatures or aggressive chemicals.
Improved Longevity: The corrosion-resistant cladding extends the lifespan of the steel, reducing the need for maintenance or replacement and improving the overall cost-effectiveness of the material over time.
Customization: Clad steel sheets can be tailored to meet specific needs, with options for varying thicknesses, surface treatments, and cladding materials, ensuring optimal performance in a wide range of industries.
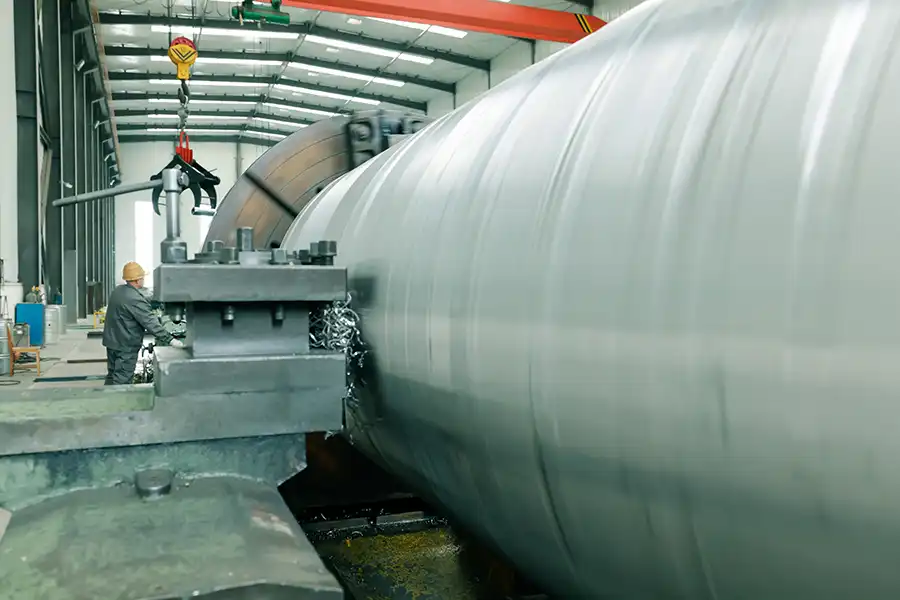
Explosive Composite Plate Production Site
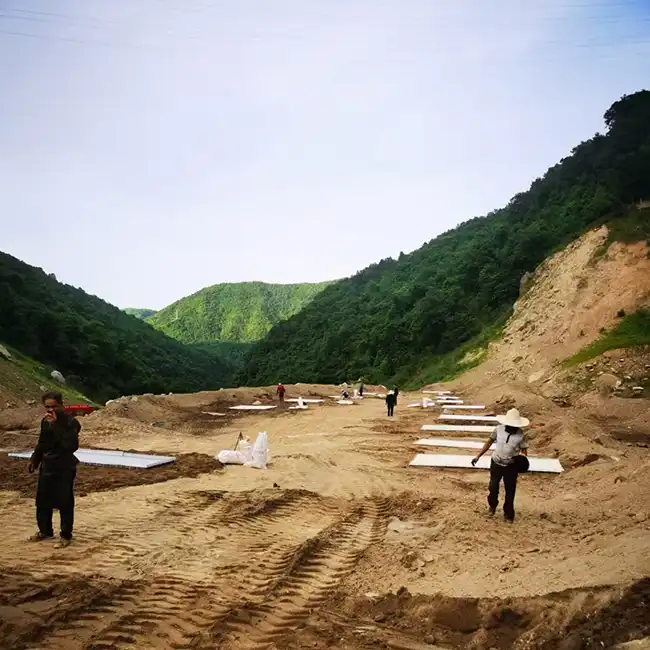
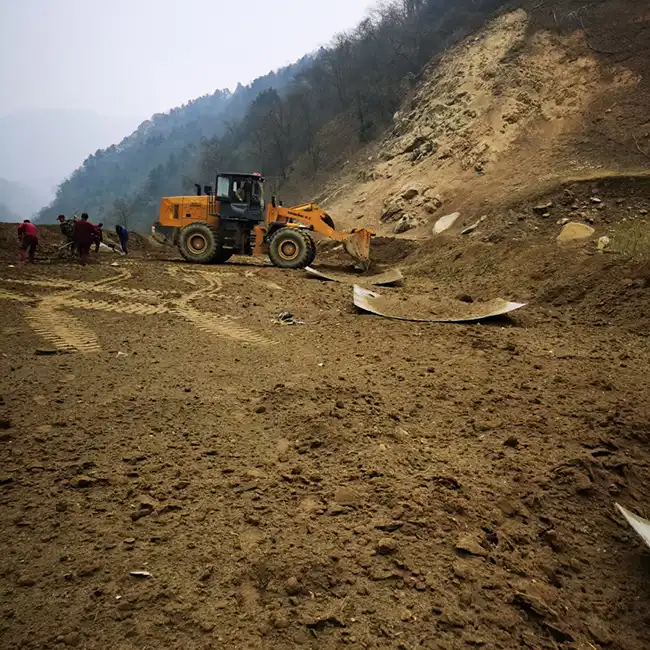
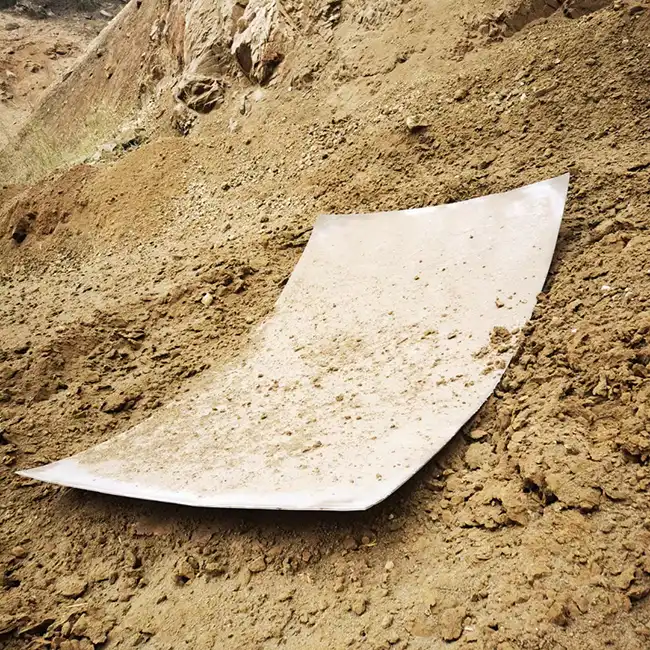
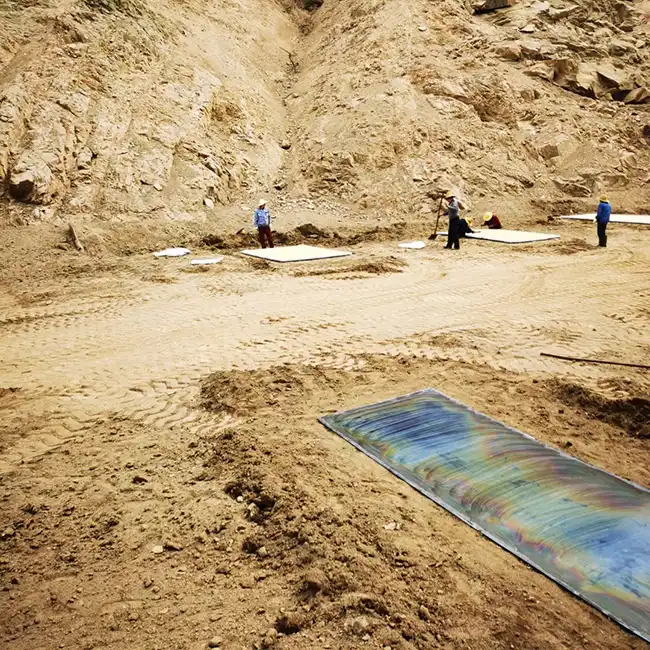




Explosion Welding Process
 |
 |
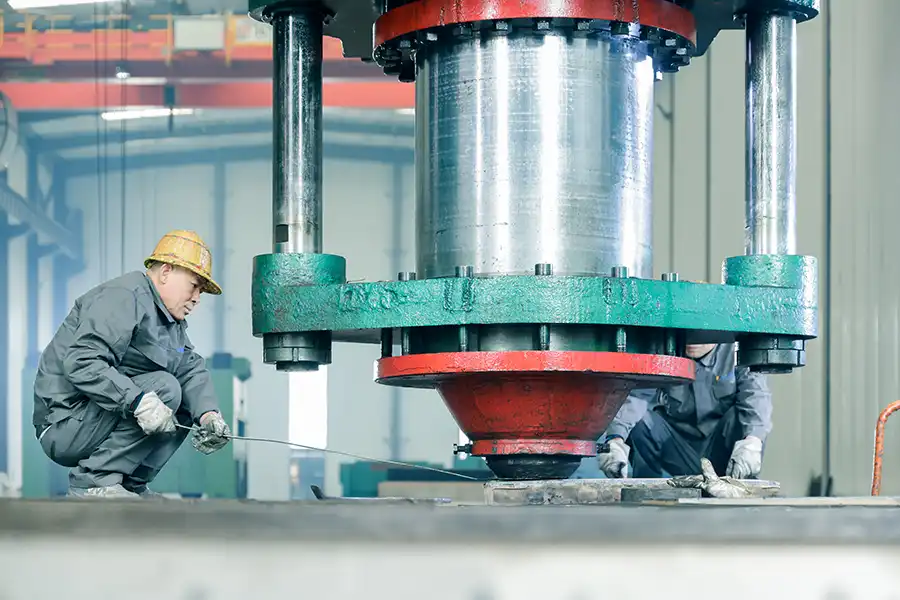
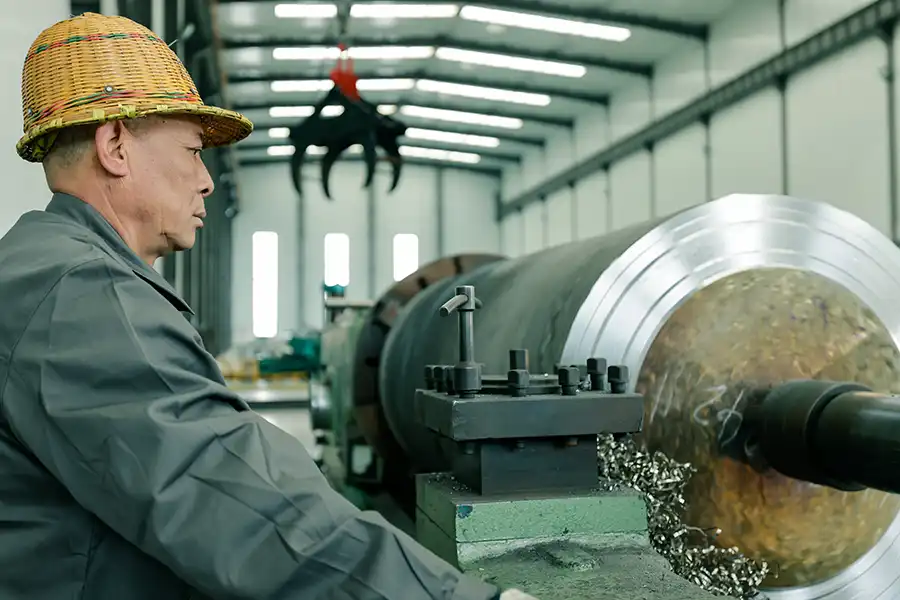
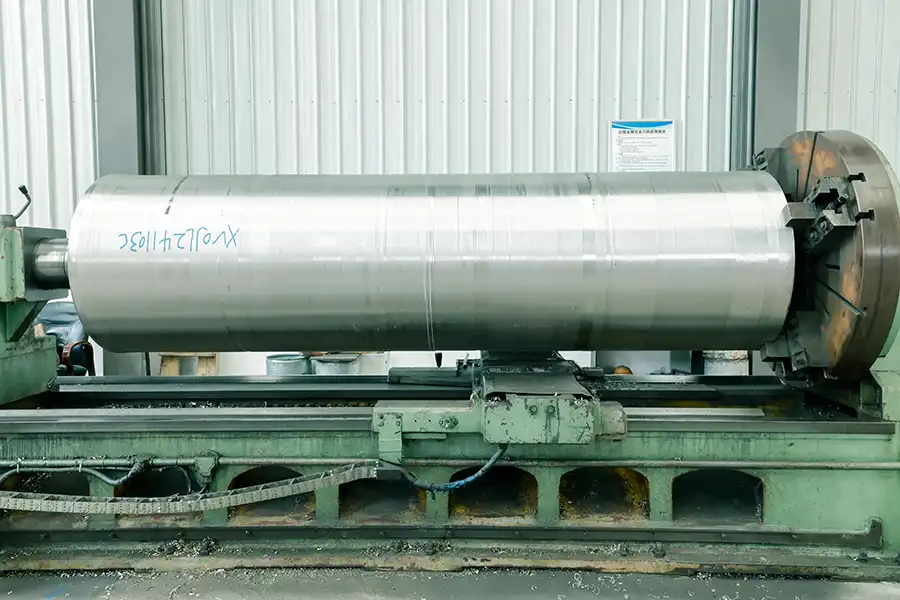
Our Factory
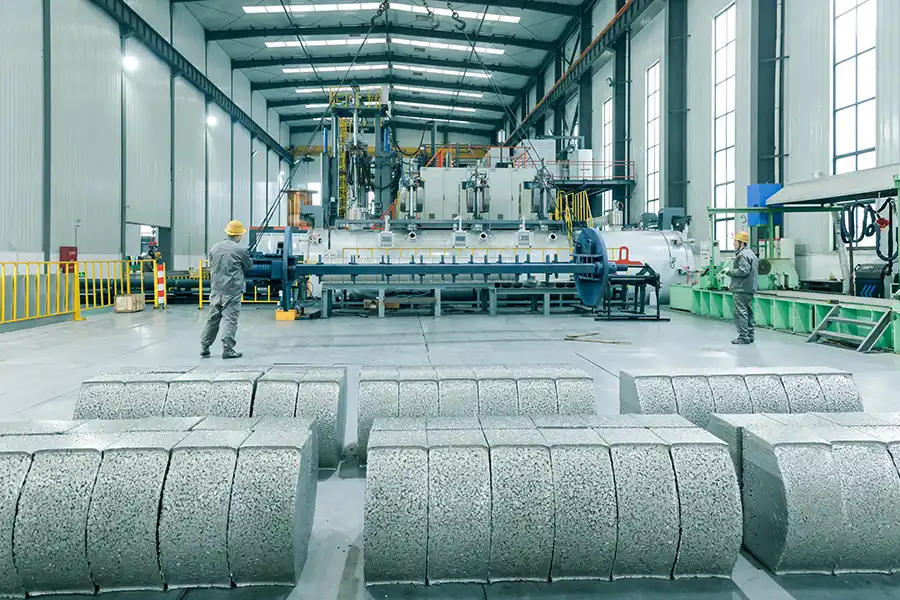
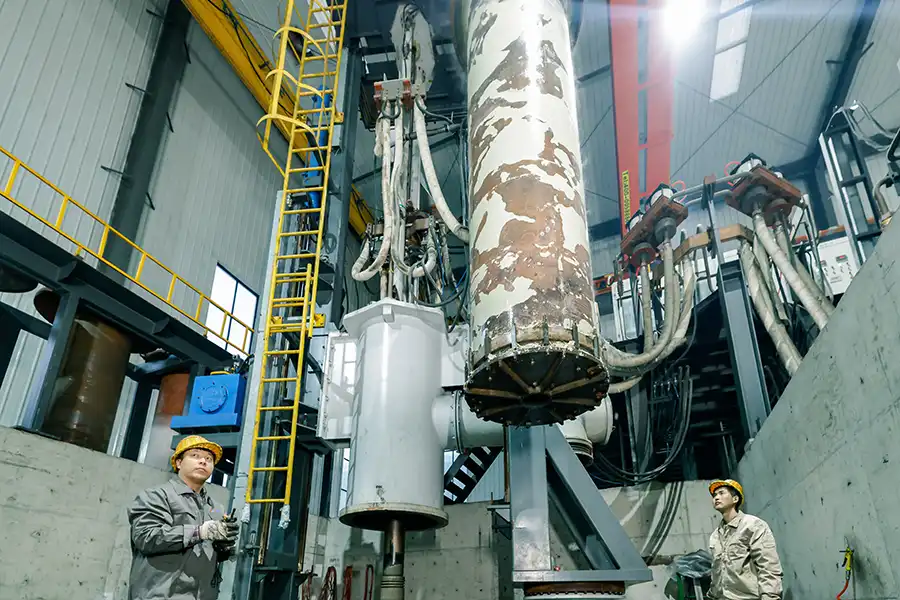
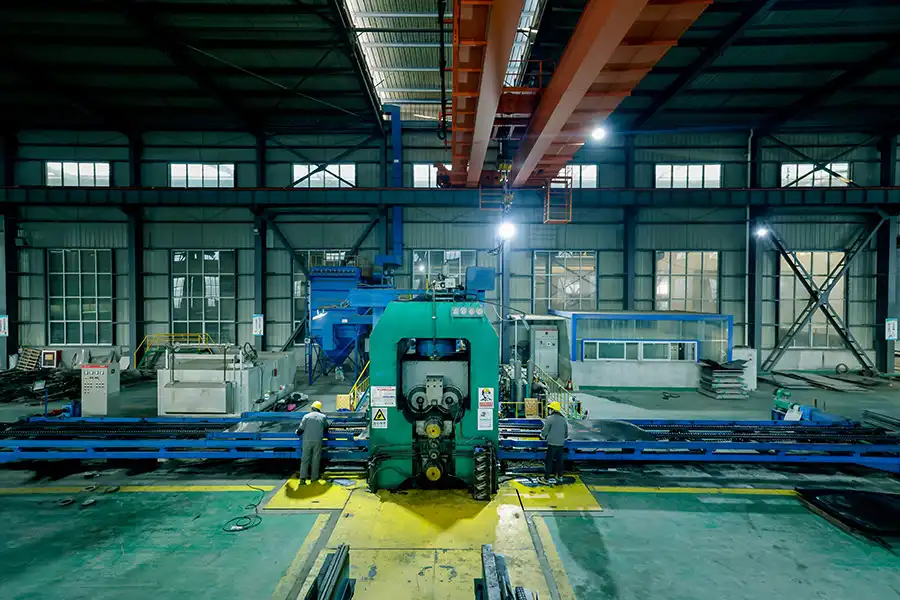
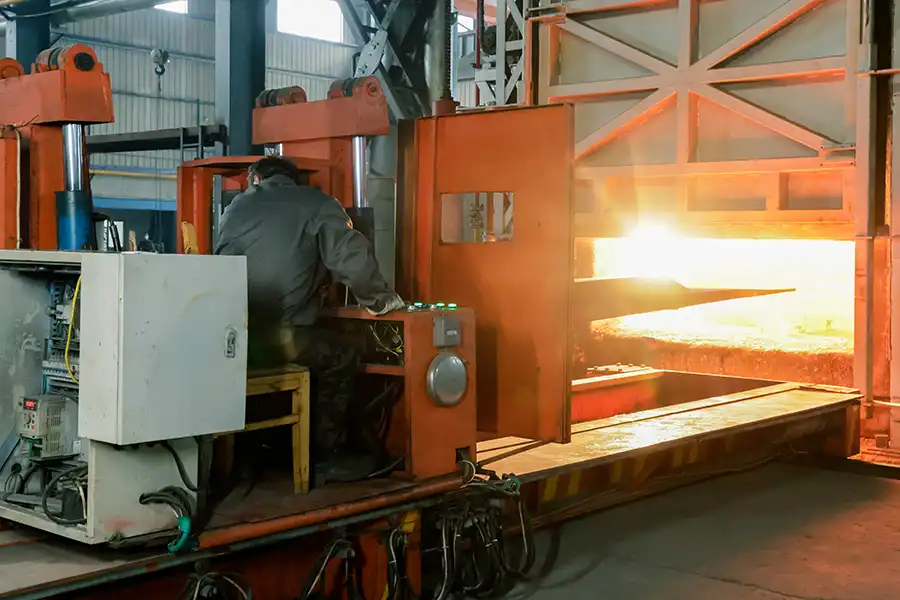
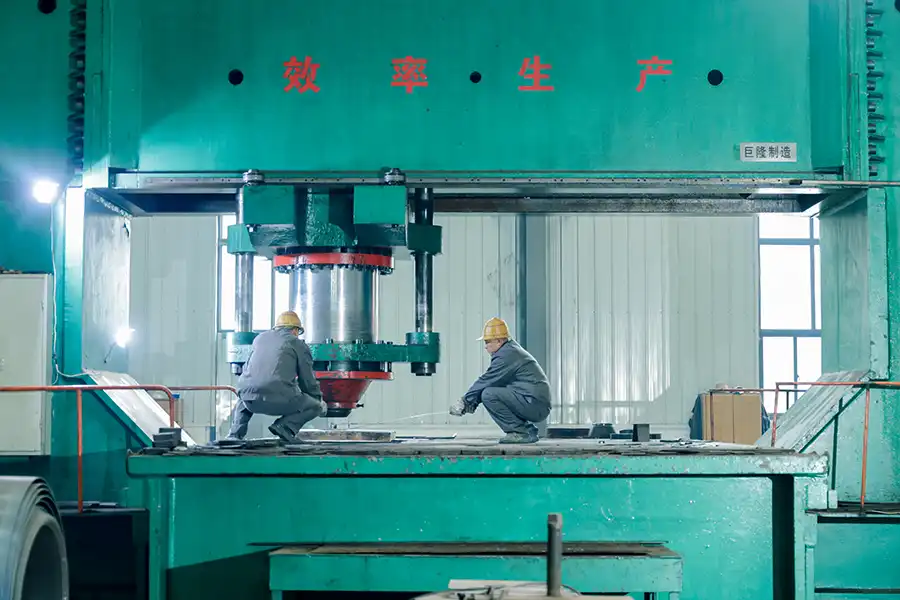
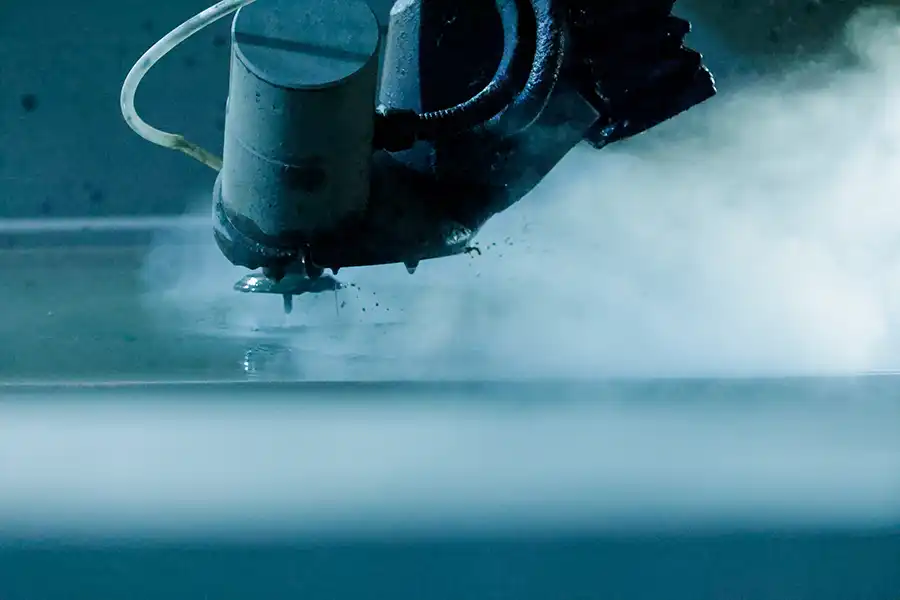
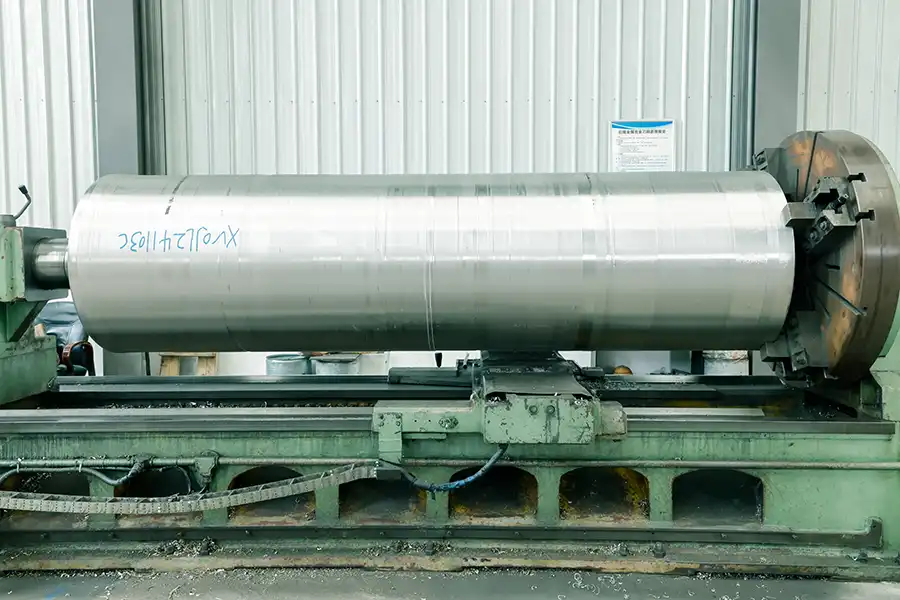










Production Site
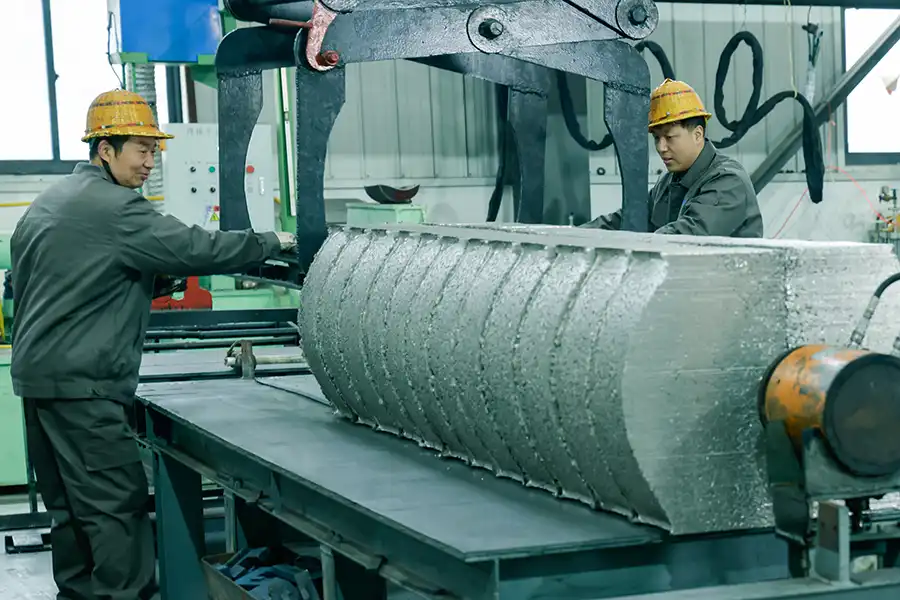
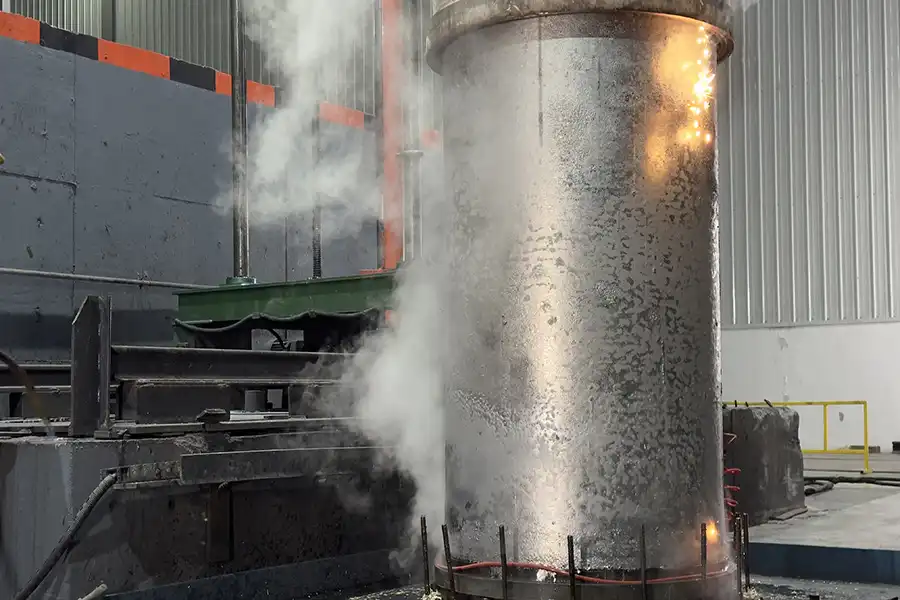
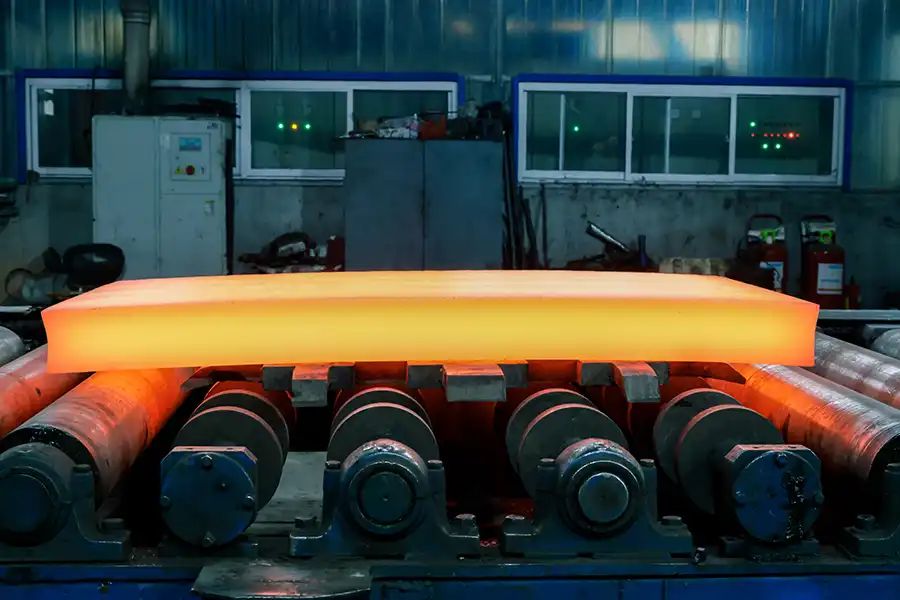


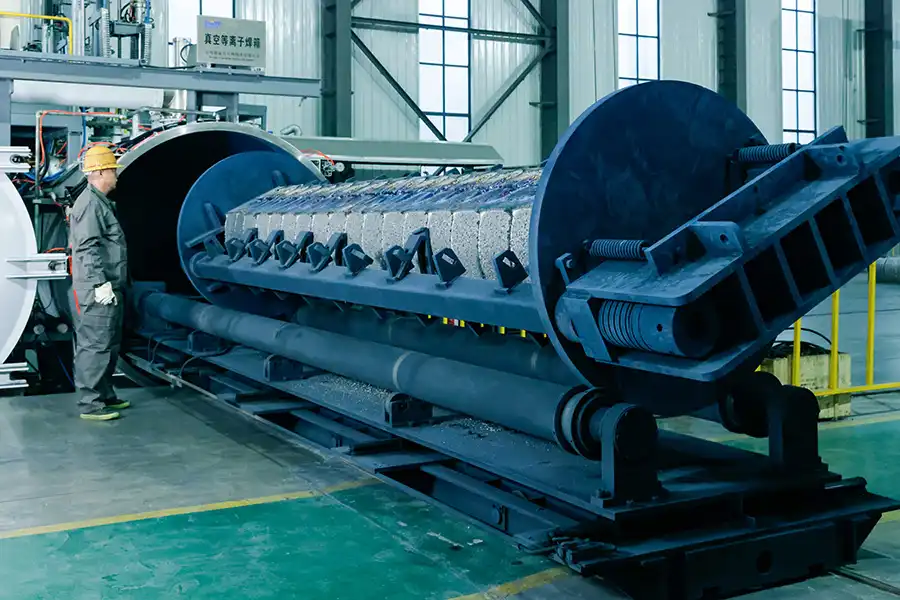
 Hot Rolling
Hot Rolling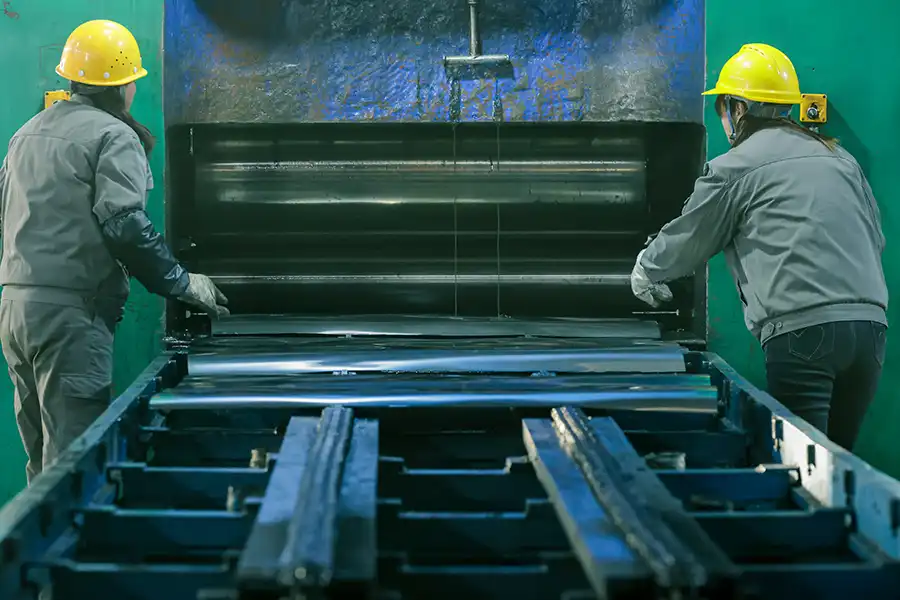







Main Products
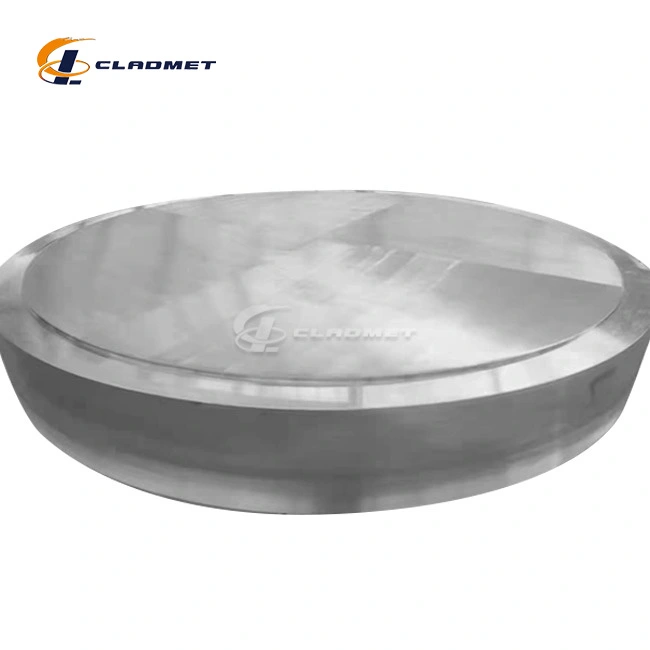


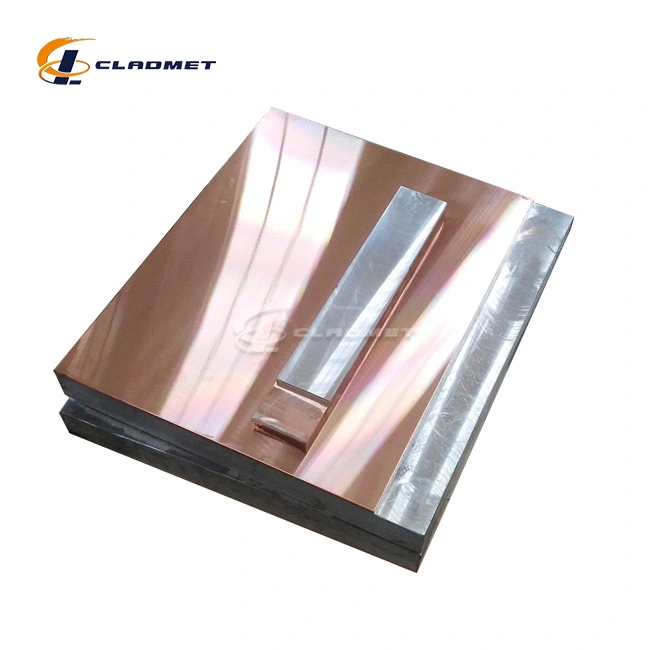
Main Application Industries




OEM Service
Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. offers complete OEM services for the steel plates. From material selection to the final product, we tailor solutions to meet your specific needs. Whether you require customized dimensions or specific cladding materials, we ensure top-quality production aligned with international standards.
FAQ
-
What industries are the steel plates suitable for?
Clad steel plates are ideal for oil and gas, chemical, nuclear energy, aerospace, marine engineering, and more. -
What is the delivery time for the steel plates?
Delivery typically takes 3-6 months, depending on order specifications and quantity. -
Can I request custom dimensions and materials?
Yes, we offer fully customizable solutions based on your industry needs. -
What certifications do your products meet?
Our products meet GB/GBT, ASME/ASTM, and JIS standards and are ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS certified.

_1737007724117.webp)