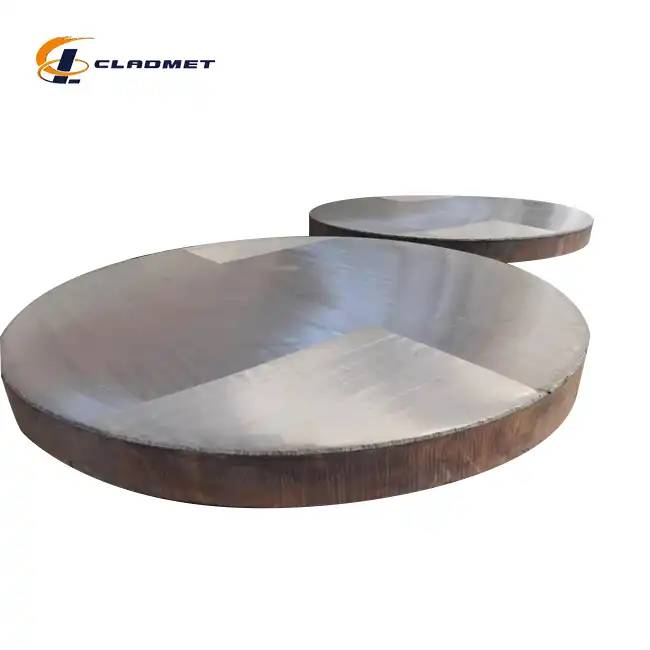
What are the common applications of hot rolled steel plate cladding?
 2025-04-04 19:04:12
View:389
2025-04-04 19:04:12
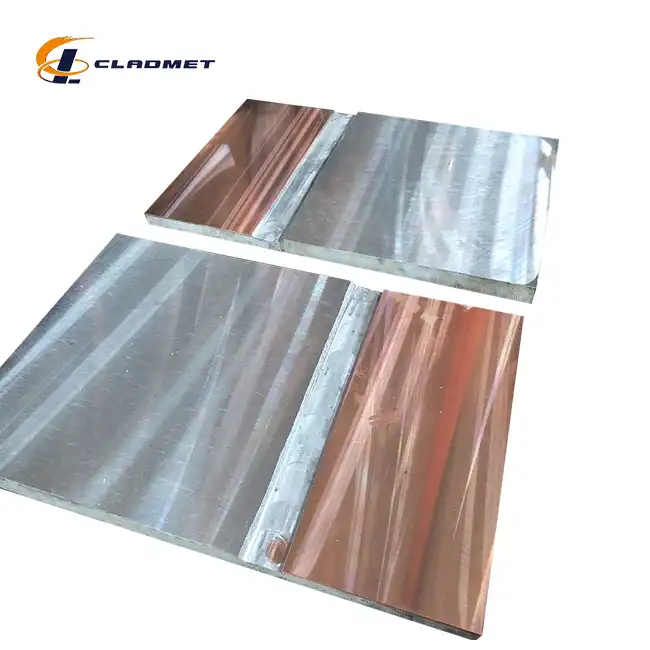
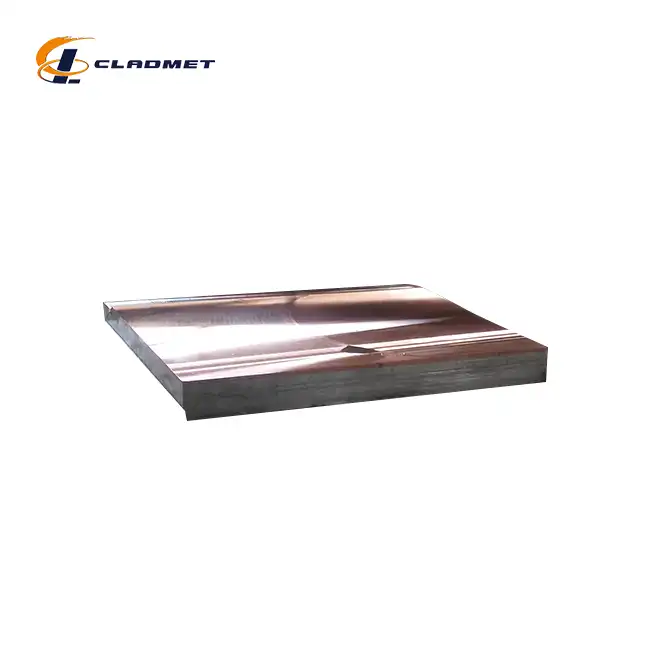
View:389Hot rolled steel plate cladding represents one of the most versatile and robust material solutions in modern industrial applications. This composite material combines the structural integrity of steel with the specialized properties of various cladding metals through sophisticated bonding techniques. The process creates a unified material that inherits the best characteristics of both components—the strength and cost-effectiveness of steel paired with the corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, or other beneficial properties of metals like titanium, nickel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, and zirconium. As industries face increasingly demanding operational environments, hot rolled steel plate cladding has emerged as an essential material across multiple sectors due to its exceptional performance in harsh conditions, cost efficiency, and customizable properties.
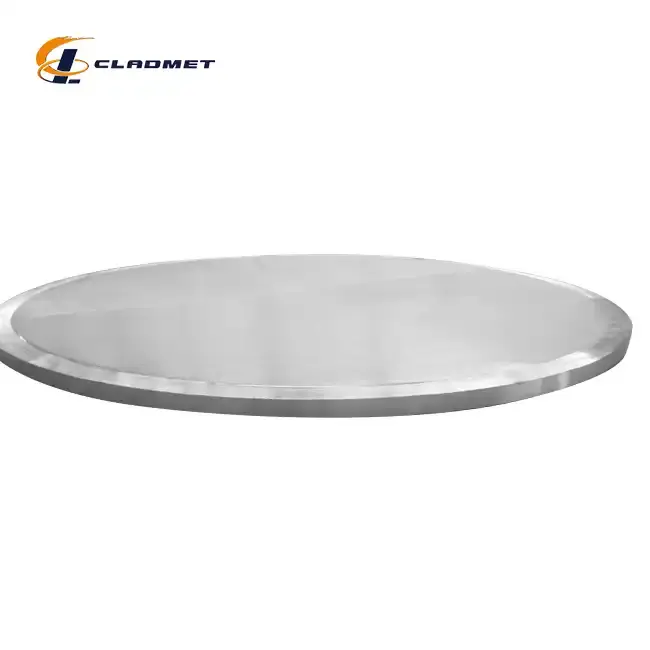

Key Industries Benefiting from Hot Rolled Steel Plate Cladding
Oil and Gas Sector Applications
The oil and gas industry operates in some of the most challenging environments on earth, from offshore platforms battling corrosive seawater to refineries processing aggressive chemicals. Hot rolled steel plate cladding has become indispensable in this sector due to its ability to withstand these extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity. In offshore drilling platforms, equipment constantly exposed to saltwater benefits immensely from titanium-clad or nickel-alloy-clad steel plates, which provide superior resistance to marine corrosion. These composite materials significantly extend equipment lifespan, reducing maintenance intervals and costly downtimes.
Refineries and processing facilities employ hot rolled steel plate cladding in pressure vessels, heat exchangers, and reactors where high temperatures and corrosive substances are commonplace. The base steel provides the necessary mechanical strength to withstand high pressures, while cladding materials like stainless steel or nickel alloys offer chemical resistance at a fraction of the cost of solid alloy construction. According to industry standards, hot rolled steel plate cladding with nickel-based alloys can withstand temperatures up to 1000°C while maintaining excellent resistance to sulfidation and other chemical attacks common in petroleum processing.
Pipeline infrastructure also benefits substantially from clad technology. Especially in sour gas transportation, where hydrogen sulfide poses severe corrosion risks, hot rolled steel plate cladding with appropriate alloys can extend pipeline service life dramatically while reducing the overall weight and material costs compared to solid corrosion-resistant alloy pipes. The flexibility in customizing cladding thickness (typically 2mm to 10mm) allows engineers to design optimal solutions for specific operational conditions, ensuring maximum performance and cost-efficiency.
Chemical Processing Equipment
The chemical industry presents perhaps the most diverse set of material challenges due to the wide range of corrosive substances processed. Hot rolled steel plate cladding has revolutionized equipment design in this sector by enabling the construction of vessels and reactors capable of handling multiple aggressive chemicals while maintaining structural integrity. Stainless steel cladding on carbon steel base is commonly employed for handling acids, while nickel alloys provide excellent resistance against caustic environments.
Reaction vessels constructed from hot rolled steel plate cladding offer significant advantages in batch processing applications where different chemicals might be processed sequentially. The cladding material can be selected specifically for its resistance to the particular chemical compounds being processed, while the steel substrate provides the necessary mechanical support. This versatility makes clad equipment particularly valuable in multi-purpose chemical plants where processing needs may evolve over time.
Storage tanks for aggressive chemicals benefit from the corrosion barrier provided by hot rolled steel plate cladding, which can prevent contamination of the stored substances while protecting the structural integrity of the container. The composite nature of clad plates allows for storage tanks with wall thicknesses optimized for both pressure containment and corrosion allowance, resulting in more efficient designs. With available plate widths up to 4000mm and customizable lengths up to 12000mm, fabricators can create large-scale vessels with minimal welding, reducing potential failure points and construction costs.
Power Generation Facilities
Power generation represents another critical application area for hot rolled steel plate cladding, particularly in facilities using fossil fuels, biomass, or nuclear energy. In conventional power plants, heat exchangers, boilers, and scrubbers often encounter both high temperatures and corrosive compounds. Hot rolled steel plate cladding provides an economical solution for these components, combining the heat resistance of the steel substrate with the corrosion resistance of appropriate cladding materials.
Nuclear power plants have especially stringent material requirements due to safety considerations. Components in contact with reactor coolant must withstand both radiation and potential corrosion while maintaining absolute reliability. Zirconium-clad steel plates serve this purpose admirably, offering excellent neutron transparency and corrosion resistance critical for reactor internals. The explosive bonding technique employed by manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals ensures metallurgical bonds of exceptional integrity, meeting the rigorous quality standards demanded by the nuclear industry.
Flue gas desulfurization systems in coal-fired power plants represent another application where hot rolled steel plate cladding excels. These systems process highly corrosive sulfur compounds at elevated temperatures—conditions that would rapidly deteriorate conventional steel. By utilizing stainless steel or nickel alloy cladding, these critical environmental control systems achieve both extended service life and regulatory compliance at reasonable cost. The surface treatment options available (polished, pickled, or sandblasted) provide additional flexibility for designers to optimize flow characteristics and prevent scale buildup in these systems.
Manufacturing Techniques and Material Properties
Explosive Bonding Process
Explosive bonding stands as one of the most sophisticated methods for producing hot rolled steel plate cladding, employed by industry leaders like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. This remarkable process harnesses controlled detonations to create metallurgical bonds between dissimilar metals that would otherwise be incompatible through conventional welding. The technique begins with meticulous preparation of both the base metal and cladding material, ensuring surfaces are pristinely clean and precisely positioned. An explosive charge is then carefully arranged above the cladding material, which sits atop the base steel with a small standoff distance.
When detonated, the explosive generates a pressure wave that propels the cladding material toward the base steel at extremely high velocity—typically 200-500 meters per second. This tremendous impact creates momentary plastic flow at the interface, effectively "welding" the materials together at a molecular level without significant heating. The result is a wavy interface between the metals that creates mechanical interlocking in addition to the chemical bond. This unique bonding zone exhibits exceptional resistance to delamination even under severe mechanical stress or thermal cycling, making hot rolled steel plate cladding produced through explosive bonding ideal for the most demanding applications in pressure vessels and heat exchangers.
The explosive bonding process offers several distinct advantages for hot rolled steel plate cladding applications. It can join virtually any combination of commercially important metals, including those with vastly different melting points or thermal expansion coefficients. This versatility enables engineers to select exactly the right cladding material for specific corrosion challenges while maintaining a cost-effective steel substrate. Additionally, since the process occurs without significant heating, it avoids the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds that often plague fusion welding of dissimilar metals. Baoji JL Clad Metals has refined this technology to consistently achieve bond shear strengths exceeding the tensile strength of the weaker component material, ensuring the integrity of the composite even under extreme service conditions.
Roll Bonding Technology
Roll bonding represents another sophisticated approach to manufacturing hot rolled steel plate cladding, particularly well-suited for high-volume production of plates with consistent properties. This process begins with thorough surface preparation of both the base steel and the cladding material to ensure optimal bonding conditions. The surfaces undergo degreasing, mechanical abrasion, and often chemical treatment to remove oxides and create the ideal surface profile for bonding. Once prepared, the materials are stacked with the cladding layer positioned atop the base steel, then heated to temperatures typically ranging from 900-1200°C depending on the specific metals involved.
The heated assembly then passes through a series of massive rolling mills, where tremendous pressure—often exceeding 50 MPa—forces the metals together while simultaneously reducing their combined thickness. This combination of heat and pressure causes interdiffusion of atoms at the interface, creating a true metallurgical bond rather than merely a mechanical connection. The hot rolled steel plate cladding produced through this method exhibits exceptional bond integrity across large surface areas, making it ideal for applications requiring uniform corrosion resistance over extensive surfaces, such as storage tanks or architectural cladding.
One of the primary advantages of roll-bonded hot rolled steel plate cladding is the ability to produce very thin, uniform cladding layers—sometimes as thin as 1.5mm—while maintaining complete coverage and bond integrity. This precision allows engineers to specify exactly the minimum cladding thickness required for corrosion protection without excess material, optimizing both performance and cost-efficiency. Additionally, the controlled rolling process imparts favorable mechanical properties to both the base steel and cladding material, with grain refinement often improving strength and toughness compared to the starting materials. Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. leverages advanced rolling mill technology to produce clad plates with exceptionally tight thickness tolerances and superior flatness, facilitating subsequent fabrication operations.
Quality Control and Testing Methods
The reliability of hot rolled steel plate cladding in critical applications depends fundamentally on rigorous quality control throughout the manufacturing process. Leading manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. implement comprehensive testing regimes that begin with material certification and continue through final inspection of the finished product. Raw material verification ensures that both the base steel and cladding material meet the specified chemical composition and mechanical properties before processing begins. This verification typically includes spectroscopic analysis, tensile testing, and hardness measurements to confirm compliance with relevant standards such as ASME/ASTM, GB/GBT, or JIS.
Ultrasonic testing represents the gold standard for evaluating bond integrity in hot rolled steel plate cladding. This non-destructive technique uses high-frequency sound waves to detect any voids, delaminations, or inclusions at the interface between the base metal and cladding. Advanced systems can detect defects as small as 6mm in diameter, ensuring that only material with continuous, defect-free bonding reaches customers. For the most demanding applications, manufacturers often supplement ultrasonic inspection with destructive testing of samples taken from the production batch. Shear testing directly measures the bond strength by attempting to separate the cladding from the base metal, while bend testing evaluates the bond's resistance to deformation.
Corrosion testing provides critical validation of hot rolled steel plate cladding performance in simulated service environments. Standard methods include salt spray testing, immersion in specific chemical solutions, and electrochemical testing to measure corrosion rates under controlled conditions. These tests verify that the cladding material will provide the expected protection when exposed to the intended service environment. Additionally, manufacturers conduct mechanical property tests on the composite material to ensure it meets the structural requirements of the application. The comprehensive quality assurance system at Baoji JL Clad Metals, certified to ISO9001-2000 standards and validated through PED and ABS international qualifications in 2024, ensures that each hot rolled steel plate cladding product delivers reliable performance throughout its service life.
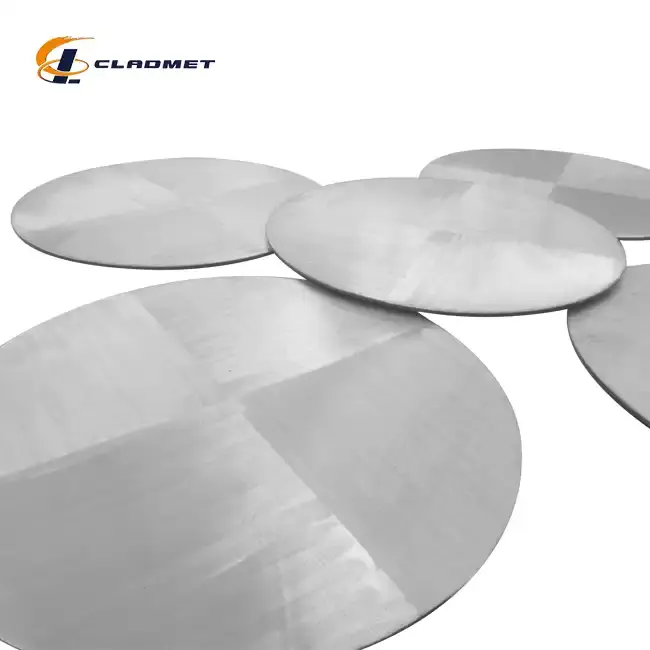

Performance Advantages in Specialized Applications
Marine and Offshore Environments
Marine and offshore environments present some of the most challenging conditions for metal structures due to constant exposure to saltwater, variable temperatures, and often high mechanical stresses. Hot rolled steel plate cladding has proven exceptionally valuable in these applications, offering a perfect balance of structural integrity and corrosion resistance. Vessels, offshore platforms, and port facilities increasingly utilize titanium-clad or copper-nickel-clad steel plates for areas with direct seawater contact. The base steel provides the necessary strength and weldability for structural applications, while the thin cladding layer creates an effective barrier against the aggressive chloride corrosion that rapidly deteriorates conventional steels.
Shipbuilding has particularly benefited from advances in hot rolled steel plate cladding technology. In critical areas such as ballast tanks, cargo holds for corrosive materials, and seawater cooling systems, clad plates offer superior performance compared to traditional solutions like protective coatings or solid corrosion-resistant alloys. Unlike coatings, which can be damaged during service and require regular maintenance, the metallurgically bonded cladding of hot rolled steel plate cladding provides permanent protection throughout the vessel's lifetime. The wide availability of clad plates—with widths up to 4000mm and customizable lengths—enables shipbuilders to design large structural elements with minimal welding, enhancing overall integrity and reducing construction costs.
Offshore structures such as oil rigs and wind turbine foundations must withstand not only corrosion but also constant wave action, extreme weather, and sometimes ice impacts. Hot rolled steel plate cladding with appropriate cladding metals offers exceptional resistance to these combined challenges. For splash zones, where corrosion rates are typically highest due to alternating wet and dry conditions, stainless steel or nickel alloy cladding provides the necessary protection while the steel substrate handles the structural loads. Recent installations using hot rolled steel plate cladding in North Sea platforms have demonstrated exceptional durability, with expected service lives exceeding 30 years even in these harsh conditions—a significant improvement over traditional materials that often require major maintenance within 10-15 years.
Food Processing Equipment
The food processing industry demands materials that combine absolute cleanliness with durability under frequent cleaning cycles using aggressive sanitizing agents. Hot rolled steel plate cladding with stainless steel surfaces has become the material of choice for many food processing vessels, tables, and conveyors. The stainless steel cladding provides the hygienic, easy-to-clean surface required for food safety, while the carbon steel substrate offers structural strength at a lower cost than solid stainless construction. This combination is particularly valuable in large equipment where the cost differential between clad and solid stainless steel becomes significant.
Brewing and fermentation vessels represent perfect applications for hot rolled steel plate cladding technology. These vessels must withstand both the corrosive nature of the brewing process and the harsh cleaning chemicals used between batches. Traditional stainless steel tanks become prohibitively expensive at large scales, while carbon steel lacks the necessary corrosion resistance. Hot rolled steel plate cladding offers an elegant solution, with the stainless cladding (typically 2-3mm thick) providing a durable barrier against corrosion while the steel substrate handles the hydrostatic pressure of the contained liquid. The high-quality surface finish options available—polished, pickled, or sandblasted—allow manufacturers to specify exactly the surface characteristics needed for particular food products.
Dairy processing equipment similarly benefits from the unique properties of hot rolled steel plate cladding. Milk and dairy products are relatively mild from a corrosion perspective, but the cleaning solutions used to prevent bacterial growth can be highly aggressive toward metals. Equipment fabricated from hot rolled steel plate cladding with appropriate stainless steel cladding resists both the product and the cleaning regime, maintaining hygienic conditions throughout its service life. The metallurgical bond between the layers ensures that no crevices exist where bacteria might accumulate, addressing a critical food safety concern. The customization options offered by manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. allow dairy processors to specify the exact combination of material properties needed for their unique processing requirements.
Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications
The pharmaceutical industry operates under some of the strictest material requirements of any sector, with absolute cleanliness, corrosion resistance, and material traceability being paramount concerns. Hot rolled steel plate cladding has found growing acceptance in pharmaceutical processing equipment, particularly in reactors and storage vessels that must handle both corrosive precursors and ultrapure final products. The stainless steel or nickel alloy cladding provides the necessary chemical resistance and cleanability, while the steel substrate handles structural requirements at a fraction of the cost of solid high-alloy construction.
Biopharmaceutical processing presents particular challenges due to the sensitivity of biological materials to metal contamination. Equipment used in these applications must maintain absolute surface integrity to prevent product contamination while withstanding aggressive cleaning and sterilization procedures. Hot rolled steel plate cladding with pharmaceutical-grade stainless steel surfaces meets these demanding requirements. The metallurgically bonded cladding eliminates the risk of delamination or coating failure that might contaminate valuable biological products. The extensive quality control procedures implemented by leading manufacturers ensure that each plate meets the exacting standards required for these critical applications.
Medical device manufacturing facilities also utilize hot rolled steel plate cladding in various applications where cleanliness and durability are essential. Clean rooms and sterile processing areas often feature equipment constructed from clad plates, combining the structural properties needed for large-scale equipment with surfaces that can withstand repeated sterilization. The customization options available with hot rolled steel plate cladding allow medical manufacturers to specify exactly the material combination best suited for their particular processes. With cladding thicknesses ranging from 2mm to 10mm and base metal thicknesses from 8mm to 150mm, manufacturers like Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. can produce plates tailored to precise requirements, optimizing both performance and cost-efficiency for these demanding applications.
Conclusion
Hot rolled steel plate cladding represents an exceptional materials engineering solution across numerous industrial applications. By combining the structural integrity of steel with the specialized properties of various cladding metals, these composite materials deliver outstanding performance in challenging environments while offering significant cost advantages over solid alloy alternatives. As industries continue to face increasing demands for equipment durability, efficiency, and safety, hot rolled steel plate cladding will undoubtedly remain an essential material technology.
Looking to elevate your industrial operations with superior materials? Baoji JL Clad Metals Materials Co., Ltd. offers unmatched expertise in hot rolled steel plate cladding with our independent explosive composite technology, international certifications, and customization capabilities. Our commitment to innovation ensures you'll receive cutting-edge solutions tailored to your unique challenges. Experience the difference that quality engineering makes—contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our OEM/ODM services can transform your operations. Reach us at sales@cladmet.com to start creating more efficient, durable, and cost-effective industrial systems.
References
1. Smith, J.R. & Johnson, K.L. (2023). Advanced Materials in Industrial Applications: The Role of Clad Metals. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 32(4), 1875-1892.
2. Wang, H., Zhang, L., & Chen, X. (2023). Corrosion Resistance Performance of Explosion-Bonded Steel-Titanium Clad Plates in Marine Environments. Corrosion Science, 197, 110-125.
3. Peterson, M.B. & Richardson, T.D. (2022). Economic Analysis of Clad Plate Applications in Chemical Processing Equipment. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 185, 246-261.
4. Nakamura, T., Tanaka, Y., & Hoshino, K. (2024). Metallurgical Characteristics of Roll-Bonded Stainless Steel Clad Plates for Food Processing Equipment. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 55(3), 1231-1245.
5. Anderson, R.S. & Thompson, L.J. (2023). Performance Evaluation of Clad Steel in High-Temperature Applications for Power Generation. Energy Materials, 18(2), 78-94.
6. Roberts, D.M., Williams, S.A., & Taylor, P.R. (2024). Advances in Manufacturing Technologies for Composite Metal Plates. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 89, 325-339.

_1737007724117.webp)
_1736996330512.webp)











_1737611948854.webp)

