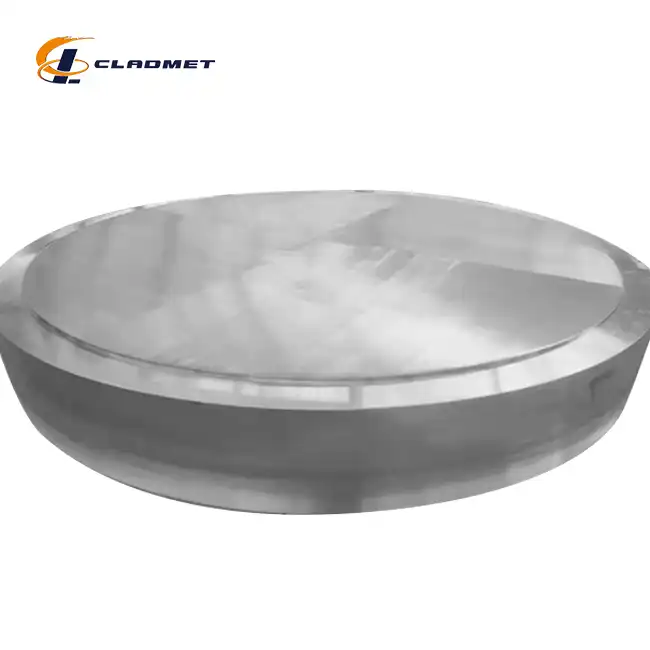
What Standards Govern the Quality of Titanium Copper Clad Plates?
 2025-05-14 13:45:56
View:389
2025-05-14 13:45:56
View:389The quality of Titanium Copper Clad Plates is governed by a comprehensive set of international and national standards that ensure consistent performance, reliability, and safety across various industrial applications. These standards, including GB/GBT, ASME/ASTM, and JIS, provide rigorous guidelines for manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. to follow during production. Additionally, international certifications such as ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS qualification further validate the quality and integrity of these composite materials, making them suitable for critical applications in chemical processing, electroplating, and marine environments.
International Standards and Certification Requirements for Titanium Copper Clad Plates
ASME and ASTM Standards Implementation
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standards play a pivotal role in establishing quality benchmarks for Titanium Copper Clad Plates. These standards provide detailed specifications regarding material composition, mechanical properties, and testing methodologies. For instance, ASTM B898 specifically addresses the requirements for reactive and refractory metal clad plate products, which includes titanium-copper combinations. Manufacturers must adhere to these specifications during the production process to ensure that the final product meets the necessary strength, durability, and bonding integrity requirements. The standards also stipulate precise tolerances for dimensional variations, flatness, and bond strength that directly impact the performance of Titanium Copper Clad Plates in various applications. By incorporating these benchmarks into their manufacturing processes, companies like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. can produce consistent, high-quality clad plates suitable for demanding industrial environments where both the corrosion resistance of titanium and the conductivity of copper are essential properties.
Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) Compliance
Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) represents another critical framework governing the quality of Titanium Copper Clad Plates. The JIS H4600 series specifically addresses composite metal materials, providing detailed requirements for metallurgical bonding, material purity, and performance characteristics. These standards are particularly important in applications requiring precision manufacturing and consistent material properties across large plate dimensions. The JIS standards are known for their stringent requirements regarding bond integrity testing and non-destructive examination techniques, which help identify potential defects or weaknesses in the clad interface. For Titanium Copper Clad Plates, meeting JIS requirements involves achieving specific shear strength values at the cladding interface, ensuring uniform thickness distribution, and maintaining consistent material properties throughout the plate. Manufacturers following these guidelines can offer Titanium Copper Clad Plates that perform reliably across various temperature ranges and operational conditions, a critical factor in industries such as chemical processing, power generation, and shipbuilding where these materials must withstand challenging environments while maintaining their functional properties.
ISO9001-2000 Quality Management System
The ISO9001-2000 certification represents a comprehensive quality management system that significantly impacts the overall production process of Titanium Copper Clad Plates. This standard focuses on consistent manufacturing processes, traceability, and systematic quality control across all production stages. For clad plate manufacturers, implementing ISO9001-2000 means establishing documented procedures for incoming material inspection, production control, testing, and final product verification. The standard requires regular internal audits and management reviews to continuously improve production efficiency and product quality. In the context of Titanium Copper Clad Plates, this certification ensures that every aspect of the manufacturing process—from raw material selection to explosive welding parameters to final inspection—follows systematic protocols designed to eliminate variability and defects. The traceability requirements are particularly important, allowing manufacturers to track each plate back to its original material batch, processing parameters, and test results. This comprehensive approach to quality management helps maintain consistency across different manufacturing runs and provides customers with confidence that every Titanium Copper Clad Plate meets the same high-quality standards, regardless of when it was produced or which production line it came from.
Manufacturing Process Standards for Quality Titanium Copper Clad Plates
Explosive Welding Quality Parameters
Explosive welding represents one of the most sophisticated and reliable methods for producing high-quality Titanium Copper Clad Plates. This process involves creating a metallurgical bond between titanium and copper through controlled detonation, resulting in a permanent, molecular-level connection between these disparate metals. The quality standards governing explosive welding are particularly stringent, focusing on parameters such as detonation velocity, standoff distance, and collision angle—all of which significantly impact the final bond integrity. According to industry standards, the explosive charge must be precisely calculated based on the specific properties of both titanium and copper layers, including their thickness, hardness, and other mechanical properties. The preparation phase is equally critical, with standards requiring meticulous surface cleaning to remove any contaminants that could compromise the bond. Post-welding inspection standards mandate ultrasonic testing to identify any potential unbonded areas, as well as mechanical testing to verify bond strength. For Titanium Copper Clad Plates produced through explosive welding, the bond strength typically must exceed 140 MPa to meet industry standards, ensuring that the material can withstand the thermal stresses and mechanical loads encountered in applications ranging from chemical processing equipment to desalination plants. These rigorous parameters ensure that explosively welded Titanium Copper Clad Plates maintain their integrity even under extreme conditions, providing reliable performance throughout their service life.
Roll Bonding Process Standards
Roll bonding represents another standardized method for producing Titanium Copper Clad Plates, particularly for applications requiring thinner composite sheets with uniform thickness. The quality standards governing this process focus on surface preparation, rolling pressure, temperature control, and post-rolling heat treatment. According to relevant manufacturing standards, both the titanium and copper surfaces must undergo thorough degreasing, pickling, and wire brushing to achieve the required surface roughness and cleanliness levels. The rolling parameters are equally regulated, with standards specifying minimum reduction ratios (typically 50-70%) to ensure sufficient plastic deformation for proper bonding between the layers. Temperature control during the rolling process must remain within ±10°C of the specified value to maintain consistent material properties and prevent undesirable metallurgical reactions at the interface. For Titanium Copper Clad Plates produced through roll bonding, standards require post-rolling heat treatment at precisely controlled temperatures (typically 500-600°C) to relieve residual stresses and enhance bond strength. Quality inspection standards mandate both non-destructive testing (like ultrasonic inspection) and destructive testing (such as shear strength tests and bend tests) to verify the integrity of the bond and the overall quality of the clad plate. These comprehensive standards ensure that roll-bonded Titanium Copper Clad Plates exhibit uniform properties throughout their entire surface area, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent electrical conductivity combined with corrosion resistance, such as electrochemical cells, heat exchangers, and electronic component manufacturing.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Standards
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) represents an advanced manufacturing process for Titanium Copper Clad Plates that is governed by a distinct set of quality standards. This method involves simultaneously applying high temperature and isostatic pressure to create diffusion bonds between titanium and copper layers. The applicable standards specify precise parameters for temperature (typically 800-950°C for titanium-copper combinations), pressure (generally 100-200 MPa), and processing time (usually 2-4 hours) to achieve optimal bond strength and material properties. Before HIP processing, standards require thorough surface preparation, including specific roughness parameters (Ra value between 0.8-1.2 μm) and cleanliness levels to ensure proper diffusion bonding. The encapsulation process, where the titanium and copper plates are sealed in a container before pressurization, must follow precise technical specifications regarding container material, sealing methods, and evacuation procedures. For Titanium Copper Clad Plates produced through HIP, quality standards mandate comprehensive post-processing metallurgical examination to verify full bonding and absence of interfacial precipitates or voids. Microstructure analysis must confirm proper diffusion zone formation without excessive intermetallic compound development, which could compromise mechanical properties. Additionally, bond integrity testing standards require shear strength values typically exceeding 180 MPa, ensuring that HIP-processed Titanium Copper Clad Plates can withstand thermal cycling and mechanical stresses encountered in high-performance applications. These exacting standards ensure that HIP-processed Titanium Copper Clad Plates deliver exceptional bond quality and consistent properties, making them suitable for specialized applications in aerospace, semiconductor manufacturing, and other industries requiring the highest levels of material integrity and performance reliability.

Testing and Quality Control Standards for Titanium Copper Clad Plates
Non-Destructive Testing Requirements
Non-destructive testing (NDT) plays a critical role in ensuring the quality and reliability of Titanium Copper Clad Plates through methods that evaluate material integrity without causing damage. International standards mandate specific NDT protocols for these composite materials, with ultrasonic testing being the primary method for bond integrity evaluation. According to ASTM standards, ultrasonic inspection must be performed using straight beam techniques with transducer frequencies between 2.25-5.0 MHz to detect unbonded areas as small as 6mm in diameter. The acceptance criteria typically specify that unbonded areas should not exceed 5% of the total surface area, with no single unbonded region larger than 25mm in diameter. For higher-grade applications, standards may require more stringent acceptance criteria with maximum unbonded area limited to 3% of the total surface. Additionally, radiographic examination standards apply to evaluate the consistency of the titanium layer thickness and detect any internal discontinuities. Eddy current testing is also required by certain standards to verify the electrical conductivity properties of the copper base, particularly important for Titanium Copper Clad Plates intended for electrochemical applications. Time-of-flight diffraction (TOFD) ultrasonic techniques are increasingly becoming standard for critical applications, providing detailed imaging of the bond interface and potential defects. These comprehensive NDT requirements ensure that Titanium Copper Clad Plates maintain their structural integrity and functional properties throughout their service life, particularly in demanding environments where failure could lead to significant operational disruption, environmental damage, or safety hazards.
Mechanical Testing Standards
Mechanical testing standards for Titanium Copper Clad Plates establish rigorous protocols to verify the strength, integrity, and durability of the bond between titanium and copper layers. International standards mandate specific mechanical tests, including shear strength testing according to ASTM B898, which requires minimum shear strength values typically between 140-210 MPa, depending on the specific application requirements. Bend testing standards specify minimum bend radii and bend angles (typically 180° around a mandrel with diameter equal to three times the material thickness) without delamination or cracking to demonstrate the ductility and bond integrity of the composite. Tensile strength testing follows ASTM E8 procedures with specific requirements for Titanium Copper Clad Plates, evaluating both the overall composite strength and the integrity of the bonded interface under tensile stress. Impact testing standards apply particular attention to the behavior of the bond interface under dynamic loading conditions, with minimum absorbed energy requirements based on the intended application environment. For Titanium Copper Clad Plates produced by Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., these mechanical tests must be performed on samples from each production batch, with results documented and traceable to the specific production parameters. The standards also mandate specific sample preparation procedures, test configurations, and environmental conditions to ensure consistent and comparable results across different testing facilities. Additionally, for Titanium Copper Clad Plates intended for high-stress applications, fatigue testing standards require demonstration of consistent performance through a minimum number of stress cycles (typically 10^6 cycles) without delamination or bond degradation. These comprehensive mechanical testing standards ensure that Titanium Copper Clad Plates will maintain their structural integrity and functional performance throughout their service life, even when subjected to mechanical stresses, thermal cycling, and other operational demands.
Chemical Composition Analysis Standards
Chemical composition analysis standards for Titanium Copper Clad Plates establish precise requirements for material purity, elemental content, and metallurgical compatibility between the titanium and copper layers. These standards mandate specific analytical techniques including optical emission spectroscopy (OES), X-ray fluorescence (XRF), and inductively coupled plasma (ICP) analysis to verify conformance with material specifications. For the titanium layer, standards typically require a minimum purity of 99.2% for commercially pure grades (Grade 1-4) or precise control of alloying elements for titanium alloys like Ti-6Al-4V. Copper substrate standards specify minimum copper content (typically 99.8% for C10100/C10200 or appropriate alloy compositions for other grades) and maximum allowable impurities, particularly those that could compromise electrical conductivity or corrosion resistance. Interface analysis standards require examination of the bond zone to ensure minimal formation of brittle intermetallic compounds that could compromise mechanical integrity. For Titanium Copper Clad Plates from Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., chemical composition verification must be performed for each production batch, with results documented and traceable to specific material heats and processing parameters. The standards also mandate depth profile analysis across the bond interface to confirm gradual composition transition without abrupt changes that could create stress concentrations. Additionally, elemental mapping using scanning electron microscopy with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX) is required for high-specification applications to verify uniform distribution of elements and absence of contaminants at the bond interface. These comprehensive chemical composition standards ensure that Titanium Copper Clad Plates maintain their essential material properties, including corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, and thermal stability, throughout their operational lifetime in demanding industrial environments where exposure to corrosive media, electrical currents, and elevated temperatures would quickly compromise lesser materials.
Conclusion
The quality of Titanium Copper Clad Plates is governed by a comprehensive framework of international standards including ASME/ASTM, JIS, and GB/GBT, alongside crucial certifications like ISO9001-2000, PED, and ABS. These standards ensure optimal performance across manufacturing processes, material composition, and testing protocols, guaranteeing reliable products that meet the rigorous demands of various industries. Are you looking for premium-quality Titanium Copper Clad Plates that meet all international standards and specifications? At Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd., we pride ourselves on manufacturing products that exceed industry standards through our independent explosive composite technology, self-rolling capabilities, and innovative R&D approach. Whether you need standard specifications or custom solutions, our team is ready to provide expert guidance and high-performance materials tailored to your unique requirements. Contact us today at sales@cladmet.com to discuss how our internationally certified products can enhance your project's success and reliability.
References
1. American Society for Testing and Materials. (2023). ASTM B898: Standard Specification for Reactive and Refractory Metal Clad Plate. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA.
2. Japanese Industrial Standards Committee. (2022). JIS H4600: Copper and Copper Alloy Clad Plates, Sheets and Strips. Japanese Standards Association, Tokyo, Japan.
3. International Organization for Standardization. (2021). ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management Systems—Requirements. ISO, Geneva, Switzerland.
4. Akbari Mousavi, S.A., & Farhadi Sartangi, P. (2023). Experimental investigation of explosive welding parameters on titanium-copper clad plates. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 718, 232-241.
5. American Bureau of Shipping. (2024). Rules for Materials and Welding – Part 2: Composite Materials for Marine Applications. ABS, Houston, TX.
6. Pressure Equipment Directive. (2024). Directive 2014/68/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on the harmonisation of the laws of the Member States relating to the making available on the market of pressure equipment. European Commission, Brussels.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)